Indian Removal Act Congress passed the Indian Removal Act on
advertisement

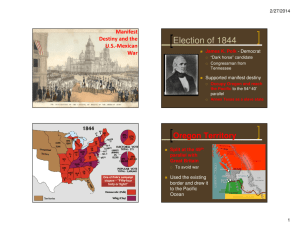
Indian Removal Act Congress passed the Indian Removal Act on May 28, 1830, during the presidency of Andrew Jackson. The law authorized the president to negotiate with Indian tribes in the Southern United States for their removal to federal territory west of the Mississippi River in exchange for their ancestral homelands. Manifest Destiny Manifest Destiny is the belief that it was America’s God-Given right to expand from coast to coast which is the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean. President Polk believed in Manifest Destiny and to act on this belief Polk wanted to gain California. Gold Rush In early 1848 gold was discovered on the American river near Sutter’s Mill. This attracted many people to California. Because of the increase in numbers crime also increased. Annex of Texas: After Polk won the election of 1844, Tyler became a lame duck president. Even though Polk won the election, Tyler was still technically president, since Polk’s term wouldn’t start until later. Tyler seized the opportunity and annexed Texas through a joint resolution. Mexican-American War: After annexing Texas, there was some confusion over the boundaries. Mexico considered the border to be the Nueces River, but the Texans considered the borders to the Rio Grande River. Polk decided to side with the Texans. Polk and Mexico were careful to not mess with the land between the Nueces River and the Rio Grande River. But an eager Polk sent John Slidell to offer $25 million for California and the territory to the east. Mexico dismissed the offer and called it an “insulting” proposition. Now Polk, being frustrated, sent four thousand men, in the control of General Zachary Taylor, to go from the Nueces River to the Rio Grande, near the Mexican forces. When Mexico didn’t respond to the movement, Polk asked Congress to declare war on Mexico, but Congress decided that it would be better to declare war when Mexico attacked first. Then on April 25, 1846, Mexico troops had crossed the Rio Grande and attacked. After hearing the news, Polk quickly asked Congress to declare war, Congress quickly agreed. The war ended and the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo was created. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo: The Mexican-American War finally ended with the signing of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. The treaty said that Mexico would recognize the Rio Grande as the southern border of Texas and that the US would take possession of the former Mexican provinces of California and New Mexico, known as the Mexican Cession, for $15 million dollars. The Compromise of 1850: With the addition of new states, the topic of whether the states would be free or not arose. The Compromise of 1850 led to 5 new rules: 1) California would be admitted as a free state 2) New fugitive slave law 3) No slave trade in Washington D.C. 4) Divide the remaining mexican cession into Utah and New Mexico allowing the people to solve the slavery issue over popular sovereignty. Gadsden Purchase: The Gadsden Purchase was an agreement between US and Mexico during mid 1850s. President Franklin Pierce managed to buy thousands of acres from Mexico for $10 million dollars for railroad. Mexican Cession All Mexican territory from Texas to California that was north of the Rio Grande was given to America since Mexico ceded it to the U.S. Reform Women were prominent in reform crusades, especially in their own struggle for suffrage. For many middle class women the reform campaigns provided a unique opportunity to escape the confines of the home and enter the arena of public affairs. Dorothea Dix Dorothea was a New England teacher and author who spoke against the inhumane treatment of insane prisoners. People who suffered from insanity were treated worse than criminals. She traveled over 60,000 miles in 8 years gathering information for her reports. Elizabeth Cady Stanton Elizabeth Cady Stanton was a member of the women's rights movement in 1840. She was a mother of seven, and she shocked other feminists by advocating suffrage for women at the First Women's Right's Convention in Seneca, New York 1848. Stanton read a "Declaration of Sentiments" which declared, "All men and women are created equal." Wilmot Proviso: With the addition of new land gained from Mexico, the problem of whether the states would be free and slave arose. In 1846, David Wilmot, congressman, proposed that amendment to forbid slavery in all the new states gained from Mexico. The Wilmot Proviso passed the House of Representatives but was turned down at the Senate. The Wilmot Proviso sparked further tensions between the North and South. The North supported the Wilmot Proviso but the South opposed it. The Wilmot Proviso was the introduction of the Civil War. Underground Railroad: The Underground Railroad was a network of secret houses and routes that helped slaves escape to the North or in Canada. The runaway slaves were led by either free blacks from the North or ex-slaves, like Harriet Tubman. Harriet Tubman was an escaped slave that made 19 trips from the North to the South to help slaves escape. She helped at least 300 slaves escape to the North.