Earth Science Chapter 19 Vocabulary Rewrite each definition in
advertisement

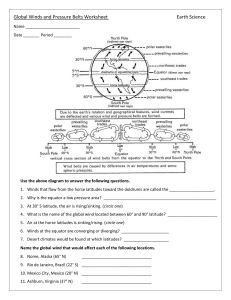
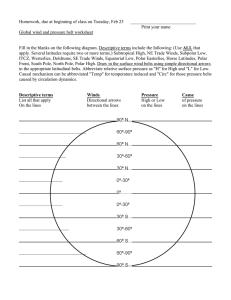
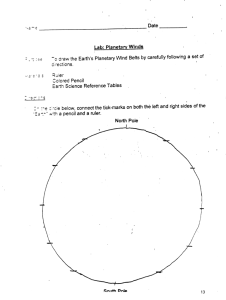
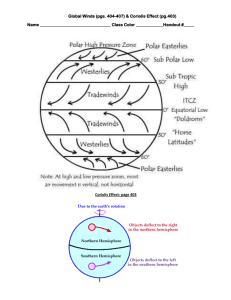
Earth Science Chapter 19 Vocabulary Rewrite each definition in your own words and draw a picture to illustrate the meaning. Air pressure: The force air exerts per unit area. Coriolis effect: The effect of Earth’s rotation that causes the deflection of moving objects toward the right in the Northern Hemisphere and toward the left in the Southern Hemisphere. High pressure area: An area in which the barometric pressure in greater than that of the surrounding air. Isobars: A line on a weather map that joins points having the same barometric pressure. Jet stream: A high-altitude air current forms a narrow band of very strong westerly winds flowing above the middle latitudes; travel up to and beyond 400 kilometers per hour (approximately 250 miles per hour) at altitudes of 15 to 25 kilometers (about 10 to 25 miles) Low-pressure area: An area in which the barometric pressure is lower than that of the surrounding air. Middle latitudes: the area between about 30 degrees and 60 degrees latitude, where surface winds are determined by the locations of transient high- and low-pressure systems. Monsoon: A wind of Southeast Asia and the Indian Ocean that changes direction seasonally, from the northeast from November until March and the southwest from April until October, when it is accompanied by heavy rains. Polar front: The boundary at which air flowing away from the polar regions collides with warmer air from the lower latitudes. Pressure gradient: The rate at which atmospheric pressure declines over a given distance. Prevailing winds: Winds, such as the trade winds and polar easterlies, that usually blow from the same direction. Trade winds: Steady winds that blow across the equator, from about 30° north latitude to about 30° south latitude.