History of Computers
advertisement

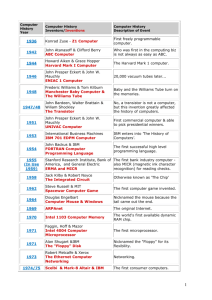
History of Computers Originated as Calculating Machines Abacus – Babylonians 3000 B.C. Napier's Bone − John Napier (1617 ) − Multiplication and Division Slide Rule − William Oughtred in England in 1632 − Logarithm, roots − Most common before the the development of digital computers. − Until 1960s Mechanical calculators − Schickard's Clock − German professor Wilhelm Schickard (1623) Pascaline Blaise Pascal (1642) Punched card − Frenchman Joseph Marie Jacquard (1801) Difference Engine English mathematician Charles Babbage (1822) Steam driven Polynomial , logarithmic , trigonometric functions Never functional Analytic Engine 1837 Powered by 6 stem engines General purpose computer Programmable and data stored using Punched card technology of Jacquard Loom. Storage Unit called 'Store' and processing unit 'Mill'. Correspond to modern day CPU and memory concept. Conditional statement (different from calculator) Mark I Harvard University and IBM (1944) First fully automated digital computer Not purely electronic − Switches, rotating shafts, clutches hundreds of miles of wire, 16 m in length, 2.4 m in height, It had a weight of about 10,000 pounds (4500 kg). Operated on numbers 23 digits wide. − add or subtract two of these numbers inn 3/10 th of a second, − multiply them in 4s, and divide them in 10 seconds. ABC computer Earliest attempts to build an allelectronic (no mechanical parts) digital computer in 1937 by J. V. Atanasoff and Clifford Berry. By 1941 they build a machine that could solve 29 simultaneous equations with 29 unknowns. First to store data as a charge on a capacitor memory (same mechanism as DRAM). Used binary arithmetic ENIAC Was the first general purpose electronic computer Ability of being reprogrammed for different problems University of Pennsylvania between 1943 and 1945 by two professors, John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert. Got funding from the war department to compute table for artillery gun positions and was used in the calculation for hydrogen bombs. filled a 20 X 40 ft room, weighed 30 tons, and used more than 18,000 vacuum tubes. Could only hold 20 numbers at a time. Faster than the Mark I: a multiplication that required 6 seconds on the Mark I could be performed on ENIAC in 2.8 thousandths of a second. Commercial Computers Mauchly and Eckert set up their own company which produced the first commercial computer the UNIVAC − (Universal Automatic Computer) By 1955 IBM was selling more computers than UNIVAC IBM model 650 is one of the first widely used computers. In 1957 IBM 305 used magnetic disk for the storage (tapes were used prior to that) 1959 IBM introduced two desk-sized computers IBM 1401 for business and IBM 1620 for scientist. The invention of transistors (which replaced vacuum tubes) and Integrated Circuit (Texas Instruments) enabled the shrink in the size of computers Programming languages By 1959 more than 200 programming languages were created. 1960 COBOL, - Grace hopper. 1965 John Kemeny of Dartmouth - BASIC programming language Microcomputers By 1964 – 18,000 computers 1970 – Large scale integration − Enabled the fabrication of large number of circuits in a single chip I971 Microprocessors (uP) was invented in Intel − A microprocessor (uP) is a processing unit that is fabricated on an integrated circuit (IC) or a chip. − Intel was the first to succeed in cramming an entire processing unit on a single chip (IC). − The Intel 4004 was first such chip In 1975 MITS Inc. produced the first microcomputer, the Altair using Intel 8080. It was sold for less than $400. Used Altair BASIC from Microsoft − Developed by Bill Gates and Paul Allen 1976 Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak build the first Apple Computer Hand built Apple II (1977) − First successfully massproduced micro computers 1980 – IBM offered microsoft to build operating system. Microsoft developed MS-DOS − IBM PC became the largest share in market for PCs by 1981. − Helped the tremendous growth of microsoft 1984 Apple - Macintosh computer with Graphical User Interface (GUI) and a mouse. 1992 – microsoft released Windows 3.1 − 3,000,000 copies sold in 2 months 1993 several companies introduced computers by using Pentium processors. 1990s – 2000s − Yahoo, Amazon, ebay, were established. − Java programming language was developed by Sun Microsystems − Google was founded in 1998 2003 – myspace.com 2004 - facebook.com 2005 – youtube.com 2004 Apple sleek iMac G5. System unit housed inside the display box. 2006 Intel - Core 2 duo processors family 2006 IBM – fastest supercomputer Blue Gene. 28 trillion calculations in 1 / 10 th of a second