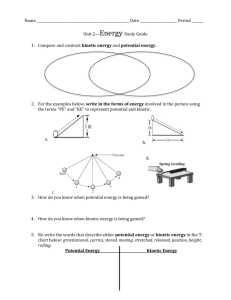
Q: What is energy? Q: What is work? Q: Potential Energy Q: Kinetic
advertisement

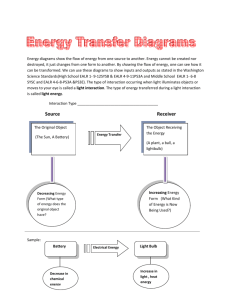
Q: What is energy? Energy is the ability to do work. Q: What is work? Work is done when a force causes an object to move. Q: Potential Energy The energy of an object due to its position, shape, or condition Q: Kinetic Energy The energy of an object due to the object’s motion Q: Elastic Potential Energy Potential energy that is caused by a change in the shape of an object Q: Examples of items with Elastic Potential Energy Bow and arrow, Spring, Slinky, Rubber band Q: Chemical Potential Energy Potential Energy that is caused by the condition of an object Q: Examples of items with Chemical Potential Energy Energy stored in a battery, piece of wood, or food Q: Gravitational Potential Energy Energy an object has because of where it is in relation to the surface of the Earth. Q: What two things affect an objects gravitational potential energy? How much the item weighs and how high it is off of the ground. Q: Examples of items with Gravitational Potential Energy A book on a shelf, a box on top of a building, a pencil on your desk Q: What is the unit for energy found in food called? Calories Q: What is weight? Weight is the force of gravity on an object. Q: In Science class, what do we use to measure weight in Newtons? A spring scale Q: What do we use to measure how high something is off of the floor? A ruler or tape measure Q: How do we calculate the Gravitational Potential Energy (GPE) of an object? GPE = Weight x Height Q: What unit do we use for Gravitational Potential Energy? The unit we use for GPE is the Joule (J) Q: All moving objects have what kind of energy? Kinetic Energy Q: How do we calculate how much Mechanical Kinetic Energy (MKE) an object has? MKE = Mass x Speed2 2 Q: What unit do we use for Mechanical Kinetic Energy? The unit we use for MKE is the Joule (J) Q: What are the seven forms of kinetic energy? Mechanical, Thermal, Chemical, Electric, Sound, Radiant (light), and Nuclear Energy Q: What is Mechanical Energy? The energy an object has because of its motion (kinetic energy) and position (potential energy) Q: What is Thermal or Heat Kinetic Energy? Thermal or heat energy is the kinetic energy of a substance’s atoms Q: What does thermal energy have to do with whether an object is a solid, liquid, or a gas? The atoms in solids do not have a lot of kinetic energy. The atoms in liquids have more kinetic energy than in solids. The atoms in gases have the most kinetic energy. Q: What is Electrical Energy (Electricity)? It is the energy of moving electrons. Q: What is Sound or Acoustic Energy? It is the energy caused by an object’s vibrations. Q: Why do we hear a guitar when it is played? The vibrating strings cause the air around the string to vibrate. The vibrating air travels to your ear. Your body hears these vibrations as sound. Q: What are the kinds of energy that make up the Electromagnetic Scale? Radio waves, infrared waves, visible light waves, ultraviolet waves, X-rays, and gamma rays. Q: How do we remember the colors of the rain bow? ROY G BIV = red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo, and violet Q: Why does a leaf look green? The leaf absorbs all of the colors of the rainbow except green. The green color is reflected off of the leaf. Q: Why does something look black? The black item is absorbing all of the colors of the rainbow. Wearing something that is black in the winter helps you keep warm. Q: Why does something look white? The white item is reflecting all of the colors of the rainbow. Wearing something white in the summer will help to keep you cool. Q: Does light and other radiant energy need air to travel through like sound does? No, light and other types of radiant energy travel from the sun to the Earth through space. Space does not have any air. Q: What is nuclear energy? Nuclear energy is the energy that comes from changes in the nucleus of an atom. Q: What is fusion? Fusion = the joining of two atoms’ nuclei. This happens on the sun. It produces a lot of light and other types of energy. Q: What is fission? Fission = the splitting of an atom’s nuclei. Fission is used in nuclear power plants to make electrical energy. Q: What is another name for the ability to do work? Energy Q: What form of energy runs your TV? Electrical Q: What form of energy comes from the sun? Radiant Q: What form of energy powers most cars, trucks, and busses? Chemical Q: What is the Law of Conservation of Energy? Energy can not be created or destroyed, but it can change form. Q: What is “energy transformation”? Energy transformation is the change of energy from one form to another. Example: When you turn on a flashlight, you are transforming, or changing, the chemical potential energy stored in the battery in to light and heat energy. Q: Which energy change happens inside a light bulb? Electrical energy turns into light energy. Q: What kind of energy does a battery store? Chemical potential energy Q: What kind of object allows all light to pass through? (Example: glass) Transparent Q: What kind of object allows some light to pass through? (Example: paper) Translucent Q: What kind of object does not allow light to pass through? (Example: book) Opaque Q: What causes a pencil to seem to bend when you put it in a cup of water? Light is refracting, or bending Q: When light bounces off of an object, we say that the light has _________ off of the object. Reflected Q: What is the speed of light? 186,000 miles / second Q: How are radiant energy waves classified? By wavelength Q: What is the measure of how hot or cold an object is? Temperature Q: “Heat energy from the sun heats water on The Water Cycle Earth’s surface. The heated water evaporates and the water vapor rises into the air. As the water vapor rises, it cools and condenses around dust particles, and returns to Earth surface as precipitation.” What is this a description of? What type of heat transfer can occur without matter present? Radiation, convection, or conduction? Radiation Q: Heat moves from ______ areas to ______ areas. Heat moves from warm areas to cold areas. Q: A ____ object is one whose atoms and molecules are excited and show rapid movement. A warm object is one whose atoms and molecules are excited and show rapid movement. Q: A ______ object’s atoms and molecules are less excited and show less movement. A cooler object’s atoms and molecules are less excited and show less movement. Q: What is the transfer of energy through matter from particle to particle? Example: A spoon handle gets hot after it is put in a cup of hot chocolate. Conduction Q: What do we call an object that conducts heat well? Example: metal A conductor Q: What do we call an object that does not conduct heat well? Example: a wool hat, wood, or most fabrics An insulator Q: What is the flow of electrical power or charge called? Electricity Q: What kind of electricity is usually caused when certain materials are rubbed against each other, like wool on plastic or the soles of your shoes on the carpet. Static Electricity Q: What are really good at transforming electrical energy into other forms of kinetic energy (sound, light, heat)? We find resistors in radios, light bulbs, and ovens. Resistors