PRECIPITATION REACTIONS AND SOLUBILITY
advertisement
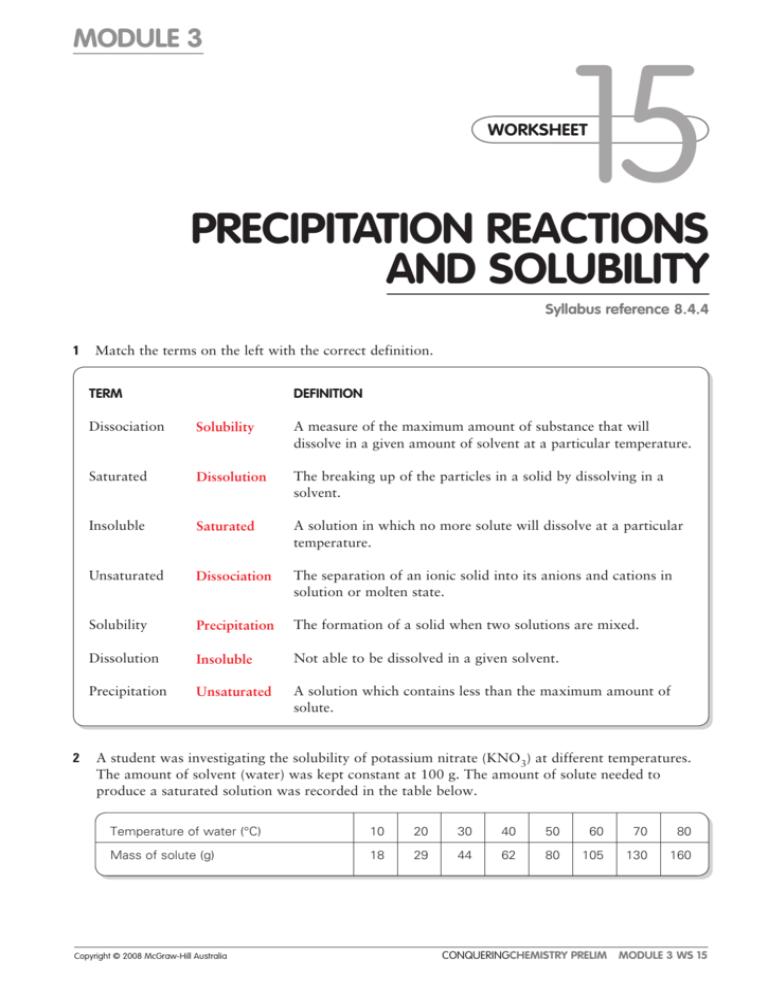
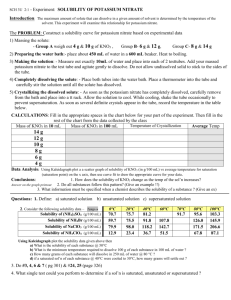
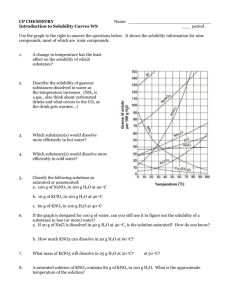
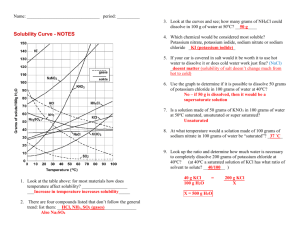
MODULE 3 15 WORKSHEET WORKSHEET PRECIPITATION REACTIONS AND SOLUBILITY Syllabus reference 8.4.4 1 Match the terms on the left with the correct definition. TERM 2 DEFINITION Dissociation Solubility A measure of the maximum amount of substance that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a particular temperature. Saturated Dissolution The breaking up of the particles in a solid by dissolving in a solvent. Insoluble Saturated A solution in which no more solute will dissolve at a particular temperature. Unsaturated Dissociation The separation of an ionic solid into its anions and cations in solution or molten state. Solubility Precipitation The formation of a solid when two solutions are mixed. Dissolution Insoluble Not able to be dissolved in a given solvent. Precipitation Unsaturated A solution which contains less than the maximum amount of solute. A student was investigating the solubility of potassium nitrate (KNO3) at different temperatures. The amount of solvent (water) was kept constant at 100 g. The amount of solute needed to produce a saturated solution was recorded in the table below. Temperature of water (°C) 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 Mass of solute (g) 18 29 44 62 80 105 130 160 Copyright © 2008 McGraw-Hill Australia CONQUERINGCHEMISTRY PRELIM MODULE 3 WS 15 a Draw a graph of solubility versus temperature on the grid below. ��� ��� ��� ��� ��� ���������������������������� ��� ��� �� �� �� �� �� �� �� �� �� �� �� �� �� �� ���������������� �� �� �� b Would points on the graph below the curve represent a saturated or unsaturated solution? Unsaturated c Write a balanced equation to show the dissociation of KNO3 in water. KNO3(s) → K(aq) NO3(aq) d How much KNO3 will dissolve in 200 g of water at 65°C? From the graph 116 / 1g dissolve in 100 g water at 25ºC so 232 / 2g will dissolve in 200 g water at 25ºC. Copyright © 2008 McGraw-Hill Australia CONQUERINGCHEMISTRY PRELIM MODULE 3 WS 15 e If 25 g of KNO3 was dissolved in 100 g of water at 25°C, how much more KNO3 must be added to make a saturated solution at that temperature? From the graph 36 / 1 g will dissolve in 100 g water at 25ºC so another 11 / 1 g will dissolve. f What is the minimum mass of water at 45°C needed to dissolve 20 g of KNO3? From the graph 72 / 1 g will dissolve in 100 g water at 45ºC. Mass of water needed to dissolve 20 g 20/72 100 28 mL. 3 Use the solubility table from your textbook to determine whether or not a precipitation reaction will occur when the following reactants are mixed. Where a reaction occurs write the balanced neutral species equation for the reaction. a potassium chloride and zinc nitrate no precipitate b ammonium bromide and lead nitrate precipitate 2NH4Br(aq) Pb(NO3)2(aq) → PbBr2(s) 2NH4NO3(aq) c ammonium sulphide and magnesium acetate no precipitate d strontium chloride and zinc sulfate precipitate SrCl2(aq) ZnSO4(aq) → SrSO4(s) ZnCl2(aq) 4 Write balanced ionic equations for the reactions that occur when the following solutions are mixed: a barium chloride and sodium sulfate Ba2(aq) SO42(aq) → BaSO4(s) b copper(II) sulfate and potassium hydroxide Cu2(aq) 2OH(aq) → Cu(OH)2(s) c calcium chloride and sodium carbonate no precipitate d silver nitrate and sodium chloride Ag(aq) Cl(aq) → AgCl(s) e lead(II) nitrate and potassium iodide Pb2(aq) 2I(aq) → PbI2(s) Copyright © 2008 McGraw-Hill Australia CONQUERINGCHEMISTRY PRELIM MODULE 3 WS 15 5 What solutions would you mix to produce each of the following precipitates? a lead sulfate lead(II) nitrate and sodium sulfate b iron(II) silfide iron(II) nitrate and potassium sulfide c magnesium hydroxide magnesium nitrate and sodium hydroxide Copyright © 2008 McGraw-Hill Australia CONQUERINGCHEMISTRY PRELIM MODULE 3 WS 15