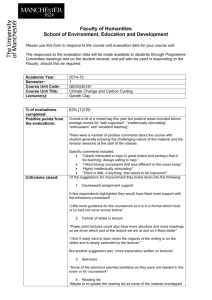
CORPORATE FINANCE
Course code
FIN117
Course title
Corporate Finance
Type of course
Compulsory
Semester
5th
ECTS credits
6: 24 hours of lectures, 24 hours of seminars, 112 hours of
individual work, 4 hours of consultations
Coordinating lecturer
Dr. Bogdan Stacescu
Course prerequisites
Introduction to Finance, Financial Accounting, Principles
of Financial Management
Language of instruction
English
Annotation
Aims of the course
This is a follow-up financial management course, which
covers both theoretical and practical decisions of
corporate financing, determination of cost of capital,
investment project and corporate valuation. This course
examines the main financial decisions related to
valuation of securities (stocks, bonds, options) and
investment projects with respect to their risk. The
course focuses on the impact of financial markets on
company‘s value and its financing decisions.
The main aim of this course is to provide theoretical
knowledge about models and methods of corporate
financial management and practical skills to apply this
knowledge to real situations by analysing and
evaluating strategic financial corporate decisions.
1
Subject learning outcomes (SLO)
Subject learning outcomes (SLO)
SLO1. Calculate weighted average cost of
capital (WACC) of a corporation, to take taxes
into account.
SLO2. Compare different WACC calculation
methods.
SLO3. Calculate and interpret cost of debt,
cost of equity, beta, cost of capital of an
investment project.
SLO4. Describe and compare net income
payout methods, dividend policy, share
repurchases.
SLO5. Explain the application of option theory
to investment project valuation.
SLO6. Overview the process of corporate
M&As.
SLO7. Apply and compare main corporate
valuation methods (discounted cash flows,
real options, relative valuation).
Study methods
Assessment methods
Lectures, seminars, individual
study
Coursework, final exam
Lectures, seminars, solving
exercises, self-study
Coursework, final exam
Lectures, seminars, solving
exercises, self-study
Midterm test, final exam
Lectures, seminars, self-study
Midterm test, coursework
Lectures, seminars, solving
exercises, individual study
Final exam
Lectures, seminars, self-study
Final exam
Lectures, seminars, self-study
Final exam
Study methods
Lectures, seminars, solving exercises, case studies, self-study.
Quality issues
The lecturer assures a variety of teaching and testing methods. The feedback for assessments is provided.
Cheating issues
The teaching and testing methods are chosen taking into account the purpose of the minimization of
cheating opportunities. The ISM regulations on academic ethics are fully applied in the course.
Topics:
Week
Topic
Contact hours
Lectures
Seminars
Readings
1
Introduction to corporate finance
2
2
CH. 1
2
Equity financing: stock markets
2
2
CH. 23
3
Debt financing: bond markets
2
2
CH. 24
4
Capital structure in perfect markets
2
2
CH. 14
5
Capital structure in imperfect markets
2
2
CH. 15, 16
6
Payout policy
2
2
CH. 17
Mid-term
7
Risk-return relationship. CAPM, beta.
2
2
CH. 12
8
Capital budgeting: WACC, APV, etc.
2
2
CH. 18
9
Options
2
2
CH. 20, 21
10
Real options
2
2
CH. 22
11
Mergers and acquisitions
2
2
CH. 28
12
Corporate valuation
2
2
Case will be
provided
Final exam
2
Total:
24
24
Individual work and assessment:
TYPE
Midterm test
Coursework
Final exam
Total:
TOTAL HOURS
EVALUATION, %
30
32
50
112
25
30
45
100
Course requirements:
1. Midterm test
It will be held in week 7 of the term. It counts towards 25% of the final grade. The midterm test will be based on
topics 1-6. Calculators may be used, provided they cannot store text.
2. Coursework
Students work individually to prepare a financial analysis of a chosen publicly listed corporation. Details on the
coursework will be provided during the first week. Coursework must comply with ISM requirements.
Coursework counts towards 30% of the final grade. The deadline for the written report is week 10, before the lecture.
3. Final exam
The exam counts towards 45% of the final grade. It will be based on topics
7-12. Calculators may be used, provided they cannot store text.
Assessment methods comply with ISM regulation of studies.
The final grade is calculated as a weighted average.
In case of a negative final grade, students are allowed a re-sit exam. It will cover all course material. The weight of a
re-sit is 70%. Coursework cannot be rewritten but its evaluation (if positive) is not annulled.
Main readings:
1.
Berk, J., DeMarzo, P., 2011. Corporate Finance, 2nd international ed. Boston: Pearson Addison Wesley.
Additional readings
1. Brealey, R.A., Myers, S.C., Franklin, A., 2006. Corporate Finance. Boston: McGraw-Hill Irwin.
2. Ross, S.A., 2005. Corporate Finance. New York: McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
Role of the subject in reaching learning outcomes of Finance study programme
Special learning outcomes
S1. To describe the main economic theories and theoretical models, to adapt them to the theoretical and
practical issues (for example, demand and supply elasticity theory, economic cycles, classical economic
theory, Keynesianism, monetarism, rational expectations theory, cost-benefit analysis);
S2. To describe and to analyse economic, legal, political and social environment of companies and other
organizations; to identify and to evaluate internal and external changes and to make necessary decisions to
keep the firm’s or organization’s economic and financial stability.
S3. To forecast the influence of economic and financial decisions not only in a financial context, but also in
the wider context of business or organization management, to estimate the effect of economic and financial
decisions on the processes of a company or an organization, the motivation of company’s human
resources, product and service quality, customer satisfaction, brand strength, corporate social
responsibility;
S4. To select mathematical, statistical, econometric and other appropriate research methods and to conduct
individually a simple economic analysis of a country, a sector or a company (to collect, to organize and to
interpret the data).
S5. To be able to analyse a company or an organization as an integral unit, which strives for certain goals in
(CLO)
CLO1, CLO2
CLO2
CLO1, CLO2,
3
a market or social environment by effectively distributing their finite resources among objects and business
activities and obtains synergies from coordinated function planning, organization and management;
S6. To describe and to analyse financial management and financial decision making processes in
companies and other organizations, to solve problems of different levels of complexity in financial and
management accounting ;
S7. To explain the corporate social responsibility and to be able to apply its principles in practice for a
company operating in a local as well as international markets.
S8. To select adequate research methods for the company’s internal and external analysis and to conduct
individually simple research of internal and external environment (to collect, to organize and to interpret
data, based on them to make managerial decisions).
S9. To describe the basic financial theories and theoretical models, to adapt them to the theoretical and
practical issues (for example, time value of money, evaluation of investment projects, risk-return
relationship, investment portfolio theory, stock and other securities pricing models, capital costs, risk
management, exchange rates, financial intermediaries)
CLO3, CLO4
S10. To explain the link between finance theory and practice, and to apply this knowledge in financial
information evaluation (e.g., effective market hypothesis, anomalies, capital structure);
S11. To describe and to analyse the financial management and financial decision-making processes in
business and other organizations.
S12. To describe the function of financial markets and institutions, and to analyse their activities;
S13. To describe main financial products and services, to evaluate their advantages and disadvantages
from the perspective of both a client and a supplier;
S14. To prepare, to analyse and to evaluate the financial part of investment projects and business plans.
General learning outcomes
G1. To apply modern information technologies in the data gathering, analysis and communication;
CLO2, CLO4
G2. To apply a systematic, critical and constructive thinking in problem identification and solving;
CLO2, CLO4
G3. To be able to communicate well and express thoughts in writing and orally, both in English and native
language; to communicate with specialists and non-professional audiences;
G4. To prepare research papers according to proper language, writing style and general bibliographic
citation requirements;
CLO1
G5. To develop independent learning skills necessary to continue studies on a higher level;
G6. To communicate and to work effectively in an intercultural and interdisciplinary group or team.
CLO1
3
G7. To know and to apply in practice certain aspects of various social sciences (history, geography,
sociology, logics, philosophy, arts, etc.), to supplement effectively the education of business or economics
by general knowledge.
4