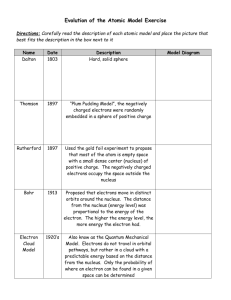
If two elements have similar chemical properties, you would expect
advertisement

If two elements have similar chemical properties, you would expect them to have _____ A.) similar atomic radii B.) the same number of electrons in the highest energy level C.) the same number of energy levels D.) similar atomic mass Properties are based on the number of valence electrons Periodic Trends A property that changes predictably as you travel down a group or across a period Nuclear charge measures charge on nucleus, based on number of protons Period (Nuclear Charge increases) Group (Nuclear Charge increases) Electrons are attracted to the nucleus due to opposite charges Electrons in lower energy levels “shield” the electrons in outer energy levels from the nucleus The attraction between electrons and the nucleus weakens as you move towards higher energy levels Describes the size of an atom Period (Atomic Radius decreases): Li +3 same F +9 number of shells of electrons but an increasing nuclear charge (+) pulls the electrons (-) closer to the nucleus causing the radius to decrease Group (Atomic Radius increases): Fr Li increasing number of inner electron shells shields the positive charge of the nucleus causing the radius to increase The size of an atom ________________ as you go from left to right on the periodic table A.) decreases B.) increases C.) remains constant D.) varies at random The atomic radius of F, Br, and I are 64, 114, and 138 pm respectively. From this estimate a reasonable atomic radius of Cl. A.) 53 pm B.) 89 pm C.) 126 pm D.) 162 pm E.) 196 pm Size of atom after losing or gaining electron(s) Metals tend to lose electrons Radius of a metal ion is smaller than atom Li Li+ Nonmetals tend to gain electrons Radius of a nonmetal ion is larger than atom F F- Why is the radius of a negative ion always greater than the radius of its neutral atom? A.) because repulsion between electrons increases B.) because electron speeds are reduced C.) because the electron clouds contract themselves D.) because the number of energy levels in reduced amount of energy required to remove outermost electron Period (Ionizations Energy increases): Increasing nuclear charge makes electrons more tightly bound to nucleus making electrons harder to remove Group (Ionization Energy decreases): Outer electrons are farther from the nucleus and more shielded, making them easier to remove As you move through a period from metals to non-metals the ionization energy A.) decreases B.) increases C.) remains constant D.) varies at random Atoms get smaller and electrons are held tighter as you move across a period Which of the elements below would you predict to have the highest first ionization energy? A.) Sodium B.) Aluminum C.) Calcium D.) Sulfur Which of the following factors contributes to the lower ionization energy of the higher atomic number elements in a family? A.) greater distance from the nucleus B.) smaller distance from the nucleus C.) greater nuclear charge D.) same number of shells of electrons Metals hold their electrons loosely and thus lose them easily Period (Metallic Character decreases) Outer electrons are held increasingly tighter to the nucleus (M SM NM) Group (Metallic Character increases) Electrons are held increasingly looser by the nucleus Which element in Group 15 has the strongest metallic character? A.) Bi Metal B.) As Metaloid C.) P Nonmetal D.) N Nonmetal Electronegativity = attraction for electrons when bonding Scale is from 0 – 4.0, with Fluorine the most electronegative element assigned the highest value, 4.0 Period (Electronegativity increases) Increased nuclear charge while number of shells remains constant strengthens pull on available electrons Group (Electronegativity decreases): Increased shielding of nuclear charge by adding shells of electrons weakens its pull on available electrons As atoms of elements in Group 16 are considered in order from top to bottom, the electronegativity of each successive element A.) decreases B.) increases C.) remains the same Moving Across a Period: Same number of shells of electrons and an increase in nuclear charge causes the electrons to be more tightly bound to the nucleus Moving Down a Group: Adding shells of electrons shields the outer electrons, causing them to be loosely held Vocabulary: Nuclear Charge, Shielding, Atomic Radius, Ionization Energy, Ionic Radius, Metallic Character, Electronegativity Atomic Radius decreases Ionization Energy increases Metallic Character decreases Electronegativity increases Atomic Radius increases Ionization Energy decreases Metallic Character increases Electronegativity decreases Francium is the most reactive metal Metal reactivity increases as you get closer to Francium Fluorine is the most reactive nonmetal Nonmetal reactivity increases as you get closer to Fluorine The least reactive element in Group 17 is A.) Fluorine B.) Chlorine C.) Bromine D.) Iodine Nonmetals become less reactive as they move away from fluorine (less electronegative) Which of the following increases with increasing atomic number in group 2? A.) ionization energy B.) valence electrons C.) atomic radius D.) electronegativity