Chemistry for Engineers Homework 5 (part 2) B O N D I N G Answer
advertisement

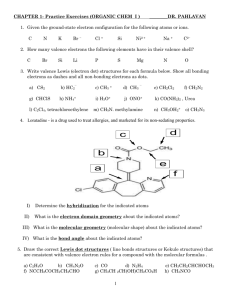
************************************************* Chemistry for Engineers Homework 5 (part 2) BONDING Answer Key ************************************************************************************************** Hand in by Wednesday Chemistry for Engineers 25 October 13:00 Homework 5 (part 2): Bonding ************************************************************************************************** Q1: Identify the correct labelling for the polarity of these molecules e.g. “d) - Y)”. For each molecule, deduce the oxidation state of each element. W) X) F F F δ+ δ− δ− F F δ+ δ+ δ− δ− H H δ− δ− δ+ δ+ S H H δ+ I δ− S δ− δ− δ+ δ− H …...of the following molecules: Si I S S H I F δ+ F F δ+ δ+ c) δ− δ− δ+ δ+ Si I I F F I F S i δ+ Si I F F δ− δ− δ+ F F δ− I b) i) geometry of bonding (including likely bond angles) at the atoms indicated ii) molecule polarity δ− Se Se Se Se F δ+ H H δ+ δ+ (9 marks) Q2:By counting (and stating) the number of valence electrons possessed by each of the following species, write Lewis structures for: IBr SF3+ SiF5COCl2 (12 marks) Q3: For the following different species: PF6 - PF3 Q4: Draw Lewis structure then use VSEPR to describe the….. Z) δ+ δ+ δ− a) Y) PF4 a) b) c) d) e) Al in AlCl3 S in SF2 C in HCCH Kr in KrF2 I in ICl3 (20 marks) Q5: a) Draw the Lewis resonance structures of the phosphate anion (PO43-) b) What is the charge on each oxygen atom? + PF2 - a) deduce the oxidation state of phosphorus b) how many valence electron pairs are there? Draw the Lewis structure c) What is the P-O bond order? (11 marks) Total: 70 marks c) what is the geometry of bonding (e.g. linear, trigonal bipyramidal etc) d) Hence list the four species in order of increasing F-P-F bond angle (smallest angle to largest) (18 marks) 1 Q1: Identify the correct labelling for the polarity of these molecules e.g. “d) - Y)”. For each molecule, deduce the oxidation state of each element. W) X) δ+ F F a) F F δ− F δ+ F δ+ F F Se δ− Se δ+ Se δ+ δ− δ− F δ+ δ− I δ− I Si I δ+ δ+ F I Si δ+ F δ− δ− δ− H c) Z) δ− δ− Se I b) Y) δ− H S δ+ F δ− H F F δ+ δ+ δ+ δ+ H H H S is -2 H is +1 S S δ− δ− δ+ I δ+ δ+ H S Si is +4 F is -1 I is -1 I δ− Si I δ− H δ+ δ+ F Si F Se is +2 F is -1 (Q1: 3 x 3 marks) Q2:Write Lewis structures for: IBr SF3+ SiF5- COCl2 IBr Count up valence electrons Count up valence electron pairs = 14 =7 Determine which atoms are bond to which (struc. formula) = Br I Form single bonds between neighbouring atoms: (3 electron pairs remain unused) Br I Use remaining electron pairs to complete octets of each atom: Br I (Q2: 4 x 3 marks) 2 Q2:Write Lewis structures for: IBr SF3+ SiF5- COCl2 SF3+ Count up valence electrons Count up valence electron pairs = 26 = 13 F Determine structural formula: Form single bonds between neighbouring atoms: (10 electron pairs remain unused) F S F Use remaining electron pairs to complete octets of each atom: (F octet must be completed first) leaves one lone pair on S F S F + F (Q2: 4 x 3 marks) Q2:Write Lewis structures for: IBr SF3+ SiF5- COCl2 SiF5Count up valence electrons Count up valence electron pairs = 40 = 20 _ Determine structural formula: Form single bonds between neighbouring atoms: (15 electron pairs remain unused) F F F Si F F Use remaining electron pairs to complete octets of each atom: (F octet must be completed first) leaves no lone pairs on Si F F _Si F F F (Q2: 4 x 3 marks) 3 Q2: COCl2 Count up valence electrons Count up valence electron pairs = 24 = 12 O Determine structural formula: Cl Place C at centre and form single bonds between neighbouring atoms: (9 electron pairs remain unused) Use remaining electron pairs to complete octets of each electronegative atom: C Cl _ + C F O F Not enough electrons to complete carbon’s octets so C=O double bond must form using O lone pair: (Q2: 4 x 3 marks) F C F O (1 mark) Q3: For the following species: PF6- PF3 PF4+ PF2- a) deduce the oxidation state of phosphorus b) how many valence electron pairs are there? Draw the Lewis structure c) what is the geometry of bonding (e.g. linear, trigonal bipyramidal etc) d) Hence list the four species in order of increasing F-P-F bond angle (smallest angle to largest) (Q3: 4 + 8 + 4 + 2 marks) 4 Q3: For the following species: PF6+5 48 24 P ox. state valence electrons valence electron pairs F _ F P F F F F F-P-F bond angle geometry F F P PF4+ +5 32 16 PF3 +3 26 13 PF2+3 20 10 F F F P+ F F _ P F F PF690º PF2~106º octahedral tetrahedral distorted by two lone pairs PF4+ 109.5º PF3 ~108º tetrahedral distorted by one lone pair tetrahedral (Q3: 4 + 8 + 4 + 2 marks) Q4: Use VSEPR to describe the i) geometry of bonding (including likely bond angles) at the atoms indicated ii) molecule polarity of the following molecules: a) b) c) d) e) Al in AlCl3 S in SF2 C in HCCH Kr in KrF2 I in ICl3 (Q3: 5 x 4 marks) 5 Recap: how to determine hybridisation: Strategy: The steps for determining the hybridization of the central atom in a molecule are: -count total number of valence electrons -draw Lewis Structure to determine no. of electron pairs around central atom sp2 sp sp3 -use VSEPR to determine the bonding geometry -relate geometry to hybridisation using: sp3d sp3d2 a) Al in AlCl3 - 24 valence electrons (12 pairs) single bonds - 3 pairs complete Cl octets so: Cl lone pairs - 9 pairs Cl Cl Cl cannot complete Al octet AlCl3 is electron deficient Al sp2 sp sp3 Al - 3 bonding pairs trigonal geometry (non-polar) sp3d sp3d2 6 b) S in SF2 - 20 valence electrons (10 pairs) single bonds - 2 pairs complete F octets so: F lone pairs - 6 pairs F F S 2 pairs left to complete S octet S - 4 surrounding electron pairs sp3 sp2 sp distorted tetrahedral geometry -polar F-S-F bond angle < 109.5º sp3d sp3d2 c) C in C2H2 - 10 valence electrons (5 pairs) single bonds - 3 pairs reamining electrons must be put on C - 2 pairs C octets incomplete - must form triple bond multiple bonds have no affect on geometry each C surrounded by 2 bonding pairs H C H C C H H sp2 sp C sp3 linear geometry (non-polar) sp3d sp3d2 7 d) Kr in KrF2 - 22 valence electrons (11 pairs) single bonds - 2 pairs complete F octets so: F lone pairs - 6 pairs 3 electron pairs remain must be placed on Kr (octet exceeded) F F Kr F Kr - 5 surrounding electron pairs -trigonal bipyramidal geometry -lone pairs in equator -molecule is linear ⇒ non-polar F e) I in ICl3 - 28 valence electrons (14 pairs) single bonds - 3 pairs complete Cl octets so: Cl lone pairs - 9 pairs Cl I Cl Cl 2 electron pairs remain must be placed on I (octet exceeded) Cl I - 5 surrounding electron pairs Cl -trigonal bipyramidal geometry -lone pairs in equator -molecule is distorted T-shaped (angles < 90º) ⇒ polar Cl 8 Q5: a) Draw the Lewis resonance structures of the phosphate anion (PO43-) valence electrons = 32 (16 pairs) place P as central atom and use 4 pairs – single bonds _ _ + P O _O O O_ _ O P can expand valency so double bond can be drawn: now move π bond: _ _ O _O P O O_ O _O P _ _ O O_ O P O O P O_ _O _ _ O O_ O _O P O O (Q5: 8 + 1.5 + 1.5 marks) Total: 70 marks b) What is the charge on each oxygen atom? - 0.75 c) Given that the strength of a typical P-O single bond is 200 kJ/mol, estimate the P-O bond strength in the phosphate ion. Bond order = 1.25 Bond strength expected = 250 kJ/mol. (Q5: 8 + 1.5 + 1.5 marks) Total: 70 marks 9