Music Theory Creating
advertisement

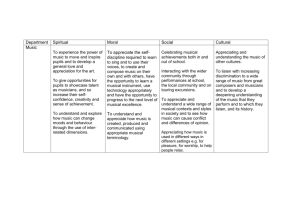
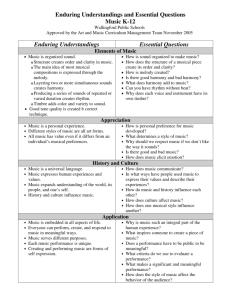
Music Theory Creating Essential Questions: 1. How do artists generate and select creative ideas? 2. How do artists make creative decisions? 3. How do artists improve the quality of their creative work? Essential Vocabulary: treble, bass, and c clefs, note names of the musical alphabet, appropriate notation for whole note, dotted half note, half note, quarter note, eighth note and the corresponding rests, basic tempo terms(largo, andante, moderato, allegro, presto), basic dynamic terms (p, mp, mf, f), basic forms (binary, ternary, fugue, variation, chorale), basic musical textures (monophonic, homophonic, polyphonic), basic forms (binary, ternary, fugue, variation, chorale, rondo, sonata), basic musical textures (monophonic, homophonic, polyphonic), note names of the musical alphabet, tonality (major, minor, diminished, augmented, modal) Anchor Standard 1: Generate and select among multiple musical ideas relevant to a personal experience, interest, or specific purpose Enduring Understandings The creative ideas, concepts, and feelings that influence artists’ work emerge from a variety of sources. Students will know… Students will understand that… Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Vocabulary: Required: • music uses a symbolic • use individual notes, chords, Students will be able to… • treble, bass, and c clefs system to represent aural and chord progressions to • apply foundational skills sounds. analyze the structure of • note names of the musical from K-5. given musical selections. alphabet • music can be composed with different pitches and lengths • appropriate notation for of sounds. whole note, dotted half note, half note, quarter note, • music can be composed with eighth note and the different speeds. corresponding rests • music can be composed with • basic tempo terms different volume levels. (largo, andante, moderato, allegro, presto) • basic dynamic terms (p, mp, mf, f) Adopted April 14, 2014 Anchor Standard 2: Develop a plan for using/presenting selected musical ideas. Enduring Understandings Artists’ creative choices are influenced by their experience, context and expressive intent. Students will know… Students will understand that… Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Vocabulary: Required: • an individual , group, or • develop, document, and Students will be able to… • basic forms (binary, ternary, time period can be identified explain a plan for creating an • apply foundational skills fugue, variation, chorale) with a certain style in music. original composition. from K-5. • basic musical textures • composers use different (monophonic, homophonic, musical forms as a means of polyphonics expressing emotions Anchor Standard 3: Develop and modify musical ideas to create a work that meets appropriate criteria. Enduring Understandings Artists evaluate and refine work through feedback, flexibility, and persistence. Students will know… Students will understand that… Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Vocabulary: Required: • composing music is a step by • compose a short Students will be able to… • basic forms (binary, ternary, step process and can be representational work in the fugue, variation, chorale, changed and edited many following forms: binary, • apply foundational skills from K-5. rondo, sonata) times. ternary, fugue, variation, chorale. • basic musical textures • quality compositions are a (monophonic, homophonic, synthesis of many well• peer-review and edit other polyphonic) written aspects of music. student’s musical compositions for accuracy in • treble, bass, and c clefs. notation. • note names of the musical • re-write their compositions alphabet based on peer-review edits • appropriate notation for and teacher feedback. whole note, dotted half note, • evaluate the quality of a half note, quarter note, given composition based on eighth note and the its formal and compositional corresponding rests structure. • basic tempo terms • tonality (major, minor, diminished, augmented, modal) Adopted April 14, 2014 Music Theory Responding Essential Questions: 1. How do individuals choose music to experience? 2. How does understanding the structure and context of the music influence our response? 3. How do we discern the creator’s and/or performer’s expressive intent? 4. How do we judge the quality of artistic work and performance(s)? Essential Vocabulary: composer, arranger, performer, listener, style, standard music history eras and dates (Antiquity, Medieval Period 500-1500 AD, Renaissance 1450-1600 AD, Baroque 1600-1750 AD, Classical 1750-1820, Romantic 1820-1900, Modern 1900-present day), modern music styles (popular music, jazz, rock, world music), basic music elements (melody, harmony, rhythm, timbre), basic music forms (sectional, variation, fugal, sonata, free form), opera, symphony, concerto, style/genre, basic dynamics (p, mp, mf, f), basic tempos (largo, andante, moderato, allegro, presto), tempo related terms (ritardando, accelerando), word painting, texture, tonality (major, minor, diminished, augmented, modal), critic Anchor Standard 1: Support the choice of music for a specific purpose or situation. Enduring Understandings Individual selection of work is influenced by their interests, experiences, understandings and purposes. Students will know… Students will understand that… Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Vocabulary: Required: • musical selections are best • use specific criteria for Students will be able to… • composer appreciated by being making informed, critical • apply foundational skills considerate the roles of evaluations of musical • arranger from K-5. composer, performer, and selections. • performer listener in the final product. • listener • musical compositions are a • style synthesis of the composer’s personality and the time and place the composer was working when the selection was created. Adopted April 14, 2014 Anchor Standard 2: Explain how your analysis of the structure and context of the work influence your response. Enduring Understandings Understanding the structure and context of the work influences your response. Students will know… Students will understand that… Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Vocabulary: Required: • Western Musical History can • classify by genre/style and Students will be able to… • standard music history eras be divided into several eras. historical period unfamiliar • apply foundational skills and dates (Antiquity, examples of music and • there are 4 basic elements of from K-5. Medieval Period 500-1500 explain the reasoning behind music. AD, Renaissance 1450-1600 their classification. • there are standard AD, Baroque 1600-1750 AD, • compare and contrast how organizational forms that Classical 1750-1820, musical elements, artistic composers utilize to create Romantic 1820-1900, Modern process, and organizational music. 1900-present day) categories are used in • modern music styles musical compositions. (popular music, jazz, rock, world music) • basic music elements (melody, harmony, rhythm, timbre) • basic music forms (sectional, variation, fugal, sonata, free form) • opera • symphony • concerto Adopted April 14, 2014 Anchor Standard 3: Support an interpretation of a work that reflects the creator’s/performer’s expressive intent. Enduring Understandings Through their use of the elements and structures of the art form, creators and performers provide clues to their expressive intent. Students will know… Students will understand that… Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Vocabulary: Required: • a composition should reflect • demonstrate the expressive Students will be able to… • style/genre the creator/performer’s qualities in a given musical • apply foundational skills expressive intent by selection and describe how • basic dynamics (p, mp, mf, f) from K-5. selecting appropriate they relate to the • basic tempos (largo, andante, musical elements. composer’s/performer’s moderato, allegro, presto) intent. • music can be composed with • tempo related terms one or several layers of (ritardando, accelerando) sound. • word painting • music can be composed with • texture different tonalities to convey • tonality (major, minor, emotion. diminished, augmented, modal) Anchor Standard 4: Support their personal evaluation of work(s) and/or performance(s) based on analysis, interpretation, and established criteria. Enduring Understandings Quality performances are influenced by analysis, interpretation, and established criteria. Students will know… Students will understand that… Students will be able to… Prior Background Knowledge Vocabulary: Required: • personal preference for • describe and justify personal Students will be able to… • critic music is influenced by a responses to given musical • apply foundational skills variety of given criteria. selections using appropriate from K-5. musical vocabulary. Adopted April 14, 2014