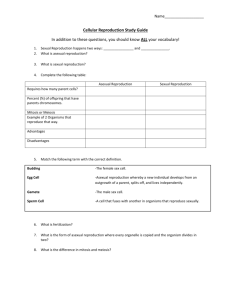
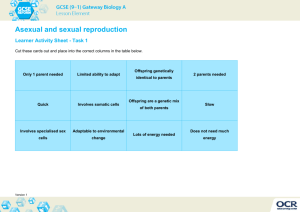
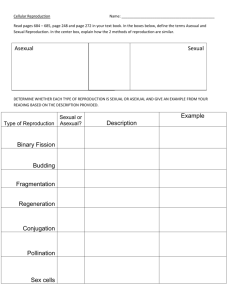
While asexual reproduction only involves one organism, sexual
advertisement

While asexual reproduction only involves one organism, sexual reproduction requires both a male and a female. Some plants and unicellular organisms reproduce asexually. Most mammals and fish use sexual reproduction. Some organisms like corals and komodo dragons can reproduce either sexually or asexually. But in the long term (over several generations), lack of sexual reproduction compromises their ability to adapt to the environment because they do not benefit from the genetic variation introduced by sexual reproduction. Moon Jellies has two main stages in its life cycle – polyp stage (asexual reproduction) & medusa stage (sexual reproduction) Types There are several different types of asexual reproduction. These include budding, where the offspring grows out of the body of the parent, and gemmules, where the parent releases a specialized mass of cells that will become a new individual. There are two types of sexual reproduction. Syngamy is the permanent fusion of two haploid gametes to create a zygote. In humans, this is called fertilization. Conjugation, on the other hand, is temporary fusion using a cytoplasmic bridge. This is particularly seen in bacteria, which pass DNA across the bridge. Process Asexual reproduction is reproduction that occurs without any interaction between two different members of a species. Cells divide using mitosis, in which each chromosome is copied before the nucleus divides, with each new cell receiving identical genetic information. Cell division in asexual and sexual reproduction Sexual reproduction is reproduction that requires a male and a female of the same species to contribute genetic material. Special cells called gametes are produced through meiosis, which halves the number of chromosomes in each resulting cell. These cells are called haploid gametes. Fertilization occurs when two gametes – one from a male and one from a female – combine, producing a diploid zygote with its own individual genetic makeup. Examples Asexual reproduction is used by many plants, e.g. spider plants, bacteria, hydra, yeast, and jellyfish. It is also involved in the creation of identical twins, when one zygote splits into two identical copies. Sexual reproduction is used by most mammals, fish, reptiles, birds and insects. Advantages and Disadvantages Asexual reproduction is well suited for organisms that remain in one place and are unable to look for mates, in environments that are stable. It is usually used by simple organisms such as bacteria. However, asexual reproduction does not lead to variation between organisms, meaning that entire groups can be wiped out by disease, or if the stable environment changes. Sexual reproduction allows for variation, the most fundamental element of evolution. It therefore creates species that can adapt to new environments and that cannot be wiped out by a single disease. However, sexual reproduction requires significant energy on the part of the organism to find a mate. It is not well suited to organisms that are isolated or stuck in place. References The Two Methods of Reproduction - BioTopics Types of Sexual Reproduction - Tutorvista.com Related Comparisons Eukaryotic Cell vs Prokaryotic Cell Diploid vs Haploid Gamete vs Zygote Mitosis vs Meiosis DNA vs RNA Abiotic vs Biotic