Quadrilaterals & Parallelograms Worksheet: High School Geometry
advertisement

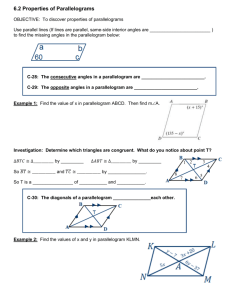
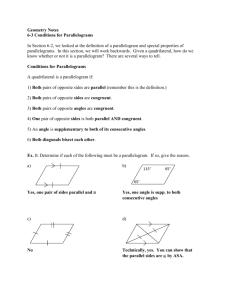
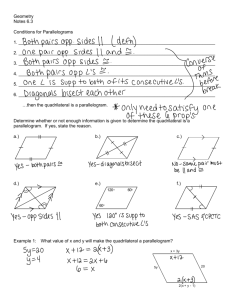
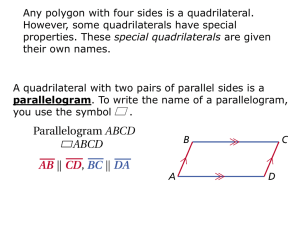
Name:________________________________________________________ Date:_________________ Period: _______ Chapter 10: Quadrilaterals Topic 1: Family Tree & Parallelograms A _________________ is a polygon with __________ sides. Figure ABCD is an example of a quadrilateral. Refer to ABCD as the parts of a quadrilateral that are defined below. Diagram: Parts of a Quadrilateral: - Opposite sides are sides that do not share a common endpoint. - Consecutive (adjacent) sides share a common endpoint. - Opposite Angles are angles whose vertices are not right next to each other. - Consecutive Angles are angles that are right next to each other, either clockwise or counter-clockwise. - Diagonals of a quadrilateral are line segments whose endpoints are pairs of opposite vertices. Quadrilateral Family Tree: True/False Examples: 1) All trapezoids are quadrilaterals. _______________ 5) All parallelograms are trapezoids. _______________ 2) All rectangles are parallelograms. _______________ 6) All quadrilaterals are squares. _______________ 3) All squares are rhombuses. _______________ 7) All isosceles trapezoids are quadrilaterals. ________ 4) All rhombuses are rectangles. _______________ 8) All quadrilaterals are rhombuses. __________ Parallelogram: - A parallelogram is a quadrilateral in which both pairs of opposite sides are parallel and congruent. Diagram: Properties: Opposite sides are congruent and parallel. Opposite angles are congruent. Consecutive angles are supplementary. Diagonals bisect each other. Diagonals divide the parallelogram into two congruent triangles. Word Problems: 1) In parallelogram ABCD, m<A = 3x - 60 and m<C = 40 - x. Find the value of x and the measures of each of the angles. 2) In parallelogram ABCD, if the measure of <A exceeds the measure of <B by 30, what is the measure of <B? 3) In parallelogram DAWN, the measure of <D is represented by 3x+10 and the measure of <A is represented by 2x + 20. What is the value of x? 4) In a parallelogram, the measures of two consecutive angles are 2x-5 and 3x + 10. Find the measure of each angle and the value of x. 5) The measure of <A and <B in parallelogram ABCD are in the ratio 6:3. Find the measure of each angle of the parallelogram. 6) In parallelogram WXYZ, WX = 9x - 2 and YZ = 4x + 33. What is the value of x? 7) In parallelogram ABCD, the measure of <ABC = 6x - 3 and the measure of <CDA = 4x + 23. Find the value of <ABC. 8) Quadrilateral RSPQ is a parallelogram. The diagonals RP and SQ intersect at T. If QT = 5y and TS = 2y + 12, find the value of y. What is the length of QS? Name:________________________________________________________ Date:_________________ Family Tree & Parallelograms Homework Directions: Answer the following questions completely. If needed, include a diagram with your answer. For questions 1-6, answer the following with the response of True or False: 1) The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. ____________________ 2) In a parallelogram, opposite sides are parallel. ____________________ 3) A square is a rhombus. ____________________ 4) A rectangle is a trapezoid. ____________________ 5) A quadrilateral is a rectangle. ____________________ 6) A rectangle is a rhombus. ____________________ 7) In parallelogram 𝑃𝑄𝑅𝑆, the ratio of the measure of < 𝑄 to the measure of < 𝑅 is 1: 5. Find 𝑚 < 𝑄. 8) In parallelogram 𝐴𝐵𝐶𝐷, 𝐴𝐵 = 5𝑥 − 6 and 𝐶𝐷 = 3𝑥 + 8. Find the value of 𝑥. 9) In parallelogram 𝐴𝐵𝐶𝐷, 𝑚 < 𝐷 = 6𝑥 + 40 and 𝑚 < 𝐵 = 4𝑥 + 70. Find the value of 𝑥. Find 𝑚 < 𝐶. (Hint: First find 𝑚 < 𝐷 𝑜𝑟 𝑚 < 𝐵). ̅̅̅̅ and 𝑅𝑇 ̅̅̅̅ intersect at point 𝐸. If 𝑄𝐸 = 4𝑥 + 3 and 𝐸𝑆 = 23, find the value of 𝑥. 10) In parallelogram 𝑄𝑅𝑆𝑇, diagonals 𝑄𝑆 11) In parallelogram 𝐴𝐵𝐶𝐷, 𝑚 < 𝐴 = 3𝑥 − 40 and 𝑚 < 𝐶 = 7𝑥 − 100. Find the measure of all of the angles in this parallelogram. Review Section: _____ 12) A rectangle right prism is shown. Which pair of edges are not coplanar? (1) BF and CG (2) BF and DH (3) EF and CD (4) EF and BC _____ 13) In the figure, m<AED = 104. Which of the following statements is false? (1) m<AEB = 76 (2) <BEC and <CED are adjacent angles (3) m<BEC = 104 (4) <AEB and <DEC are supplementary angles 14) The vertex angle of an isosceles triangle measures 15 degrees more than one of its base angles. How many degrees are there in a base angle of the triangle? 15) In the diagram of ∆𝐴𝐵𝐶, DE//BC. What is the length of BC?