aroma 1 all
advertisement

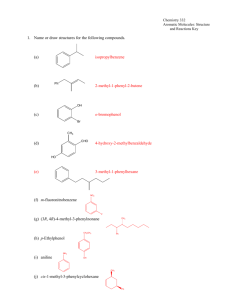
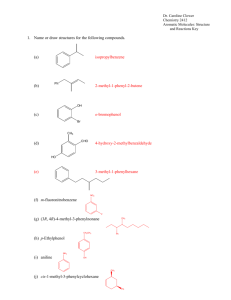
Exam Name___________________________________ MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is an incorrect description of benzene? A) The molecule is planar. B) The molecule is aromatic. C) The molecule can be drawn as a resonance hybrid of two Kekule structures. D) The CCC bond angles are all equal to 120°. E) The molecule is a 6-membered ring which contains alternating single and double carbon-carbon bonds. 1) ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 2) Why does benzene undergo a substitution reaction with Br2 while cyclohexene undergoes an addition reaction. 3) What is suggested by the fact that benzene's molar heat of hydrogenation is 36 kcal less than three times the molar heat of hydrogenation of cyclohexene? SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 4) Cyclic hydrocarbons which can be represented as structures containing alternating single and double bonds are called __________. 4) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 5) In the molecular orbital representation of benzene, how many π molecular orbitals are present? A) 8 B) 1 C) 2 D) 6 E) 4 5) 6) How many distinct nodal planes which are perpendicular to the molecular plane are present in the π4 * orbital of benzene? A) 0 B) 1 C) 2 D) 4 E) 5 6) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 7) Provide a diagram which depicts the relative energies of the π molecular orbitals of benzene. Show which molecular orbitals are filled in benzene's ground state. 7) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 8) How many pairs of degenerate π molecular orbitals are found in benzene? A) 3 B) 5 C) 2 D) 6 8) E) 4 ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 9) Show how the participating p orbitals interact to form the highest energy π molecular orbital of benzene. 10) List the criteria which compounds must meet in order to be considered aromatic. 11) Which is more stable, cyclobutadiene or 1,3-butadiene? Explain. 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 12) Aromatic molecules contain __________ π electrons. A) 4n + 1 (with n an integer) B) unpaired C) 4n + 2 (with n an integer) D) 4n (with n an integer) E) no 12) ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 13) Is cyclooctatetraene a planar molecule? Explain. 14) Is the all-cis form of [10]annulene aromatic? Explain. 15) Is the [10]annulene shown below aromatic? Explain. 16) Provide the major resonance structures of the ion which results when the most acidic hydrogen of cyclopentadiene is lost. 17) Explain the relative acidities of cyclohexene (pKa of 46) and cyclopentadiene (pKa of 16). 18) Why would the reaction below proceed at an extremely slow rate if at all? 19) When cycloheptatriene is deprotonated, an anion with seven resonance forms of equal energy can be drawn. Given this fact, explain why cycloheptatriene is only slightly more acidic than propene. 20) 3-Chlorocyclopropene is solvolyzed in methanol at a much higher rate than is chlorocyclopropane. Offer an explanation. 21) Classify 1,3,5-heptatriene as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 22) Classify cyclopentadienyl cation as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 23) Classify cyclopropenyl cation as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network 24) Classify cycloheptatrienyl cation as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 25) Classify naphthalene as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 2 26) Classify pyridine as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 27) Classify the compound below as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 28) Classify the compound below as aromatic antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 29) Classify the compound below as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 30) Classify cycloheptatriene as aromatic antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 31) Classify cyclopentadiene as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 32) Which is more basic, pyridine or pyrrole? Explain. 33) Why are researchers interested in the properties of large polynuclear aromatic hydrocrobons? 34) Provide the structure of the major organic product which results when phenanthrene is treated with Br2 in carbon tetrachloride. 35) Provide an acceptable name for the compound below. 3 36) Provide an acceptable name for the compound below. 37) Provide an acceptable name for the compound below. 38) Provide an acceptable name for the compound below. 39) Provide an acceptable name for the compound below. 40) Provide the structure of m-nitrophenol. 41) Provide the structure of anisole. 42) Provide the structure of indole. 43) Provide the structure of o-bromostyrene. 44) Provide the structure of 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzoic acid. 45) Provide the structure of 4-isopropylbenzaldehyde. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 46) Which of the following compounds has the lowest boiling point? A) 1,2,4-tirchlorobenzene B) p-dichlorobenzene C) 1,2,3-trichlorobenzene D) o-dichlorobenzene E) m-dichlorobenzene 4 46) 47) Which of the following compound has the highest melting point? A) toluene B) p-dichlorobenzene C) o-dichlorobenzene D) benzene E) m-dichlorobenzene 47) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 48) The IR spectrum of m-xylene contains stretches which are characteristic of most aromatic hydrocarbons. List the peaks (in cm-1) associated with the aromatic CC stretch and the aromatic CH stretch. 48) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 49) In the proton NMR, in what region of the spectrum does one typically observe hydrogens bound to the aromatic ring? A) 1.0-1.5 ppm B) 2.0-3.0 ppm C) 4.5-5.5 ppm D) 7.0-8.0 ppm E) 9.0-10.0 ppm 49) 50) In the carbon NMR, in what region of the spectrum does one typically observe carbons which are part of the aromatic ring? A) -10-0 ppm B) 40-60 ppm C) 80-100 ppm D) 120-150 ppm E) 200-220 ppm 50) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 51) How might one distinguish the isomers of trimethylbenzene by noise-decoupled 13C NMR? 51) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 52) Which of the following compounds has the most signals in the noise-decoupled 13C NMR spectrum? A) o-dibromobenzene B) m-dibromobenzene C) 1,2,3,4-tetrabromobenzene D) 1,3,5-tribromobenzene E) p-dibromobenzene 52) 53) In the mass spectrum of isobutylbenzene, the base peak occurs at m/z: A) 119 B) 105 C) 133 D) 91 53) E) 134 ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 54) Describe the benzenoid band which appears in the UV-visible spectrum of most aromatic hydrocarbons. 5 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 55) In the UV-visible spectra of the following compounds, in which does lambda max appear at the highest wavelength? A) isopropylbenzene B) 1-phenylpropene C) 3-phenylpropene D) benzene E) n-octylbenzene 55) 56) How many distinct trichlorobenzene isomers are possible? A) 3 B) 2 C) 4 56) D) 6 E) 5 57) Which of the following is another accepted name for methyl phenyl ketone? A) cresol B) anisole C) acetophenone D) cresone E) benzophenone 57) 58) Which of the following undergoes SN2 reaction with sodium methoxide most rapidly? A) PhCH2CH2 Br B) PhCH2Br C) PhCH2CH2 CH2 Br D) Ph3CBr E) PhBr 58) 59) Which of the following undergoes solvolysis in methanol most rapidly? A) Ph3CBr B) PhCH2CH2 Br C) PhCH2CH2 CH2 Br D) PhCH2Br E) PhBr 59) 60) Which of the following is not a fused-ring heterocycle? A) pyrimidine B) benzofuran C) indole D) purine E) quinoline 60) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 61) When cyclohexene is treated with KMnO4 , H2 O, the syn-1,2-diol is produced. What reaction occurs when benzene is similarly treated? 6 61) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 62) Which of the following is another name for cyclobutadiene? A) [6]annulene B) antibenzene C) Dewar benzene D) [4]annulene E) [2]annulene 62) SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 63) Classify pyrrole as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 63) ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 64) Provide the structure of pyrimidine. SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 65) __________ is similar to furan, with a sulfur atom in place of the oxygen. 65) ESSAY. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 66) Provide the structure of anthracene. 67) Provide an acceptable name for PhSO3 H. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 68) Which of the following is also an acceptable name for 3-nitrophenol? A) m-nitrophenol B) p-nitrophenol C) hydroquinone D) 3-cresol E) o-nitrophenol 68) 69) Which of the following is also an acceptable name for 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene? A) 1,3,5-xylene B) styrene C) cumene D) cymene E) mesitylene 69) 70) Which of the following is the same as the tropylium ion? A) cyclopropenyl anion B) cyclopentadienyl cation C) cyclopentadienyl anion D) cycloheptatrienyl anion E) cycloheptatrienyl cation 70) 7 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 71) Classify the compound below as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 71) 72) Classify the compound below as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 72) 73) Classify the compound below as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 73) 74) Classify the compound below as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 74) 8 75) Classify the compound below as aromatic, antiaromatic, or nonaromatic. Assume planarity of the π network. 75) 76) Provide an acceptable name for the compound below. 76) 77) Provide the structure of m-xylene. 77) 78) Provide the structure of o-toluic acid. 78) 79) Provide the structure of 2,5-dichlorophenol. 79) 80) Name two of the three common allotropes of carbon. 80) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 81) What is the bond order of the carbon-carbon bonds in benzene? A) 0.5 B) 2 C) 1 D) 3 81) E) 1.5 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 82) Describe the occupied p molecular orbitals in the gound state of cyclobutadiene. 82) 83) What compound results when cyclooctatetraene is treated with excess potassium metal? 83) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 84) Nitrogen's lone pair electrons occupy what type of orbital in pyridine? A) p B) s C) sp D) sp2 9 84) E) sp3 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 85) Provide the structure of o-chlorotoluene. 85) 86) Provide the structure of tropylium bromide. 86) 87) Provide the structure of p-aminobenzoic acid. 87) 88) Provide the structure of sodium cyclopentadienide. 88) 89) Provide the structure of 2,4,6-trichlorophenol. 89) 90) Provide the structure of m-iodobenzoic acid. 90) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 91) What is the major difference between an antiaromatic and aromatic compound? A) Aromatic compounds cannot have a charged atom in the structure B) Antiaromatic compounds can assume a chair-like structure while aromatic compounds are nearly flat C) Antiaromatic compounds have at least one sp3 hybridized atom in the ring D) Only aromatic compounds follow Huckle's rule. E) The structure must be cyclic for aromatic but not antiaromatic compounds? 10 91) 92) Which of the following structures is aromatic? A) 92) B) C) D) E) 11 93) Which of the following structures, if flat, would be classified as antiaromatic? A) B) C) D) E) 12 93) 94) Which of the labeled H atoms (1 -5) in the following molecule would be predicted to be the most acidic? A) 2 B) 3 C) 4 D) 1 E) 5 95) Rank the following in order of increasing pKa (from lowest to highest pKa) A) 1 < 2 < 3 B) 2 < 1 < 3 C) 3 < 2 < 1 13 D) 2 < 3 < 1 94) 95) E) 3 < 1 < 2 Answer Key Testname: AROMA_1_ALL 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) E Addition of Br2 to benzene is highly unfavorable because it would result in a nonaromatic product. This suggests that the type of π bonding in benzene lends special stability to the molecule. annulenes D C 8) C 9) All adjacent interactions are antibonding. 10) 1. The structure must be cyclic. 2. Each atom in the ring must have an unhybridized p orbital. 3. The structure must be planar or nearly planar so that overlap of these p orbitals is effective. 4. The π network must contain 4n + 2 electrons (where n is a whole number), so that delocalization of the π electrons results in a lowering of the molecule's electronic energy. 11) 1,3-Butadiene is more stable. Cyclobutadiene is antiaromatic since it contains 4 (i.e., 4n) π electrons. Antiaromatic systems are less stable than their open-chain counterparts. 12) C 13) No. In addition to increasing other forms of strain, a planar conformation would make this molecule antiaromatic. 14) No. Planarity, which is required for aromaticity, is precluded due to excessive angle strain. 15) No. The ring cannot achieve a planar conformation since such a conformation would result in severe and unfavorable steric interactions between the two H's oriented inside the ring. 16) 17) The conjugate base of cyclopentadiene is aromatic. 18) The carbocation intermediate involved in this reaction is antiaromatic. Based on Hammond's Postulate, one can surmise that the activation energy required to produce this intermediate would be very high. 19) Each resonance form of the cyclopehtatrienyl anion is antiaromatic. 20) Cyclopropenyl cation, the carbocationic intermediate in the case of 3-chlorocycloprene, is aromatic and via Hammond's Postulate we can say that the activation energy required to form it is lower. 21) nonaromatic 14 Answer Key Testname: AROMA_1_ALL 22) antiaromatic 23) aromatic 24) aromatic 25) aromatic 26) aromatic 27) aromatic 28) aromatic 29) aromatic 30) nonaromatic 31) nonaromatic 32) Pyrrole is a much weaker base than pyridine. When pyrrole is protonated, the system's aromaticity is destroyed. 33) These compounds are formed to some extent in nearly all combustion reactions of organic compounds and are known to be potent carcinogens. 34) 35) aniline or aminobenzene or benzeneamine 36) para-dichlorobenzene or 1,4-dichlorobenzene 37) 2,4-dinitrotoluene 38) imidazole 39) ortho-xylene or 1,2-dimethylbenzene 40) 41) 42) 43) 15 Answer Key Testname: AROMA_1_ALL 44) 45) 46) B 47) B 48) CC: around 1600 cm-1 CH: just above 3000 cm-1 (usually around 3030 cm-1 ) 49) D 50) D 51) 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene: 3 signals 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene: 9 signals 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene: 6 signals 52) B 53) D 54) Band centered at 254 nm; 3-6 small, sharp peaks; weak molar absorptivity. 55) B 56) A 57) C 58) B 59) A 60) A 61) No reaction takes place. 62) D 63) aromatic 64) 65) Thiophene 66) 67) benzenesulfonic acid 68) A 69) E 70) E 71) antiaromatic 72) aromatic 73) nonaromatic 74) nonaromatic 75) aromatic 16 Answer Key Testname: AROMA_1_ALL 76) 1,3,5-trinitrobenzene 77) 78) 79) 80) diamond; graphite; fullerenes (like buckminsterfullerene) 81) E 82) Two electrons are paired in a bonding p molecular orbital, while the other two electrons are unpaired and singly occupy two nonbonding p molecular orbitals. 83) dipotassium cyclooctatetraene dianion 84) D 85) 86) 17 Answer Key Testname: AROMA_1_ALL 87) 88) 89) 90) 91) D 92) E 93) E 94) D 95) B 18