E-business strategy Strategic analysis Strategic objectives E
advertisement
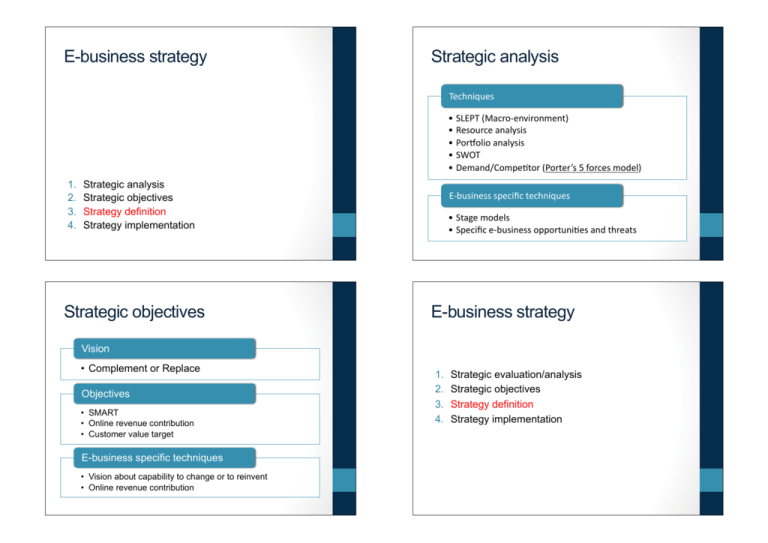
E-business strategy Strategic analysis Techniques' • SLEPT'(Macro.environment)' • Resource'analysis' • Por;olio'analysis' • SWOT' • Demand/CompeCtor'(Porter’s'5'forces'model)' 1. 2. 3. 4. Strategic analysis Strategic objectives Strategy definition Strategy implementation Strategic objectives E.business'specific'techniques' • Stage'models' • Specific'e.business'opportuniCes'and'threats' E-business strategy Vision • Complement or Replace Objectives • SMART • Online revenue contribution • Customer value target E-business specific techniques • Vision about capability to change or to reinvent • Online revenue contribution 1. 2. 3. 4. Strategic evaluation/analysis Strategic objectives Strategy definition Strategy implementation Strategy definition Strategy definition • Strategy definition is • formulation, • review and • selection of strategies to • achieve strategic objectives OpCons' • OpCon'generaCon' • OpCon'evaluaCon' • OpCon'selecCon' E.business'strategic'decision' • 1.'Channel'prioriCes' • 2.'Market'and'product'development' • 3.'PosiConing'and'differenCaCon'strategies' • 4.'Business'and'revenue'models' • 5.'Marketplace'restructuring' • 6.'Supply.chain'management'capabiliCes' • 7.'Internal'knowledge'management'capabiliCes' • 8.'OrganizaConal'resourcing'and'capabiliCes' • Preceded by • Generating options • Evaluation of options • Selection of options Matrix Model for options (Tjan, 2001) Viability 0"Points" 100"points" Market'value'potenCal' <'10'M€' >'1000'M€' Time'to'posiCve'cash'flow' >'5'years' <'1'year' Personnel'requirement' >'20'people' <'5'people' Funding'requirement' >'35'M€' <'3'M€' Fit" Alignment'with'core'capabiliCes' Alignment'with'other'company'iniCaCves' Fit'with'organizaConal’s'structure' Fit'with'organizaConal’s'culture/values' Ease'of'technical'implementaCon' Low" Medium" High" Strategy alternatives matrix Strategy definition decisions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Decision 1: Channel priorities Channel priorities Market and product development Positioning and differentiation strategies Business and revenue models Marketplace restructuring Supply-chain management capabilities Internal knowledge management capabilities Organizational resourcing and capabilities “Getting the right mix of bricks and clicks” Gulati and Garino (2000) Channel priorities • Internet pureplay: Company trading online with limited or no physical presence, e.g. as retail units • Particularly start-ups • Impractical for many businesses • Right channeling: • The right person • At the right time • Using the right communication channel • With a relevant offer, product or message. Strategy definition decisions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Channel priorities Market and product development Positioning and differentiation strategies Business and revenue models Marketplace restructuring Supply-chain management capabilities Internal knowledge management capabilities Organizational resourcing and capabilities Channel priorities • Right-channeling applications: Example Application and tactics Account-managed relationships Face-to-face and phone with large, high-sales-volume clients Sell to and serve SME online Internet sales and extranet service Encourage customer to online channels ??? Provide offline conversion during sales Phone callback or live chat from within web sales Migrate customers to web selfservice Self-manage accounts for lowercost-to-serve Selective service levels for different customer types Integrated CRM systems Development strategies • Question: • What is sold? • Who is it sold to? • Market and Product development matrix: Strategy definition decisions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Positioning and differentiation Porter (1985, 2001): Profitability is determined by: 1. Industry structure 2. Sustainable competitive advantage Cost and price advantage achieved through: 1. Operational effectiveness 2. Strategic positioning Channel priorities Market and product development Positioning and differentiation strategies Business and revenue models Marketplace restructuring Supply-chain management capabilities Internal knowledge management capabilities Organizational resourcing and capabilities Positioning and differentiation Operational effectiveness (OE) = • Performing similar activities better than rivals perform them. • Internet is (most) powerful tool for enhancing OE Productivity frontier = • Maximum value a company can deliver at a given cost, given best available technology, skills, management techniques… Competition leads to: • Absolute improvement in OE (for all) • Relative improvement in OE to no one Positioning and differentiation Positioning and differentiation (2) Porter’s Generic strategies “Competitive strategy is about being different” Strategic positioning = Attempts to achieve sustainable competitive advantage by preserving distinction: • Perform different activities from competitors, or • Perform similar activities in different ways. Origins of strategic positioning Porter (1996): 1. Variety-based positioning: based on choice of product or service 2. Needs-based positioning: based on choice of customer/market segment 3. Access-based positioning: based on segmenting customers who are accessible in different ways Scope: • Any positioning can be broad or narrow (based on 3 dimensions) • Level of differentiation • Relative product cost • Scope of target market • Three most viable bases for positioning: • Cost leadership • Differentiation • Focus Examples • Low-cost airline carrier (Ryanair, Easyjet) • Variety-based, narrow focus • Regular airline • Variety-based, broad focus • IKEA • Needs-based, broad focus • Apple • Variety-based, broad focus • Bang & Olufsen • Variety-based, narrow focus Trade-off and Fit Alternatives: value disciplines Trade-off: • When you choose a particular position, you choose not to use other approaches • These trade-offs are essential and make imitation difficult Fit: • Production, marketing, personnel, etc. should all be consistent: • When all activities work together as a system, imitation is difficult. Customer value Treacy & Wiersema: 1. Operational excellence: Best total cost 2. Product leadership: Best product 3. Customer intimacy: Best total service In practice: 1. Each dimension should be good 2. Choose excellence in one dimension Strategy definition decisions • Position relative to competitors: • Product quality • Service quality • Price • Fulfillment time • Deise et al. (2000) Customer value (brand perception) = Product quality × Service quality Price × Fulfilment time 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Channel priorities Market and product development Positioning and differentiation strategies Business and revenue models Marketplace restructuring Supply-chain management capabilities Internal knowledge management capabilities Organizational resourcing and capabilities Business and revenue models • Recall: Business model: A summary of how a company will generate revenue, identifying its product offering, valueadded services, revenue sources and target customer • Revenue model: Describe methods of generating income • Observations from practice: • Change and flexibility ≠ Losing focus on core business • Innovation often through acquisition Marketplace restructuring • Review options for: • Disintermediation • Re-intermediation • Countermediation Strategy definition decisions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Channel priorities Market and product development Positioning and differentiation strategies Business and revenue models Marketplace restructuring Supply-chain management capabilities Internal knowledge management capabilities Organizational resourcing and capabilities Strategy definition decisions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Channel priorities Market and product development Positioning and differentiation strategies Business and revenue models Marketplace restructuring Supply-chain management capabilities Internal knowledge management capabilities Organizational resourcing and capabilities Supply-chain management capabilities • Questions: • Integrate more closely with suppliers? • Which materials and interactions should we support through e-procurement? • Can we participate in online marketplaces to reduce costs? Knowledge Every day knowledge essential to your business walks out of your door, and much of it never comes back. Saunders (2000) Knowledge: • Combination of data and information, • With added expert opinion, skills and experience • Explicit / Tacit • Individual and/or collective Strategy definition decisions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Channel priorities Market and product development Positioning and differentiation strategies Business and revenue models Marketplace restructuring Supply-chain management capabilities Internal knowledge management capabilities Organizational resourcing and capabilities Knowledge management Knowledge management: • Techniques and tools for disseminating knowledge • Main activities: • Identify • Create • Store • Share • Use Technologies for KM Classes of KM applications (Binney, 2000): 1. Transactional: Helpdesk, customer service apps 2. Analytical: Data mining/warehousing for CRM apps 3. Asset management: Document and content management 4. Process support: Web 2.0 for KM Approaches: • Content management systems • Internal blogs • Micro-blogging: www.yammer.com • Social networks: www.cyn.in, www.ning.com • Wiki Total quality management, benchmarking, BPR 5. Developmental: Enhancing skills / competencies, training, e-learning 6. Innovation and creation: Communities, collaboration, virtual teamwork Strategy definition decisions 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Channel priorities Market and product development Positioning and differentiation strategies Business and revenue models Marketplace restructuring Supply-chain management capabilities Internal knowledge management capabilities Organizational resourcing and capabilities Organizational resourcing and capabilities • Decide how organization needs to change to achieve the priorities set for e-business. • Gulati & Garino (2000): • In-house division (integration) • Joint venture (mixed) • Strategic partnership (mixed) • Spin-off (separation) • QUESTION: what are the advantages of • Integration • Spin-off? E-business strategy Strategy implementation ImplementaCon' 1. 2. 3. 4. Strategic evaluation/analysis Strategic objectives Strategy definition Strategy implementation • Planning' • ExecuCon' • Control' ImplementaCon'issues' • Supply'chain'management'strategies'(Chapters'6'and'7)' • E.markeCng'strategies'(Chapters'8'and'9)' • Planning,'scheduling'and'change'management'(Chapter'10)' • E.business'analysis'and'design'(Chapter'11)' • ImplementaCon,'maintenance'and'control'(Chapter'12)' Success or failure • Failures due to: (Miller, 2003): • Overestimation of adoption • Unrealistic replacement expectations • Timing errors • Lack of creativity • Offering free services • Over-ambition • Classic mistakes: • Situation analysis • Objective setting • Strategy definition • Implementation Outline • Intro • Strategic Analysis • Strategic Objectives • Strategy Definition • Strategy Implementation • Information systems strategy and e-business strategy IS strategy vs. e-business strategy Strategic Information Systems matrix • Question: how does IS strategy supports change? • Business-alignment IS strategy: • Top-down • How can IS be used to directly support a defined ebusiness strategy? • Strategic IS matrix • Business-impacting IS strategy: • Bottom-up • New opportunities from deployment IS may impact positively on business strategy? • Redesign business processes? • Value chain analysis Strategic Information Systems Three types of Information Systems: 1. Financial information systems: • Mechanization and control of financial systems • Accounting, budgeting, HR,… 2. Operational / Service information systems: • Control details and cost effectiveness of business • Ordering, inventory control, planning,… 3. Strategic information systems: • Profound impact on profitability and competitive advantage • Links/aligns business and computer strategies Summary • Key characteristics of an e-business strategy model: • Based on assessment of internal and external environment • Have clearly defined SMART objectives backed up by vision • Have strategies, tactics and implementation that select the best techniques to achieve these strategies • Have monitoring and control that assess whether the objectives are being achieved and a feedback loop to ensure corrective action occurs.