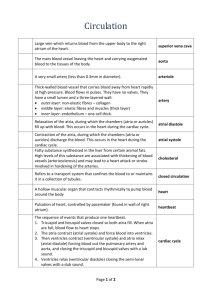
Circulatory systems
advertisement

Anatomy list, lab 6 Vertebrate Structure, Summer 2015 Pages and figure numbers are provided as a guide, not as absolutes. Please study all available material including other figures, summary chapters, indices, etc. You are responsible for knowing all “reading material” and definitions of all structures below unless otherwise states. Know the flow of blood through both the fish and mammal hearts (see p. 199 for an overview) as well as through the body (ex: “The left brachiocephalic vein drains into the ___ vein”). SHARK CIRCULATORY (PP. 55‐63; fig. 5‐1 through 5‐5, 5‐7) Model (diagram/definition‐only terms are noted) Heart: Semilunar valve (diagram), Atrioventricular aperture (diagram) Arteries: Internal carotid artery, Stapedial artery, Esophageal artery, Efferent branchial artery (IV), Subclavian artery, Dorsal aorta, Ventral aorta, Afferent branchial artery (IV), Hypobranchial artery, Pericardial artery Veins: Subclavian vein, Anterior cardinal vein, Common cardinal vein Specimen Heart: Conus arteriosus, Coronary artery, Atrium, Ventricle, Sinus venosus Arteries: Dorsal aorta, Celiac artery, Gastrohepatic artery, Hepatic artery, Gastric artery, Pancreaticomesenteric artery, Anterior intestinal artery, Annular artery, Posterior intestinal artery, Gastrosplenic artery, Posterior mesenteric artery, Iliac artery Veins: Gastric vein, Caudal vein, Lateral abdominal vein Hepatic portal system: Hepatic portal vein, Pancreaticomesenteric vein, Lienomesenteric vein, Anterior splenic vein, Anterior intestinal vein, Annular vein, Posterior splenic vein, Posterior intestinal vein CAT CIRCULATORY, including bloodflow through the mammalian heart (pp.199‐223) Know what the following vessels supply. Summary tables begin on p. 216. You do not need to know the site of origin, though knowing it can be helpful for studying. You do not need to provide “right” or “left” for vessels on the practical unless otherwise noted below. You do not need to know the full definition (i.e. all tributaries) for these vessels unless otherwise stated. You might, however, see a partial “definition” in a question to help you on a supply question. Heart model: Base, apex, ventricles (right and left), atria (right and left), auricles (right and left), pulmonary trunk (what type of blood?), aorta, brachiocephalic artery, pulmonary vein (what type of blood?), vena cava, ligamentum arteriosum (diagram), tricuspid valve, bicuspid valve, semilunar valves (aortic and pulmonary), papillary muscles, chordeae tendinae 1 Anatomy list, lab 6 Vertebrate Structure, Summer 2015 Cat heart (diagram/definition): Pericardial cavity, parietal pericardium, visceral pericardium, conus arteriosus, atrioventricular orifice, venosus sinus Cat heart (specimen): Pericardial sac, aorta, superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, coronary arteries, coronary veins ARTERIES Definition (what the arteries supply): Vertebral, Internal carotid, Lingual, Hepatic, Cystic, Superior mesenteric, Umbilical Specimen: anterior Aorta (know full definition), Brachiocephalic, Arch of the aorta, Right Subclavian, Axillary, Brachial, Subscapular, Right common carotid, External carotid, Left common carotid, Left Subclavian posterior Deep Femoral, Femoral, Caudal, Internal Iliac, External iliac, Iliolumbar, Inferior mesenteric, Genital, Renal, Adrenolumbar VEINS Definition (what these veins supply): Internal jugular, Vertebral, Posterior facial, Hepatic, Umbilical Specimen: anterior Transverse jugular, Cephalic, Brachial, Axillary, Left and Right Subclavians, Superior vena cava (know full definition), Azygos, Left and Right Brachiocephalics, Subscapular, External jugular, anterior facial posterior Inferior vena cava (know full definition), Left and Right Adrenolumbars, Left genital, Left and Right renals, Iliolumbar, Common iliac, External iliac, Internal iliac, Femoral, Deep femoral, Caudal 2