Clampers -- Overview Lab Overview Equipment Theory
advertisement

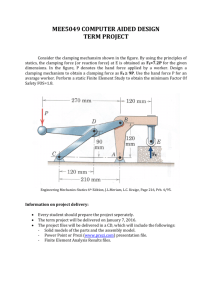
Clampers -- Overview Lab Overview After performing this lab exercise, learner will be able to: • Design positive and negative clampers • Design biased positive and negative clampers • Build the clamper circuit and observe the output Equipment To carry out this experiment, you will need: • TBS 1000B-EDUOscilloscope from Tektronix. • Voltage probe (provided with oscilloscope) / BNC cables • Breadboard and connecting wires • Circuit components - Resistor 1K, 0.25W, Diode 1N4002 /IN4148/equ, Regulated DC supply 0-30V DC, Signal /Function generator 10Hz to 1 Mhz Theory • Clamper is a circuit that "clamps" a signal to a different DC level without changing the shape of the applied signal Clamping circuit introduces a DC level into an ac signal. • The different types of clampers are positive, negative and biased clampers A clamping network must have a capacitor, a diode and a load resistor. • The magnitude R and C must be chosen such that the time constant RC is large enough to ensure that the voltage across the capacitor does not discharge significantly during the interval when the diode is non- conducting. • By connecting suitable DC voltage in series with the diode, clamping level can be varied. Design Assume C, and for clamping to occur select R such that RC >> T, (Assume RC = 100 T) where T is the period of the input signal. If C = 1uF, then from above equation R= 100K. Circuit Diagram Expected Waveforms Clampers -- Procedures Step 1 Study the circuit, expected waveform and transfer characteristic. Step 2 Place the components on bread board /connection board and connect them as given in circuit diagram fig 1. Use the patch cords/ wires for connection as required. Step 3 Switch on the signal generator and set voltage to 10V P-P and frequency to 1kHz Step 4 Set DC voltage to 0 V DC (Positive clamping). Step 5 Connect the input and output of the circuit to the two channels of the CRO. Observe the input and output waveforms( in DC mode only) and ensures that it matches with expected wave form. Step 6 Vary the DC voltage and observe the level of clamping. Step 7 Set VDC to 2V and note down input & output waveform and draw it on graph sheet (Positive Biased Clamping) . Step 8 Repeat this for negative clamping circuit. Step 9 In both cases change the polarity of the VDC and observe the output waveforms. Step 10 Result Positive and Negative clamping circuits and biased clamping circuits are tested and output waveforms observed.