Circulation Q & A
advertisement
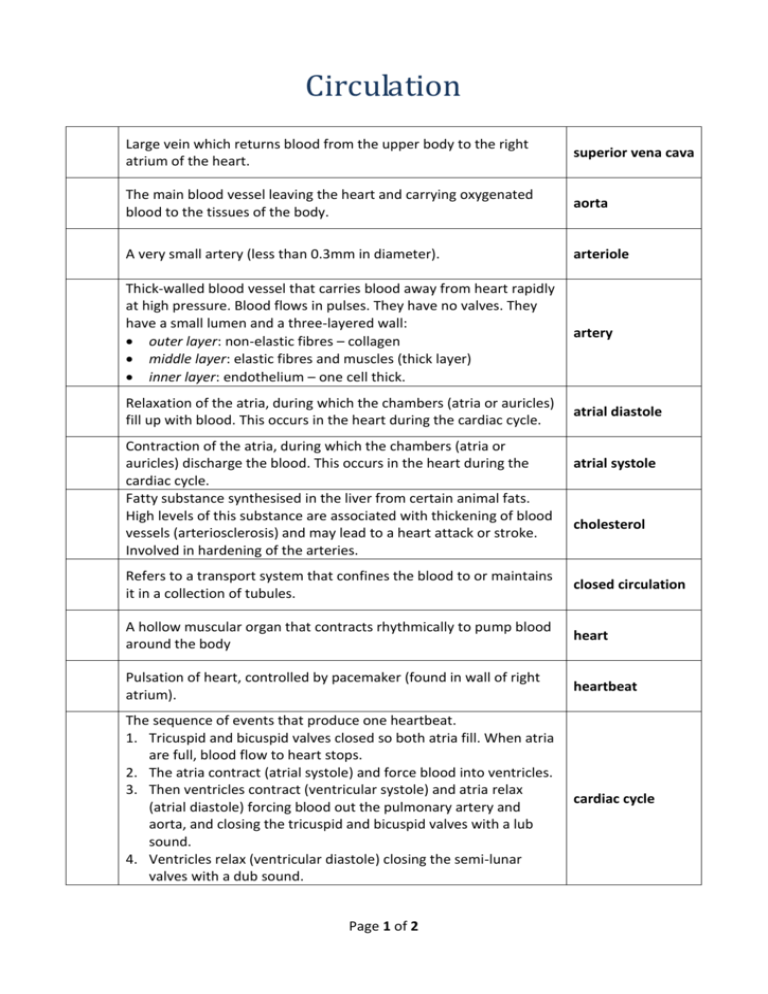
Circulation Large vein which returns blood from the upper body to the right atrium of the heart. superior vena cava The main blood vessel leaving the heart and carrying oxygenated blood to the tissues of the body. aorta A very small artery (less than 0.3mm in diameter). arteriole Thick-walled blood vessel that carries blood away from heart rapidly at high pressure. Blood flows in pulses. They have no valves. They have a small lumen and a three-layered wall: outer layer: non-elastic fibres – collagen middle layer: elastic fibres and muscles (thick layer) inner layer: endothelium – one cell thick. artery Relaxation of the atria, during which the chambers (atria or auricles) fill up with blood. This occurs in the heart during the cardiac cycle. atrial diastole Contraction of the atria, during which the chambers (atria or auricles) discharge the blood. This occurs in the heart during the cardiac cycle. Fatty substance synthesised in the liver from certain animal fats. High levels of this substance are associated with thickening of blood vessels (arteriosclerosis) and may lead to a heart attack or stroke. Involved in hardening of the arteries. atrial systole cholesterol Refers to a transport system that confines the blood to or maintains it in a collection of tubules. closed circulation A hollow muscular organ that contracts rhythmically to pump blood around the body heart Pulsation of heart, controlled by pacemaker (found in wall of right atrium). heartbeat The sequence of events that produce one heartbeat. 1. Tricuspid and bicuspid valves closed so both atria fill. When atria are full, blood flow to heart stops. 2. The atria contract (atrial systole) and force blood into ventricles. 3. Then ventricles contract (ventricular systole) and atria relax (atrial diastole) forcing blood out the pulmonary artery and aorta, and closing the tricuspid and bicuspid valves with a lub sound. 4. Ventricles relax (ventricular diastole) closing the semi-lunar valves with a dub sound. cardiac cycle Page 1 of 2 Number of times the heart beats per minute. Heart/pulse rate Blood vessel carrying blood from the heart (aorta) to the liver. hepatic artery Large vein that drains the digestive system and carries blood containing absorbed food (glucose, amino acids, minerals and vitamins) from the villi of the small intestine to the liver. hepatic portal vein Blood vessel carrying blood from the liver towards the heart (vena cava). hepatic vein Large vein which returns blood from the lower body to the right atrium of the heart. inferior vena cava A passageway or cavity within a tube, tubule or cell. lumen Refers to a transport system that does not confine the blood to a collection of tubules, e.g. insects. The blood leaves the tubules and flows among the body cells. open circulation A circulatory system in which capillaries drain into a vein that opens into another capillary network, i.e. it begins and ends in capillaries. portal blood system Blood vessel that brings blood from the heart to the lungs. It is the only artery to carry deoxygenated blood. pulmonary artery The pathway of the blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart again. pulmonary circulation Blood vessel that brings blood to the heart from the lungs. It is the only vein to carry oxygenated blood. pulmonary vein Branch of the aorta bringing blood from the heart to the kidney. renal artery Blood vessel bringing blood from the kidney to the inferior vena cava renal vein towards the heart. Large vein which returns blood from the upper body to the right atrium of the heart. Page 2 of 2 superior vena cava