Election of 1844
advertisement
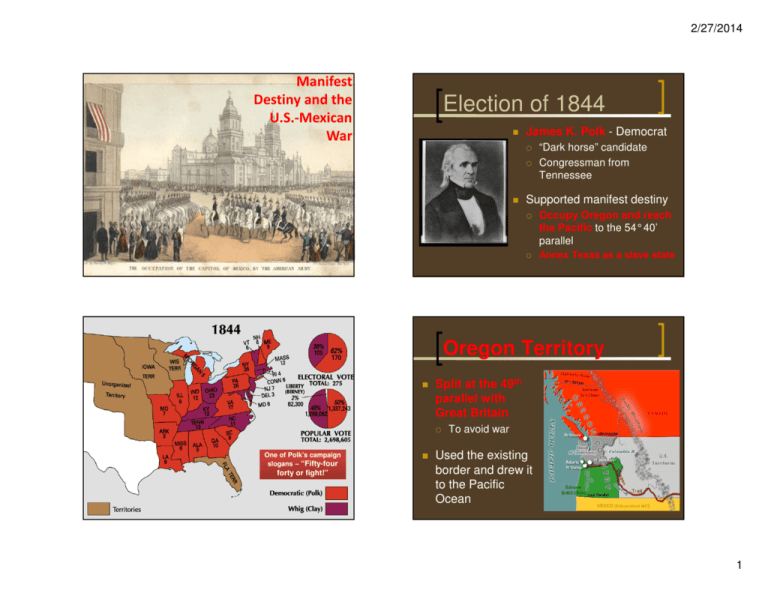
2/27/2014 Manifest Destiny and the U.S.-Mexican War Election of 1844 James K. Polk - Democrat “Dark horse” candidate Congressman from Tennessee Supported manifest destiny Occupy Oregon and reach the Pacific to the 54°40’ parallel Annex Texas as a slave state Oregon Territory Split at the 49th parallel with Great Britain One of Polk’s campaign slogans – “Fifty-four forty or fight!” To avoid war Used the existing border and drew it to the Pacific Ocean 1 2/27/2014 Relations with Mexico Texas Annexation Northerners opposed annexation of Texas By a joint-resolution in the U.S. Congress Polk sent diplomat John Slidell to Mexico to negotiate December 1845 Border dispute ensues U.S. – Rio Grande River Mexico – Nueces River Offered $25 million for California, the New Mexico territory, & Rio Grande as the Texas border President of Mexico refused and broke off diplomatic relations Polk’s Appeal to Congress General Zachary Taylor ordered beyond the Nueces River Camped at the Rio Grande In April 1846, Mexican soldiers crossed the Rio Grande River & attacked Polk saw Mexican attack as an act of war His cabinet agreed “…invaded our country and shed American blood on American soil.” Congress declared war on May 13, 1846 Northerners called it American aggression against a weaker neighbor to extend slavery 2 2/27/2014 War in the West Gen. Taylor invaded northern Mexico General Winfield Scott invaded Mexico City from the Gulf of Mexico Gen. Stephen Kearny marched west and captured Santa Fe, and supported revolt in California John C. Fremont leads the Bear Flag Revolt by Americans in California Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo End of the war Signed at Basilica of Guadalupe at Villa Hidalgo Rio Grande is the southern border of the U.S. Texas recognized as America Anti-slavery Democrats formed this party Because of Polk’s failing health and because he had accomplished all he wanted in one term, he did not seek reelection Paid $15 million for California and New Mexico territory 3 2/27/2014 Completion of Manifest Destiny Southerners desired a flat land for a southern transcontinental railroad Wanted to link southern land to the Pacific Gadsden Purchase In 1853, purchased from Mexico for $10 million dollars 4