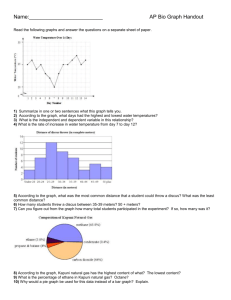
1 Confusing Terminology C3 Vs. C4 Photosynthesis Types of
advertisement
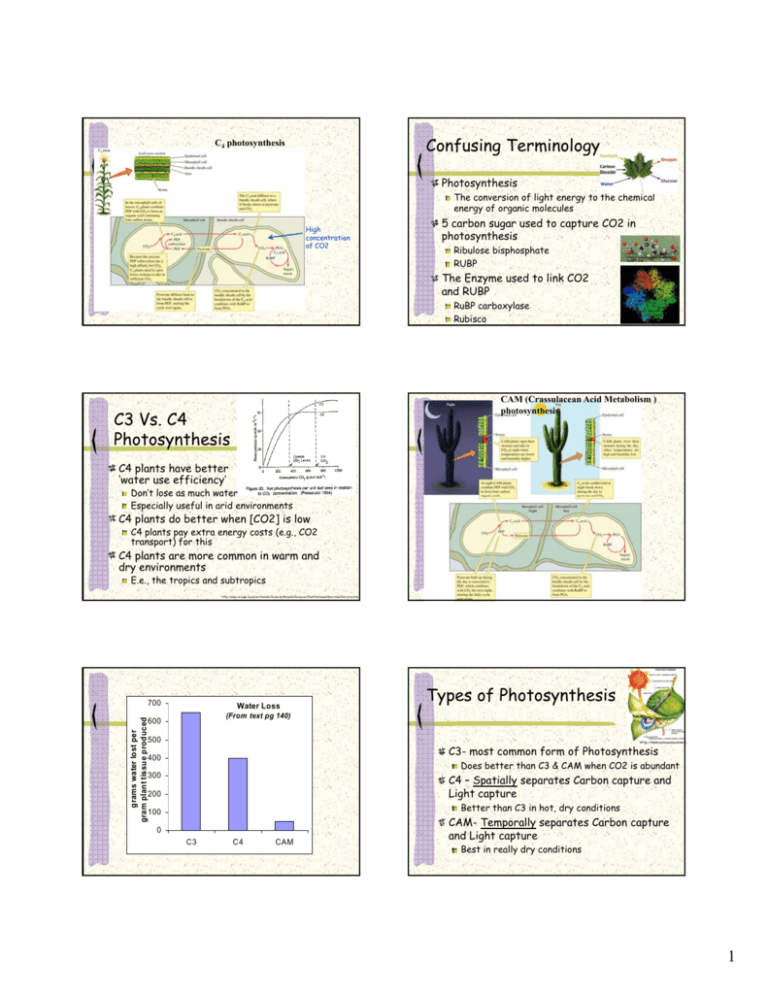
Confusing Terminology C4 photosynthesis Photosynthesis The conversion of light energy to the chemical energy of organic molecules High concentration of CO2 5 carbon carb n sugar su ar used tto capture CO2 in photosynthesis Ribulose bisphosphate RUBP https://www.msu.edu/~ngszelin /RuBP2.JPG The Enzyme used to link CO2 and RUBP RuBP carboxylase Rubisco https://www.msu.edu/~ngsze lin/calvin_cycle_players.htm CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism ) photosynthesis C3 Vs. C4 Photosynthesis C4 plants have better ‘water use efficiency’ Don t lose as much water Don’t Especially useful in arid environments C4 plants do better when [CO2] is low C4 plants pay extra energy costs (e.g., CO2 transport) for this C4 plants are more common in warm and dry environments E.e., the tropics and subtropics http://www.cartage.org.lb/en/themes/Sciences/BotanicalSciences/PlantHormones/Nutrition/Nutrition.htm 700 Water Loss Types of Photosynthesis grams wa ter lost per ssue produced gram plant tis (From text pg 140) 600 500 http://manravbioeducation.b C3- most common form of Photosynthesis 400 Does better than C3 & CAM when CO2 is abundant C4 – Spatially separates Carbon capture and Light capture 300 200 Better than C3 in hot, dry conditions 100 0 C3 C4 CAM CAM- Temporally separates Carbon capture and Light capture Best in really dry conditions 1 Types of plants in each category Chemosynthesis vs. photosynthesis Echinacea purpurea ( Coneflower); C3 pathway – most plants Zea mays (Corn) C4 pathway- many grasses Opuntia humifosa (Beavertail Cactus); Solar energy is the energy source for most food webs CAM pathway succulents http://www.swbic.org/education/webquests/photosynthmain.php http://www.bigelow.org/foodweb/chain4.html Detritivores Functional Response How are the three types different? Why do they level off? http://www.hiltonpond.org/ThisWeek040508.html What is it that limits energy consumption? http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Saprotroph http://i.pbase.com/o5/30/681730/1/68842751.kGAbQuPy.Kalkongamterpingvinung http://web.utk.edu/~ctmelear/ossabaw/RobertoOwenAsh/mushroom.gif Functional Response Peanuts to harvest and shell Handling time is shortsearching is the limiting step 20 seconds Density: 1/m2, 2, 5, 10, 100 Food intake/ 20 sec c Chemicals produced by deep sea vents (H2S) are the primary energy source in a few cases Handling time is limiting when food is abundant g time m and Both handling search time are both limiting in between Search time is limiting when food is rare 1 2 5 Peanut Density 10 100 Prey can hide better when rare Learning by predators ‘Switching’ 6-18 The book doesn’t explain what causes a type III response– this was a new omission in 4th ed! 2 Factors that may limit the performance of organismsConditions vs. Resources Factors that may limit the performance of organismsConditions vs. Resources Condition: An abiotic environmental factor which varies in space and time and affects the p performance of an organism Resource: a factor of the environment that becomes unavailable to other organisms when it is used Consumed or used up so it is not available to others Performance usually increases with abundance of a resource up to some plateau e.g., food, water, nesting sites, hiding places, etc. Not consumed or used up Performance usually peaks at an intermediate value of the condition (an optimum) e.g., temperature, relative humidity, pH, salinity, stream flow velocity, concentration of pollutants….. Chalk talk about limits Self-Test When is photosynthetic rate of Adiantum decorum limited by photon flux density? 100 500 a) Photon flux density y < 100 b) Photon flux density > 500 c) Photon flux density > 1,250 d) Photosynthetic rate is limited by photon flux density under all conditions shown Photosynthetic rate is not limited by photon flux density in these data e) µmol/m l/ 2/sec / µmol/m2/sec µmol/m2/sec 3