Curriculum Map World History Unit 1 – Ancient Civilizations
advertisement
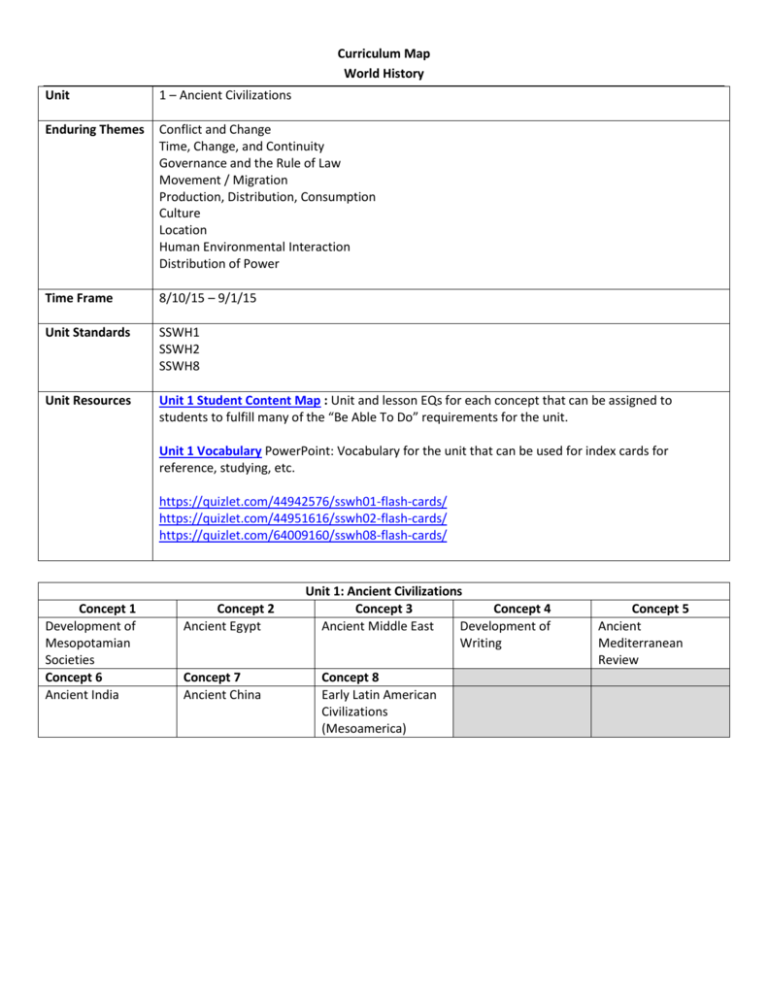
Curriculum Map World History Unit 1 – Ancient Civilizations Enduring Themes Conflict and Change Time, Change, and Continuity Governance and the Rule of Law Movement / Migration Production, Distribution, Consumption Culture Location Human Environmental Interaction Distribution of Power Time Frame 8/10/15 – 9/1/15 Unit Standards SSWH1 SSWH2 SSWH8 Unit Resources Unit 1 Student Content Map : Unit and lesson EQs for each concept that can be assigned to students to fulfill many of the “Be Able To Do” requirements for the unit. Unit 1 Vocabulary PowerPoint: Vocabulary for the unit that can be used for index cards for reference, studying, etc. https://quizlet.com/44942576/sswh01-flash-cards/ https://quizlet.com/44951616/sswh02-flash-cards/ https://quizlet.com/64009160/sswh08-flash-cards/ Concept 1 Development of Mesopotamian Societies Concept 6 Ancient India Concept 2 Ancient Egypt Concept 7 Ancient China Unit 1: Ancient Civilizations Concept 3 Concept 4 Ancient Middle East Development of Writing Concept 8 Early Latin American Civilizations (Mesoamerica) Concept 5 Ancient Mediterranean Review Concept 1: Development of Mesopotamian societies Standard: SSWH1 The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BCE to 500 BCE a. Describe the development of Mesopotamian societies; include the religious, cultural, economic, and political facets of society, with attention to Hammurabi’s law code Lesson EQ: What were the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean? Know Understand Be Able To Do (DOK 2) Tigris The Mesopotamian societies Describe the role of religion developed in the fertile land Euphrates in the development of between the Tigris and Euphrates Fertile Crescent Mesopotamian societies. rivers. Mesopotamia Describe the role of culture in Mesopotamian societies were Sumer the development of polytheistic. Ziggurats Mesopotamian societies The ziggurats (temples) built by polytheism Describe the economic facets the Sumerians demonstrate the City-state of Mesopotamian societies complexity of their society Hammurabi Describe the political facets Agriculture replaced hunting and of Mesopotamian societies gathering and societies Large numbers of people began Describe how Hammurabi’s to live together forming societies law code impacted the and social classes development of Sumerians created the first cityMesopotamian societies states Hammurabi’s Code was a uniform law for his empire that established the idea that it was the government’s job to look after it’s people *Ancient Eastern Mediterranean Power Point Resources We Do (Guided/Differentiated You Do (Independent Practice) Instruction) Mesopotamian Visual Discovery Group Hammurabi’s Guided Reading and Handout Independent Practice Development of Written Law Handout| Teacher Key Mesopotamian Visual Discovery Primary Sources *Rise of Cities Handout with Teacher Key Mesopotamian Visual Discovery Teacher Notes I Do (Teacher Point) Hammurabi’s Code PowerPoint Prezi with student notes for this concept: https://prezi.com/x9m2gqymsgef/mes opotamian-societies/ *These resources cover material for Ancient Egypt, as well. Stop at that point and come back to it in lesson for Concept 2. Hammurabi’s Code Lesson Plan Hammurabi’s Code Tiered Reading Concept 2: Ancient Egypt Standard: SSWH1 The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BCE to 500 BCE b. Describe the relationship of religion and political authority in Ancient Egypt Lesson EQ: How were religion and political authority related in Ancient Egypt? Know Understand The worship of gods, How religion impacted life in goddesses, and Pharaohs in ancient Mesopotamia Ancient Egypt How religion impacted Egyptian politics (the pharaohs were considered to be god-kings and were both religious and political leaders) Egyptian society was organized like a pyramid, with the pharaoh at the top. I Do (Teacher Point) *Ancient Eastern Mediterranean Power Point *Rise of Cities Handout with Teacher Key *These documents are a continuation from Concept 1. https://prezi.com/x9m2gqymsgef/mes opotamian-societies/ (This Prezi from Concept 1 also contains information on Ancient Egypt) Resources We Do (Guided/Differentiated Instruction) The Pharaohs Guided Reading (You can have students work on this individually then discuss answers with a partner or group or work on it with a partner and discuss the answers whole group, etc.) Be Able To Do (DOK 2) Describe the relationship between religion and political authority in Ancient Egypt. You Do (Independent Practice) Ancient Eastern Mediterranean Religion Comparison Chart (Note: At this point, you can have students complete just the Sumerian and Egyptian portions to review or summarize what they’ve learned thus far) Concept 3: Ancient Middle East Standard: SSWH1 The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BCE to 500 BCE c. Explain the development of monotheism; include the concepts developed by the ancient Hebrews, and Zoroastrianism Lesson EQ: How did monotheism develop in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean? Know Understand Monotheism Monotheism means belief in one god. Hebrews As Mesopotamian and Zoroastrianism Egyptian civilizations declined, smaller states emerged. The Israelites were a Semitic people who lived in Palestine. The Hebrews, or Israelites, worshipped one god, Yahweh. The covenant, law, and prophets were three aspects of Jewish religion. Zoroastrianism developed in Persia. Their god was called Ahura Mazda; they also believed in angels and Satan. Resources I Do (Teacher Point) We Do (Guided/Differentiated Instruction) Ancient Eastern Mediterranean Power Judaism and Zoroastrianism Research Point (This is the same PPT from Exchange Venn Diagram previous concepts; Ancient Middle East begins on slide 44). Judaism and Zoroastrianism Research Exchange Directions Ancient Middle East Student Handout Be Able To Do (DOK 2) Explain how monotheism developed in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean. Explain the beliefs of the ancient Hebrews and how they contributed to the development of monotheism. Explain the beliefs of Zoroastrianism and how the Persians contributed to the development of monotheism. You Do (Independent Practice) Ancient Eastern Mediterranean Religion Comparison Chart (This is the same chart that students could have begun in the previous concept; at this point students should be able to complete the entire chart) Concept 4: Development of Writing Standard: SSWH1 The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BCE to 500 BCE d. Describe early trading networks in the Eastern Mediterranean; include the impact Phoenicians had on the Mediterranean world e. Explain the development and importance of writing; include cuneiform, hieroglyphics, and the Phoenician alphabet Lesson EQ: How did writing develop and impact Ancient Eastern Mediterranean societies? Know Understand Be Able To Do (DOK 2) Cuneiform Cuneiform was a form of Identify which societies pictograph created by the developed cuneiform, Hieroglyphics Sumerians. It was used to hieroglyphics, and the first Phoenician alphabet keep records and to pass on alphabet. (DOK 1) Trading networks knowledge and allowed Explain the development and people to communicate in importance of writing (DOK 2) new ways Hieroglyphics were pictographs used by the Egyptians for business and trade and general use for everyday life The Phoenicians created an alphabet and introduced writing systems to trading partners Resources I Do (Teacher Point) We Do (Guided/Differentiated You Do (Independent Practice) Instruction) Ancient Eastern Mediterranean Power Development of Written Language Constructed Response Summarizer: Point (This is the same PPT from Research Activity previous concepts; Development of How did the development of writing Writing begins on slide 74). (Have students use the links impact Sumerian, Egyptian and provided on the page following the Phoenician societies? Phoenicians Student Handout graphic organizer to record information about writing in Development of Writing Student Sumeria, Egypt and Phoenicia. This Handout would be a good lesson to allow students to work with partners or in https://prezi.com/x9m2gqymsgef/mes a group so that you can circulate opotamian-societies/ and help groups who need you more (This Prezi from Concept 1 also contains than others to help them complete information on Ancient Egypt) the assignment) Concept 5: Ancient Mediterranean Review (DIFFERENTIATED LESSON) Standard: SSWH1 The student will analyze the origins, structures, and interactions of complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean from 3500 BCE to 500 BCE Lesson EQ: How did the origins, structures, and interactions of the complex societies in the ancient Eastern Mediterranean impact the development of those societies? Know Understand Be Able To Do See all items in “Know” column in See all items in “Understand” column See all items in “Be Able to Do” Concepts 1-4 in Concepts 1-4 column in Concepts 1-4 I Do (Teacher Point) Differentiated Lesson Plan_SSWH1 Facilitate Activator in Lesson Plan to capture students’ interest and review the importance of the development of writing from previous lesson. Ancient Eastern Mediterranean Power Point *Use Summary Questions from Power Point to review with students Resources We Do (Guided/Differentiated Instruction) Differentiated Lesson Plan_SSWH1 Ancient Eastern Mediterranean Formative Assessment (NOTE: This Formative Assessment should be given to students individually PRIOR to differentiated instruction to help identify the needs of the student) (Tiered Assignments) Unit 1 Vocabulary https://quizlet.com/44942576/sswh01flash-cards/ Ancient Civilizations Primary Source Documents with Questions Choice Board You Do (Independent Practice) Differentiated Lesson Plan_SSWH1 Student Content Map Concept 6: Ancient India Standard: SSWH2 The student will identify the major achievements of Chinese and Indian societies from 1100 BCE to 500 CE a. Describe the development on Indian Civilization; include the rise and fall of the Maurya Empire, the “Golden Age” under Gupta, and the emperor Ashoka b. Explain the development and impact on Hinduism and Buddhism on India and subsequent diffusion of Buddhism. e. explain how the geography of the Indian Subcontinent contributed to the movement of people and ideas Lesson EQ: What were the major achievements of Indian societies from 1100 BCE to 500 CE? Know Understand Be Able To Do (DOK 2) Maurya Empire Geography: Describe the rise and fall of o Mountains in India the Maurya Empire “Golden Age” protected the Indus Valley Describe the “Golden Age” Gupta from invasion under Gupta Emperor Ashoka o Rivers connected the Describe the Emperor Hinduism interior of the Subcontinent Ashoka Buddhism to the sea and the silt from Explain the development Geography of Indian rivers produced fertile land of Hinduism Subcontinent for agriculture Explain the impact of Aryans created the caste system Hinduism on India Ashoka was a great emperor of the Explain the development Mauryan empire; he converted to of Buddhism and spread Buddhism; India became Explain the impact of an important crossroads on Silk Buddhism on India Road Explain how geography Gupta Empire considered the contributed to the “Golden Age” because of movement of people and advancements in art, architecture, ideas in Ancient India trade, medicine and science and math Hinduism developed out of Aryan religious beliefs; Hindus are Henotheistic (believe in many gods, with one supreme god); they also believe in reincarnation and karma. Buddhism was founded by Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha); believe in nirvana and reincarnation; reject caste system Resources I Do (Teacher Point) We Do (Guided/Differentiated Instruction) You Do (Independent Practice) Caste System Activator India Map Indian Subcontinent Flowchart India Student Handout Religions of India Student Handout Prezi identifying the geographic features of Caste System Reading Ancient Asian Civilizations the Indian Subcontinent: Powerpoint https://prezi.com/n3cvrovd3jim/geography(through slide 77) of-india/ Hinduism and Buddhism PowerPoint (T-chart notes) Indian Empires Outline Indian Empires PowerPoint (goes along with Indian Empires Outline) Concept 7: Ancient China Standard: SSWH2 The student will identify the major achievements of Chinese and Indian societies from 1100 BCE to 500 CE c. Describe the development of Chinese civilization under the Zhou and Qin d. Explain the impact of Confucianism on Chinese culture; include the examination system, the Mandate of Heaven, the status of peasants, the status of merchants, and the patriarchal family, and explain diffusion to Southeast Asia, Japan, and Korea Lesson EQ: What were the major achievements of Chinese societies from 1100 BCE to 500 CE? Know Understand Be Able To Do (DOK 2) Zhou dynasty Zhou dynasty overthrew Shang Describe how the Zhou dynasty and established feudalism dynasty developed Qin dynasty in China and Mandate of Heaven Describe how the Qin Confucianism (laws of nature/heaven kept in dynasty developed Examination system order on earth by the king; helps Explain the impact of Mandate of Heaven support dynastic cycle) Confucianism on Chinese Status of peasants, Qin dynasty unified the Chinese culture merchants world and built Great Wall of China Patriarchal family (some of the original remains) Diffusion (spread) of Confucius was a Chinese Confucianism philosopher who developed a code of ethical conduct o Importance of family and right relationships o Patriarchal family (father = head) o Examination system: led to bureaucracy, civil servants must pass tests o Divide between ruler and subjects (Mandate of Heaven) o Peasants above merchants (wealth did not define social status necessarily) o Diffusion of Confucianism by moral example, did not believe in war/conquest; spread to Korea, Vietnam, Japan Resources I Do (Teacher Point) We Do (Guided/Differentiated Instruction) You Do (Independent Practice) Chinese Societies Handout Confucius Quotes Analysis Ancient China Constructed Response Summarizer Confucianism Handout Ancient Asian civilizations PowerPoint (begins on Slide 78) Early Chinese Civilizations PPT Early Chinese Civilizations Outline Concept 8 : Early Latin America (Mesoamerica) Standard: SSWH8 The student will demonstrate an understanding of the development of societies in Central and South America a. Explain the rise and fall of the Olmec, Mayan, Aztec and Inca empires b. Compare the culture of the Americas; include government, economy, religion, and the arts of the Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas Lesson EQ: How did the early societies in Central and South America develop? Know Understand Be Able To Do Olmec empire Olmec empire (1200 – 400 BC) was Explain how the Olmec farming society on the coast that empire rose and fell Mayan empire built large cities that were centers (DOK1) Aztec empire of religious rituals; the reason for Explain how the Mayan Inca empire the fall of this empire is unknown empire rose and fell Government, economy, Mayan (300-900 AD) city-states (DOK1) religion and arts of the located on Yucatan peninsula; cities Explain how the Aztec Mayans were mysteriously abandoned empire rose and fell Government, economy, around 800AD. Possible causes: (DOK1) religion and arts of the warfare, disruption of trade, over Explain how the Inca Aztecs farming, population growth, empire rose and fell Government, economy, disease, famine (DOK1) religion and arts of the Aztec’s rose to power by taking Compare the culture of the Incas neighbor’s land; flourished from Mayans, Aztecs, and Incas 1200-1500s AD; established the (DOK 3) capital city of Tenochtitlan. Fell to Spanish forces led by Cortes around 1520. Incas flourished in South America in the 1400s; Spanish arrive in 1530s, led by Pizzaro, led to smallpox outbreaks and Spanish conquest that resulted in the fall of the Incas. Understand cultural differences between Mayans, Aztecs and Incas (see key with student handout for details) Resources I Do (Teacher Point) We Do (Guided/Differentiated Instruction) You Do (Independent Practice) Mesoamerica Activator (Human Mesoamerican Empire Report Card Mesoamerica Constructed Sacrifice Attention Grabber) Olmec Reading Response Summarizer Mayan Reading Mesoamerica PowerPoint Aztec Reading Mesoamerica Summarizer (Ticket Mesoamerica Handout Inca Reading out the Door) Mesoamerica Comparison Chart (all of the “Reading” documents go along with the Report Card group activity) Mesoamerica Carousel Mesoamerica Carousel Student Handout (Note: Carousel could replace Mesoamerica PowerPoint and Handout to provide an activity that is more student-centered for delivery of material.)