Nervous system central Nervous system peripheral Nervous system
advertisement

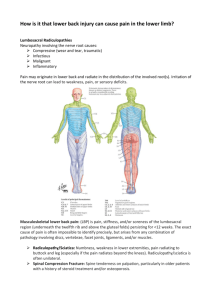
human anatomy 2015 lecture three Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon Nervous system the nervous system is divided into two main parts , the central nervous system , which consists of the Brain & spinal cord , & the Peripheral nervous system , which consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerve & 31 pairs of spinal nerves & their associated ganglia . functionly , the nervous system may be further divided into the somatic nervous system , which controls voluntary activities , & the autonomic nervous system , which control involuntary activities . central Nervous system The CNSis composed of large number of nerve cells &their processes , supported by specialized tissue called neuroglia. the neuron is the name given to the nerve cell & all its process . the nerve cell has two type of processes called dendrites & an axon .the interior of the CNS is organized into gray & white matter . gray matter consists of nerve cells embedded in neuroglia . white matter consists of nerve fiber (axon)embedded in neuroglia . peripheral Nervous system PNS P N S CONSISTS of the : Cranial Nerves ; There are 12 pairs of crania l nerve that leave the brain & pass through foramina in the skull. Spinal Nerve ; there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves that leave the spinal cord & pass through intervertebral foramina in the vertebral column; 8 cervical ,12 thoracic , 5 lumbar , 5 sacral & 1 coccygeal . Each spinal nerve is connected to the spinal cord by two roots , the anterior root &the posterior root . anterior root consists of bundles of nerve fiber carrying nerve impulses away from CNS such nerve fibers are called efferent fibers . those efferent fibers that go to skeletal muscle & causes them to contract are called motor fiber their cells of origin lie in the anterior gray horn of the spinal cord . the posterior root consist of bundle of nerve fiber that carry impulses to the CNS & are called afferent fibers are concerned with conveying information about sensation of touch , pain temperature and vibration they are called sensory fiber ,.the reference, snell clinical anatomy human anatomy 2015 lecture three Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon cell body of these nerve fibers are situated in a swelling on the posterior root called the posterior root ganglion .At each intervertebral foramen the anterior & posterior root unite to form a spinal nerve , here the motor and sensory fiber become mixed together , so that a spinal nerve is made up of mixture of motor & sensory fiber . On emerge from foramen , spinal nerve divided into large anterior ramus & smaller posterior ramus .posterior ramus passes posteriorly around the vertebral column to supply the muscles & skin of the back . anterior ramus continues antriorly to supply the muscle& skin over anterolateral body wall & all muscles & skin of the limbs Plexuses ; At root of the limbs , the anterior rami join one another to form complicated nerve plexuses . the cervical & brachial plexuses are found at the root of the upper limbs,& the lumber & sacral plexues are found at root of the l ower limbs Autonomic Nervous System Is the part of the nervous system concerned with innervations of involuntary structures such as the heart , smooth muscle & glands reference, snell clinical anatomy human anatomy 2015 lecture three Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon throughout the body . divided in to sympathetic & parasympathetic , sympathetic system prepare the body for an emergency . it accelerates the heart rate ,causes constriction of peripheral blood vessels , & arises the blood pressure .parasympathetic system aim at conserving and restoring energy . sympathetic system part of the Autonomic Nervous System Efferent Nerve Fiber . ; the gray matter of spinal cord , form the first thoracic segment to the second lumbar segment , possesses a lateral horn , or column in which are located the cell body of the sympathetic connector neuron .the myelinated axon of these cell leave the spinal cord in the anterior nerve roots & then pass via th white rami communicantes to the paravertebral gaglia of the sympathetic trunk .Once the preganglionic fibers reach the ganglia in the sympathetic trunk the may pass to the following destintion ; 1-may terminate in the ganglion they have entered by synapsing with an excitor cell in the ganglion .Asynapse may be defned as the site where two neurons com into close proximity but not into anatomical continuity the gap between the two neuron is bridged by aneurotransmitter substance , acetylcholine. these postganglionic fiber now pass to the thoracic spinal nerves as gray rami communicantes & are distributed in the branches of the spinal nerve to supply smooth muscle in the walls of blood vessels , sweat gland and arrecctor pili muscle of the skin. 2-those fibers entering the ganglia of the sympathetic trunk high up in the thorax may travel up in the sympathetic trunk to the ganglia in the cervical region . postganglionic nerve fiber leave the sympathetic trunk as gray rami communicantes & most of them join the cervical spinal nerve , many of the preganglionic fiber entering the lower part of the sympathetic trunk from the lower thoracic & upper two lumbar segments of the spinal cord travel down to gaglia in the lower lumbar & sacral region .3-the preganglionic fibers may pass through the ganglia on thethoracic part of the sympathetic trunk without synapsing . these myelinated fiber from the splanchnic nerves , of which these are three. the greater splanchnic nerves arise from the fifth to the ninth thoracic reference, snell clinical anatomy human anatomy 2015 lecture three Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon ganglia , pierces the diaphragm ,& synapses with excitor cells in the ganglia of the cliac plexus .The lesser splanchnic nerve arises from the tenth & eleventh ganglia , pierces the diaphragm , & synapses with exciter cells in the ganglia of the lower part of the celiac plexus . the lowest splanchnic nerve (when present) arises from the twelfth thoracic ganglion pierces the diaphragm , & synapses with excitor cell in the ganglia of the renal plexus . sympathetic trunks ; are two ganglionated nerve trunk that extend the whole length of the vertebral column , There are 3 ganglia in each trunk of the neck , 11 or 12 ganglia in the thoracic , 4 or 5 ganglia in the lumbar , 4 or 5 in the pelvis . The two trunks lie closed to the vertebral column & end below by joining together to form a single ganglion , the ganglion impar. Afferent Nerve Fiber The afferent myelinated nerve fiber travel from the viscera through the sympathetic ganglia with out synapsing. they enter spinal nerve via the white rami communicantes & reach their cell bodies in the posterior root ganglion of corresponding spinal nerve , the centeral axons then enter the spinal cord and may form the afferent component of local reflex arc. Others may pass up to higher autonomic center in the brain. The para sympathetic system part of the Autonomic Nervous System The connector cells of this part of the system are located in the brain & the sacral segment of the spinal , those in the brain form parts of the nuclei of origin of cranial nerve 3 , 7 ,9, 10, & the axons emerge from the brain contained in the corresponding cranial nerves. The sacral connector cells are found in the gray matter of the second, third, & fourthsacral segments of the cord . these cells are not sufficiently numerous to form a lateral gray horn. The myelinated axons leave the spinal cord in the anterior nerve root of the corsponding spinal nerve they leave the sacral nerve & form pelvic splanchnic nerve All the efferent fiber described so reference, snell clinical anatomy human anatomy 2015 lecture three Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon far are preganglionic , & they synapse with excitor cells in peripheral ganglia which usually situated close to the viscera they innervated . the cranial preganglionic fiber relay in the ciliary , pterygopalatine , submandibular & otic ganglia. the preganglionic fiber in the pelvic splanchnic nerve relay in the ganglia in the pelvic plexuses. Afferent Nerve Fibers ; afferent myelinated fiber travel from the viscera to their cell bodies located either in the sensory ganglia of the cranial nerves to the cranial nerve or in the posterior root ganglia of the sacral nerve s . the centeral axons then enter the spinal cord and may form the afferent component of local reflex arc. Others may pass up to higher autonomic center in the brain. reference, snell clinical anatomy human anatomy 2015 lecture three Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon reference, snell clinical anatomy