The Final Set of Characteristics
advertisement
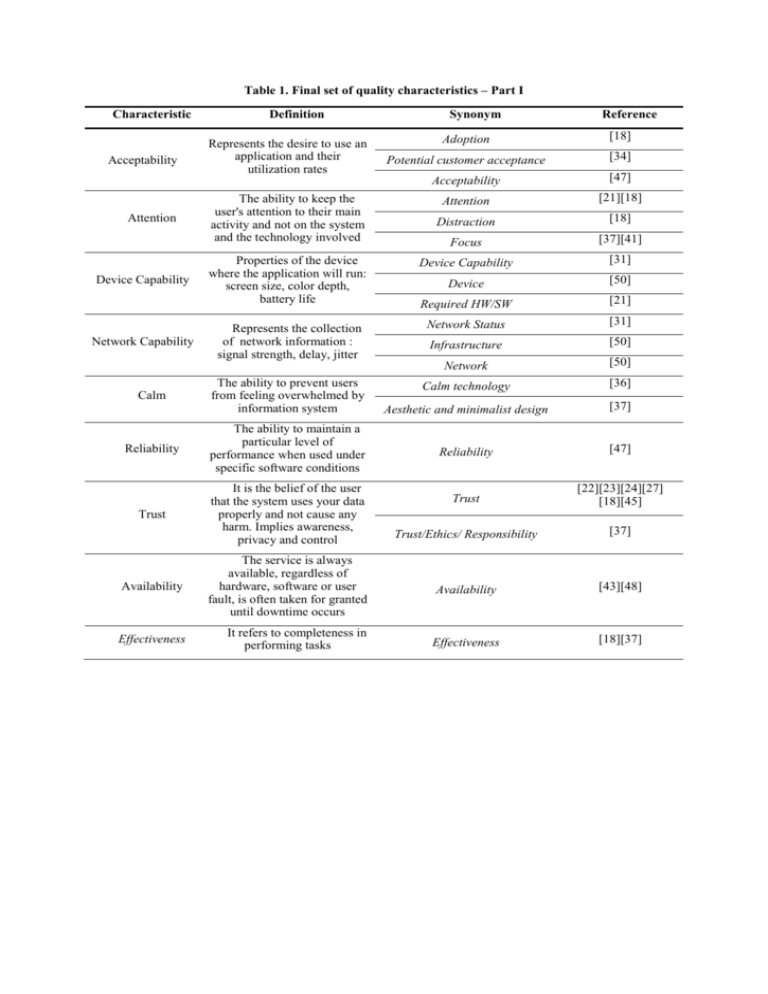
Table 1. Final set of quality characteristics – Part I Characteristic Definition Synonym Reference Adoption [18] Potential customer acceptance [34] Acceptability [47] Attention [21][18] Distraction [18] Focus [37][41] Properties of the device where the application will run: screen size, color depth, battery life Device Capability [31] Device [50] Required HW/SW [21] Represents the collection of network information : signal strength, delay, jitter Network Status [31] Infrastructure [50] Network [50] Calm technology [36] Aesthetic and minimalist design [37] Reliability [47] Trust [22][23][24][27] [18][45] Trust/Ethics/ Responsibility [37] Availability The service is always available, regardless of hardware, software or user fault, is often taken for granted until downtime occurs Availability [43][48] Effectiveness It refers to completeness in performing tasks Effectiveness [18][37] Acceptability Attention Device Capability Network Capability Calm Represents the desire to use an application and their utilization rates The ability to keep the user's attention to their main activity and not on the system and the technology involved The ability to prevent users from feeling overwhelmed by information system Reliability The ability to maintain a particular level of performance when used under specific software conditions Trust It is the belief of the user that the system uses your data properly and not cause any harm. Implies awareness, privacy and control Table 1. Final set of quality characteristics – Part II Characteristic Efficiency Scalability Definition It refers to the amount of effort and resources required to reach a certain goal in the system The ability to provide services to few or a large number of users Synonym Performance [25][49] Efficiency [18] Timeliness [37] User's performance [32] Scalability [18] Ease of Use Ease of Use Familiarity The system should be easy to use by a target user group User interactions with the system should improve the quality of their work. The user should be treated with respect. The design should be aesthetically pleasing. Interconnectivity An interconnected network between devices allows sharing Mobility The ability to provide users with continuous access to resources and information system, regardless of its location within the limits of the systems Reference [25][37] Facility of Use [30] Easy to Use [44] Perceived Ease of Use [39] Familiarity [33] Interconnectivity [19] Mobility Ubiquity [19] Flexibility [37] Multi-space support [48] [26] Predictability The ability, from past experiences, predict the result of running the system. Predictability [19] Privacy The ability to maintain information and data protected Privacy [21][23][27][18][38] [40][42] Safety The level of risk of harm to people, business, software, hardware, property or the environment in a specified context of use Driver safety [34] Degree to which a system or component can execute correctly in the presence of invalid inputs or stressful environmental conditions Application Robustness [18] User Satisfaction Customer Satisfaction [22] Appeal [18] User Satisfaction [18] Satisfaction [32] Robustness User Satisfaction The degree of user satisfaction and how the system is attractive for the user [25] Table 1. Final set of quality characteristics – Part III Characteristic Security Context-Awareness Simplicity Transparency Definition The protection to transport and to store informations and also security controls who can access, use and modify context information. The ability to perceive contextual information system and proactively adapt their functionality The user interface and the instructions should be simple The ability to hide the system, so users may not be aware of them. Moreover, the interaction is performed through natural interfaces Synonym Security [21][23][27][32] ContextAwareness Contextualization [28][35][40][44][48] Usability Utility The ability to provide value to user. Provide a contribution to user that was not available before the developed system [28][35] Context Sensitivity [32] Adaptivity [48] Simplicity [19] Diffusion Invisibility [26] [18] Interaction Transparency [18] Invisibility [37] Understandability [46] Transparency The ability of the software to be understood, learned, used and attractive to the user, when used under specified conditions Reference [48] Usability [33][34] Utility [22][39] Usefulness [33] Impact and Side Effects [18] Perceived Usefulness [47]








