Board Feet Lesson Plan: Math in Building Trades
advertisement

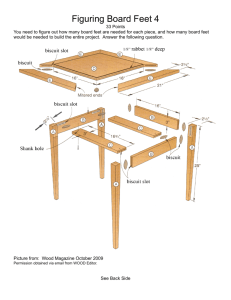
Math-in-CTE Lesson Plan Template Lesson Title: Board Feet Author(s): Bob Pearce Lesson #5 Phone Number(s): 406-324-2703 Paul Nickels 269-468-8540 E-mail Address(es): bpearce@helena.k12.mt.us paulnikels@sbcglobal.net Occupational Area: Building and Trades CTE Concept(s): Board Feet Math Concepts: Formulas for figuring board feet. Order of Operations, rates, percent increase, unit analysis Lesson Objective: Students will be able to figure how much wood is need for a project along with the cost of the lumber. Supplies Needed: Pencil and calculator TEACHER NOTES (and answer key) THE "7 ELEMENTS" 1. Introduce the CTE lesson. Answers will vary. Try to lead the students to what the wood will cost. Have a alder door and Cost of material will depend on the type of wood and the amount of wood. a oak door, ask Raised panel will have an elk or a skater dude logo design on them, made with the cnc router. students what they Prefer. 2. Assess students’ math awareness as it relates 1. Pieces x thickness x width x length / 144 = total bd.ft. to the CTE lesson. 1.Figure how to do Board Feet 2. 1’’ x12’’x12’’ 2. “What is a BD. FT.? Board foot examples: 3.“How many square inches are in a BD. FT.? 4. “How thick is a BD. FT.? 5. What is the difference between a board foot and a square foot? 6. Why is figuring a Board Foot important. 7. How is the percent 3. 144 square inches added to total? 4. 1 inch? 5. Board foot you take the thickness into account. Such as 4/4, 5/4, 6/4. It is a volume. 5. Square foot you disregard the thickness, mostly used for plywood or manmade material. This is like finding surface are. 6. To see how much lumber is needed to build something and the cost of the lumber. 7. 0.20 x the total plus the total, or 1.2 times the total 3. Work through the math example embedded in the CTE lesson. 1. 15 PIECES 1x 6’’ x 10’ shelves for garage. 2. 4 pieces 1x 6’’ x 52’’ stiles for a kitchen cabinet 3. Change a fraction to a 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. P x T x W x L divided by 12 if one is in feet 75 bd. Ft. P X T X W X L divided by 144 if all are inches. 8.67 bd.ft. 3 divided by 4 = .75 Cost per board foot alder $ 12.57 oak cost is $23.84 Stiles =8.67 x .20 = 1.73 +8.67 = 10.40 bd.ft. decimal ¾’’ 4. Cost of lumber for alder $1.45 and the cost of lumber from oak $2.75 All for the stiles for the kitchen cabinet. 5. 20% is added to total board feet for waste. 4. Work through related, 1. PX TX W X L X.007 another formula for calculating board feet. contextual math-in2. 1.008 bd. Ft. CTE examples. 1. 2 pieces 1 x 6’’ x 12’’ rails for kitchen cabinet 2. Cost of lumber for alder $ 1.46 the price from oak $ 2.77 5. Work traditional examples. through math ANSWERS are on the second page of the Math Practice Sheet See Math Practice Sheet 6. Students demonstrate WORK SHEET BELOW their understanding. ATTACHED. Work sheet with 5 problems that include p x t x w x l divided by 12 or 144 Along with another 5 questions with the type of wood and the cost of the wood per board feet. 7. Formal assessment Do the board feet for the following Corner hutch. picture of hutch *The base kitchen cabinet will be done at a later date. Kitchen cabinet to be done at a later date Key to hutch 6 shelves= 5.06 2 sides=9.44 1 top piece= .89 2 upper rails= .32 1 mid rail = .17 2 lower rails= .35 1 bottom piece = .25 1 door = 2.15 TOTAL = 18.63 X.20 = 3.73 +18.63 = 22.36 TOTAL BD.FT. Multiple by the cost of wood per board feet. Example ash $2.75. 2.75 x 22.36 = $61.45 total cost for wood NOTES: BOARD FEET WORK SHEET P X T X W X NAME_____________________________ L TOTAL BD.FT. WOOD TYPE COST BD.FT. 3 1 7 3/8 2’ PINE $1.48 15 1 6’’ 48’’ ASH $2.75 2 1 6’’ 1’ RED OAK $2.78 12 1 ½’’ 7 7/8’’ 26 3/8’’ HICKORY $3.86 22 ½ 4 5/8’’ 16 .75 WALNUT $ 5.28 P X T X W X L 3 1 7 3/8 2’ 15 1 6’’ 48’’ 2 1 6’’ 1’ 12 1 ½’’ 7 7/8’’ 26 3/8’’ 22 ½ 4 5/8’’ 16 .75 TOTAL BD.FT. WOOD TYPE COST BD.FT. WALNUT $5.28 PINE $1.48 HICKORY $3.86 ASH $2.75 RED OAK $ 2.78 TOTAL COST TOTAL COST BOARD FEET WORK SHEET P X T X W X ANSWER L NAME__KEY___________________________ TOTAL BD.FT. WOOD TYPE 3 1 7 3/8 2’ 3.69 PINE 15 1 6’’ 48’’ 30 ASH 2 1 6’’ 1’ 1 RED OAK 12 1 ½’’ 7 7/8’’ 26 3/8’’ 25.97 HICKORY 22 ½ 4 5/8’’ 16 .75 P X T X W X L 3 1 7 3/8 2’ 15 1 6’’ 48’’ 2 1 6’’ 1’ 12 1 ½’’ 7 7/8’’ 22 ½ 4 5/8’’ 5.92 TOTAL BD.FT. WALNUT WOOD TYPE 3.69 WALNUT 30 PINE COST BD.FT. $1.48 TOTAL COST $5.46 $2.75 $2.78 $3.86 $82.50 $ 2.78 $100.25 $ 5.28 COST BD.FT. $5.28 $31.25 TOTAL COST $19.48 $1.48 $ 44.40 1 HICKORY $3.86 $3.86 26 3/8’’ 25.97 ASH $2.75 $71.42 16 .75 5.92 RED OAK $ 2.78 $16.46 Name ______________________ Boardfeet Math Practice Sheet Calculate: a) 3 + 4 x 2 b) 6 + 8 ÷ 2 – 3 c)(4 + 2) x (5 + 2) d) 4 + 2 x 5 + 2 Calculate but watch the units a) If you were driving on I-15 for 3 hours at an average of 70 mph, how far would you have driven? b) If Elmer Fudd knows that he will average 80 bu/acre in a good year, how much grain can he expect if he plants 120 acres in that grain? c) If Sheeszo Smart travelled 500 miles in 7 hours, including rest stops, what was her average speed? Change the following percents to decimals. a) 25% b) 30% c) 100% Percent increase is anything over 100%. So, a 10% increase is really 110% of the original number. The new number can be found if you multiply the original by the decimal for 110% (1.10) So, the new amount after a 10% increase is really 1.10 times the original number. EXAMPLE: The cost of paint increased 10%, if the old price was $28 a gallon, what is the new price? $28 x 1.10 = $30.80 a) You calculated that you would need 30 sheets of plywood for a job, your boss tells you to add 5% for wastage. How many full sheets should you order? 1) 29 sheets 2) 30 sheets 3) 31 sheets 4) 32 sheets b) A foreman told a worker to increase their output by 20%. If the worker averaged 50 finished parts a day, what would their new quota be? 1) 44 parts 2) 48 parts 3) 52 parts 4) 56 parts Name ______________________ Boardfeet Math Practice Sheet ANSWERS Calculate: a) 11 b) 7 c) 42 d) 16 Calculate but watch the units d) If you were driving on I-15 for 3 hours at an average of 70 mph, how far would you have driven? 210 miles e) If Elmer Fudd knows that he will average 80 bu/acre in a good year, how much grain can he expect if he plants 120 acres in that grain? 9600 bushels f) If Sheeszo Smart travelled 500 miles in 7 hours, including rest stops, what was her average speed? 71+ mph Change the following percents to decimals. b) 25% 0.25 b) 30% 0.3 c) 100% 1 Percent increase is anything over 100%. So, a 10% increase is really 110% of the original number. The new number can be found if you multiply the original by the decimal for 110% (1.10) So, the new amount after a 10% increase is really 1.10 times the original number. EXAMPLE: The cost of paint increased 10%, if the old price was $28 a gallon, what is the new price? $28 x 1.10 = $30.80 b) You calculated that you would need 30 sheets of plywood for a job, your boss tells you to add 5% for wastage. How many full sheets should you order? 2) 29 sheets 2) 30 sheets 3) 31 sheets 4) 32 sheets c) A foreman told a worker to increase their output by 20%. If the worker averaged 50 finished parts a day, what would their new quota be? 2) 44 parts 2) 48 parts 3) 52 parts 4) 56 parts