Gramática en acción 6.1
advertisement

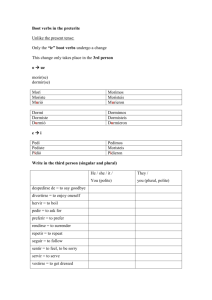
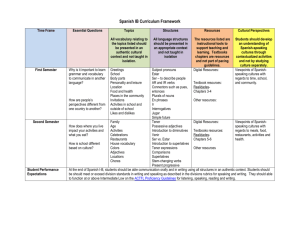
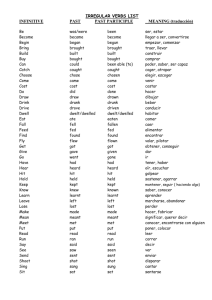
Gramática en acción 6.1 1. Ser and Estar página 200 Both ser and estar mean “to be”, but they are used differently. Use Ser for the following: - to identify people and things - to say where they are from - to describe what someone is like (characteristics, personality traits) - to give the day, date, and time - *Use ser to describe what a food or drink is normally like Use Estar for the following: - to say where someone or something is - to ask and say how you are doing - to describe how something tastes, looks, or feels at a particular moment 2. Pedir and Servir página 202 (memorize these forms) In some –ir verbs with an e in the stem, the e changes to I in all the present tense forms except nosotros & vosotros. Two examples are pedir and servir. Pedir (to ask for) Pido Pides Pide Pedimos Pedís Piden Servir (to serve) Sirvo Sirves Sirve Servimos Servís Sirven 3. Preferir, Poder, and Probar página 204 (memorize these forms) Preferir has an e to ie stem change. It can be followed by a noun to say what someone prefers or by an infintive to say what someone would rather do or prefer to do. Preferir (to prefer) Prefiero Prefieres Prefiere Preferimos Preferís Prefieren The verbs poder and probar have an o to ue stem change. Poder is usually followed by an infintive to say what someone may, is able to, or can do. Poder (to be able to, can, or may) Puedo Puedes Puede Podemos Podéis Pueden The verb probar means to try something, as in to taste. Probar (to try, taste) Pruebo Pruebas Prueba Probamos Probáis Prueban 4. Nota Cultural página 200 Corn is a food staple in many Spanish speaking countries, but Mexico claims it as its own. The first varieties of corn were grown near present day Mexico City, and can be seen in the Museum of Anthropology. In the language of the Aztecs, one word for corn was elotl which became elote in Mexican Spanish.