Nematoda (Roundworms)
advertisement

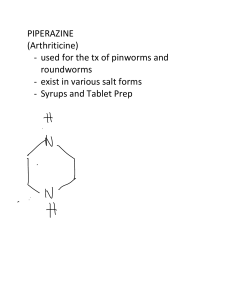
Presentations today: Derek/Travis Nick/Dustin Rachel/Arianne Erica/Jordan David/Dalton Colton/Taylor Katie/Dylan Dewayne/Ciera PHYLUM NEMATODA “The Roundworms” Nematoda (Roundworms) • widely distributed • living in soil, animals, • fresh and marine water • Most are free-living • many are parasitic. Roundworm Nematoda (Roundworms) • tapered at both ends • no segments • thick outer covering = Cuticle • protects them in harsh environments – Stomach acid • Covering is shed 4 times as they grow. Tapered ends Round body shape Nematoda (Roundworms) • no circular muscles • lengthwise (longitudinal) muscles • one muscle contracts • another muscle extends • causes them to move in a thrashing motion from side to side Nematoda (Roundworms) • Have a pseudocoelom • simplest animals with a one way digestive tract – mouth to anus Intestine Mouth Round body shape Anus Nematoda (Roundworms) • Eyespots very reduced in parasitic roundworms. • Approximately half of species are parasites • about 50 species infect humans. Examples: Ascaris, Pinworms, Trichenella, and Hookworms Ascaris • the most common roundworm infection in humans • children infected more often than adults – Why? • Eggs in soil – enter through the mouth of humans Life Cycle-– hatch in intestines – move into bloodstream – eventually to lungs – coughed up – swallowed – begin the cycle again. Pinworms • most common human roundworm parasites in U.S. • highly contagious • eggs can survive for up to two weeks on surfaces • live eggs ingested • mature in host’s intestinal tract • female pinworms exit host’s anus – itching! • lay eggs on nearby skin • eggs fall onto bedding or other surfaces • Reintroduced to intestine by mouth Trichinella • Trichinella causes a disease called “trichinosis” • Found in raw or undercooked meat • Can be sexually transmitted Trichinella Hookworms • common in humans in warm climates • Obtained when walking barefoot on contaminated soil • Hookworms cause people to feel weak and tired due to blood loss. Roundworm Parasites • Nematodes can infect and kill pine trees, cereal crops, and food plants such as potatoes. • They are particularly attracted to plant roots and cause a slow decline of the plant. • They also can infect fungi and can form symbiotic associations with bacteria that help plants obtain nitrogen from air • Nematodes also can be used to control pests • Life on Earth is very dependent on nematodes • Billions of nematodes in every one - symbiosis