FLASH CARDS Kalat's Book Chapter 1
advertisement

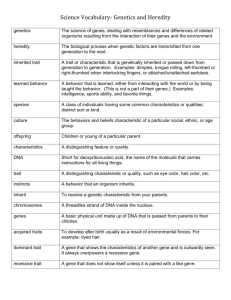
FLASH CARDS www.BiologicalPsych.com Kalat’s Book Chapter 1 Alphabetical altruistic behavior altruistic behavior Sacrificing personal welfare being to help another. Seen in many species, particularly in kin relationships. artificial selection artificial selection Also called selective breeding. Intentional breeding for favorite or special traits. Filters out unwanted traits. Darwin term. autosomal gene autosomal gene A gene on a non-sex chromosome. biological psychology biological psychology Also called physiological psychology, behavioral neuroscience, & psychobiology. The brain people of psychology & the mind people of neuroscience. Human & animal studies are used to explain human behavior through biological principles. chromosome chromosome Encoded genetic information in a single piece of DNA. Humans have 22 non-sex chromosomes and 1 sex-determining chromosome. Each chromosome can contain many genes. Darwinian evolution Darwinian evolution Theory of Charles Darwin (1808–1882). His two main assumptions were common ancestry and natural selection. deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) A spiral shaped molecule composed of two duplicate strands, headed in opposite directions. The structure is bound together by 2 sugars and four bases, and is resistant to cleavage. dizygotic twin dizygotic twin Twins but from two separate egg-sperm combinations. Also called fraternal twins. The most common type of twin. dominant gene dominant gene Trait will appear in all offspring, even if only one parent has this gene. dualism dualism Descartes dualism maintains that the mind and body are separate entities but meet in the pineal gland. easy problems of consciousness easy problems of consciousness Easy problems are how we focus attention, integrate audio streams, and make visual discriminations. Chalmers (1995) enzymes enzymes Large molecules that increase rate of chemical reactions by lowering the amount of energy needed to make a reaction. Catalysts. epigenetics epigenetics Epi (over and beyond), genetics (DNA). The study of how things other than changes in the genetic code impact the expression of genes. Why twins become less alike as they age. evolution evolution How populations change over generations. Major theories are Lamarkian and Darwinian. evolutionary explanation evolutionary explanation Uses evolution to explain current behavior. Observation that people come from a long line of hunter and gatherers is used to explain current activities. “We weren’t built to sit all day.” evolutionary psychology evolutionary psychology Explains memory, cognition, perception and other psychological phenomenon in terms of evolutionary theory. fitness fitness A concept of evolution. Likelihood a trait will survive in offspring. functional explanation functional explanation As opposed to structural. Focus is on software. Behaviors is a result of learning, experience and environmental factors. genes genes A subunit of DNA that carries a specific genetic instruction. hard problem of consciousness hard problem of consciousness Chalmers (1995) term for explaining mental phenomena by mechanical & biological processes. The hard problem is that our experience is more than the sum of the parts. We experience flavors, colors and events, not just process data. heritability heritability Either the proportion of a trait in a population or how much individual differences impact behavior. Statistically, how much does genetics influences height in a population. Or what is the relative importance of genetics, chance and the environment on a person’s behavior. heterozygous heterozygous Receive different trait characteristic from each parent. Gene information doesn’t agree. homozygous homozygous Receive same trait characteristic from each parent. Two identical copies of gene. kin selection kin selection Specifically, we are more likely to help relatives than strangers. Generally, the interaction between relatives impacts the frequency of genes in offspring. Lamarckian evolution Lamarckian evolution Theory of Jean-Baptiste Lamarck (1744–1829). His two main assumptions were that organisms move continuously toward complexity (inherent progressive tendency); and that what you learn in your life can be passed on genetically to your offspring (also called soft inheritance). mind–body problem mind–brain problem mind–body problem mind–brain problem How a material brain and a spiritual mind can exist. Usually seen as a choice between dualism and monism. monism monism Physical monists, such as Hobbes, hold that all that exists is the physical; soul and mind are illusions. Berkeley (a spiritual monist) says that all that exists is the spiritual; we all exist in God’s mind, body is an illusion. monozygotic twins monozygotic twins Twins from the same egg-sperm. Separates into two zygotes usually by Day 12 of development. Only 30% of twins are monozygotic. Also called identical twins. mutation mutation Changes in genes by virus or non-genetic influences. natural selection natural selection Gradual process where traits become more or less common because of mutations and changes in environment. Also called survival of the fittest. Darwin term. ontogenetic explanation ontogenetic explanation Behavior is a result of genes and environment. Language needs both a gene for throat development and early exposure to sounds. physiological explanation physiological explanation Behavior is the result of biological structures and processes. recessive gene recessive gene Trait will not appear in all offspring but will show when child receives two copies of recessive gene. reciprocal altruism reciprocal altruism Mutual benefit behaviors; you scratch my back, I’ll rub your feet. ribonucleic acid (RNA) ribonucleic acid (RNA) Family of single-stranded molecules that code, decode, regulate and express genetic instructions. sex-linked gene sex-linked gene A gene on a X or Y chromosome. Determine sex but also impact traits such as color blindness or hemophilia. sex-limited gene sex-limited gene Autosomal gene in both sexes but expressed differently (if at all) in each. Males strong, females timid; milk production in females, not in males. structural explanation structural explanation As opposed to functional. Focus is on hardware. Behavior is a result of physical and mechanical processes. survival of the fittest survival of the fittest Environmental changes make certain traits more or less common. If the trait helps the animal survive, it will be more common in offspring. Also called natural selection. Darwin term. www.BiologicalPsych.com