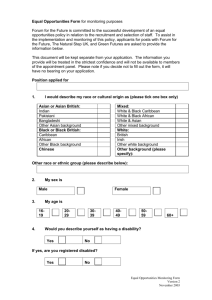
Document
advertisement

Chapter 2 Developing Marketing Strategies and Plans Dr.Pusanisa Thechatakerng thesunny@rocketmail.com © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-1 In this chapter, we address the following questions: How does marketing affect customer value? How is strategic planning carried out at different levels of the organization? What does a marketing plan include? © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-2 Opening Case Study - ZARA Known for trendy affordable clothes Zara’s secret? Total control of business Design > production > distribution Lead-time advantage - lower inventory levels Frequent line changes - exclusivity for customers © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-3 Opening Case Study - ZARA Zara’s “democratication of fashion” Advertising approach - its shop windows Expansion plans - 4,000 stores worldwide © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-4 Two Views of the Value Delivery Process Figure 2.1 © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-5 Fig 2.2 The Generic Value Chain Examine costs & performance in each activity and improve it © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-6 Marketing and Customer Value core competencies Eg Volvo’s core competency is safety Eg Nike does not manufacture own shoes Asian firms more competent Nike’s 2 core competencies -shoe design & merchandising © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-7 Marketing and Customer Value core competencies is something that a firm can do well and that meets the following three conditions 3 characteristics: 1. competitive advantage 2. applications in many markets 3. difficult for competitors to imitate © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-8 Marketing and Customer Value core competencies Asian companies - core competence: Expand quickly to capture global market opportunities Become atomizers Become asset light by using intangibles © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-9 Marketing and Customer Value The Central Role of Strategic Planning Strategic planning ensure correct marketing activities are selected & executed © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-10 Marketing and Customer Value The Central Role of Strategic Planning Figure 2.4 The Strategic Planning, Implementation, and Control Processes © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-11 Corporate & Division Strategic Planning 4 corporate planning activities: 1. Define corporate mission 2. Establish strategic business units (SBUs) 3. Assign resources to each SBU 4. Assess growth opportunities © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-12 Corporate & Division Strategic Planning 1. Define the Corporate Mission What is our business? Who is the customer? What is of value to the customer? What will our business be? 1st ? What should our business be? © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-13 Table 2.1 Sample Mission Statement © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-14 Corporate & Division Strategic Planning 1. Define the Corporate Mission Mission statements are the vision direction for company for next 10 to 20 years 3 major characteristics: 1. Focus on limited number of goals 2. Stress company’s major policies & values 3. Define competitive sphere/area company will operate in © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-15 Defining Business market definitions better than product definitions Customer-satisfying NOT goods-producing Table 2.2 Product-Oriented Versus Market-Oriented Definitions of a Business © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-16 2. Establish strategic business units (SBUs) An SBU has 3 characteristics: 1. SBU plan separate from company 2. its own set of competitors 3. has a manager for strategic planning and profit matters © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-17 3. Assign resources to each SBU The purpose of identifying the company’s strategic business units is to develop separate strategies and assign appropriate funding © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-18 4. Assess growth opportunities plan new business, downsize or terminate old business How to fill the strategicplanning gap? © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Figure 2.5 the strategic planning gap Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-19 INTENSIVE GROWTH related to a company's current operations The company first considers… – more market share with current products & markets (market-penetration strategy)? – find new markets for current products (market-development strategy)? – develop new products to current markets (product-development strategy)? – develop new products for new markets (diversification strategy)? © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-20 market-penetration strategy cafés serving gourmet coffee directly to customers in Seattle 1 market-development strategy 2 same as above throughout North America & worldwide product development strategy Increase customers’ purchases with new in-store merchandise (CDs) 1 1 3 diversification strategy Frappuccino® bottled drinks, Starbucks brand ice cream & purchase of tea retailer Tazo® Tea into grocery store aisles © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 4 2-21 INTEGRATIVE GROWTH a firm acquires some other element of the chain of distribution of which it is a member. INTEGRATIVE GROWTH: backward, forward or horizontal integration within its industry acquire suppliers -backward integration acquire retailer-forward integration acquire competitors-horizontal integration If unsuccessful, diversification © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-22 Integrative Growth II LVMH (Luis Vuitton +Moet Hennessy) © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective Christian Dior (CD) Gucci Channel Givenchy Marc Jacobs Prada Fendi Kenzo DKNY 2-23 DIVERSIFICATION GROWTH When good opportunities are found outside present businesses Good opportunity is when industry is attractive & company has strengths to be successful © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-24 Diversification Growth Richemont Group (Cartier, Dunhill, Chloe) © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Stationary: Monblanc 5 billion Euros (2006) Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-25 Organization and Organizational Culture Corporate culture “the shared experiences, stories, beliefs & norms that characterize an organization” corporate culture, structure & policies are key when implement new strategy © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-26 Organization and Organizational Culture What drive successful Asian businesses? 4 organizational factors 1. 2. 3. 4. Market orientation/direction Innovativeness Corporate culture Organizational climate © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-27 Organization and Organizational Culture How to adopt new view of crafting strategies? Get fresh ideas from: – employees with youthful perspectives – employees who are out stationed – employees who are new to industry Choose among different views of the future © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-28 Business Unit Strategic Planning - the business mission Each business unit needs to define its specific mission within the broader company mission © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-29 Business Unit Strategic Planning – SWOT Analysis SWOT Analysis Overall evaluation of a company’s strengths weaknesses opportunities & threats opportunities threats monitor external & internal environment © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective SWOT Analysis strengths weaknesses 2-30 Business Unit Strategic Planning – EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT (OPPORTUNITY & THREAT) ANALYSIS A business unit has to identify opportunities and threats. How? By monitoring key macroenvironment & microenvironment factors that affect ability to earn profits © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective opportunities threats SWOT Analysis strengths weaknesses 2-31 Business Unit Strategic Planning – SWOT Analysis 3 main sources of market opportunities 1. Supply something that is in short supply 2. Supply existing product in new way 3. Totally new product or service © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-32 Business Unit Strategic Planning – Market Opportunity Analysis (MOA) 2. Can target markets be reached with cost-effective media & trade channels? 1. Can benefits convince target markets? Market Opportunity Analysis (MOA) To evaluate opportunities To determine attractiveness & probability of success 4. Are benefits better than competitors? © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan 3. Possess resources to deliver benefits? 5. Is it profitable? Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-33 © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-34 Business Unit Strategic Planning – INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT (STRENGTHS/WEAKNESSES) ANALYSIS Checklist to evaluate INTERNAL strengths & weaknesses opportunities threats SWOT Analysis strengths weaknesses Go for opportunities where it has required strengths? Go for opportunities where it has to develop certain strengths? © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-35 Business Unit Strategic Planning – goal formulation Goals objectives specific to magnitude/greatness & time Goal formulation goals for planning period done after doing SWOT analysis © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-36 Business Unit Strategic Planning – goal formulation Managing by Objectives (MBO) is successful if: 1.Objectives arranged hierarchically 2.Objectives are quantitative where possible 3.Goals are realistic 4.Objectives are consistent © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-37 Business Unit Strategic Planning – strategic formulation Goals indicate what business wants to achieve Strategy is a game plan for getting there marketing strategy compatible technology strategy sourcing strategy © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-38 Business Unit Strategic Planning – strategic formulation PORTER’S GENERIC STRATEGIES Overall cost leadership Differentiation Focus achieve lowest costs to price lower than competitors & win large market share superior performance in area valued by large part of market focuses on narrow market segments © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-39 Business Unit Strategic Planning – strategic formulation STRATEGIC ALLIANCES Companies need strategic partners to be effective. Many strategic alliances take the form of marketing alliances. A celebration at a Star Alliance brings together 16 airlines that cover most of the globe 4 major categories: 1. 2. 3. 4. Product or service alliances Promotional alliances Logistics alliances Pricing collaborations © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-40 Business Unit Strategic Planning – strategic formulation STRATEGIC ALLIANCES 4 major categories: 1. Product or service alliances 2. Promotional alliances 3. Logistics alliances 4. Pricing collaborations Visa has promotional alliance with Hong Kong Disneyland © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-41 Business Unit Strategic Planning - Program Formulation & Implementation STEP ONE Once strategies work out detailed programs developed STEP TWO Once marketing programs marketing must estimate costs formulated STEP THREE Activity-based cost (ABC) whether results to justify the cost accounting applied STEP FOUR Implementing not lose sight of stakeholders & their needs strategy © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-42 Business Unit Strategic Planning – feedback and control Marketplace will change – review & revise implementation, programs, strategies or objectives HAIER is a good example: Started with inferior-quality products Later, sales went up China’s leading maker of washing machines Faces competition in Chinese market Partner with Sanyo in production alliances Makes digital TVs with LG Electronics Diversify into finance, computers, cell phones © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-43 Business Unit Strategic Planning - Contents of a Marketing Plan marketing plan A summarized written document about marketplace & plans to reach marketing objectives 1. Is the plan simple? 2. Is the plan specific? 3. Is the plan realistic? 4. Is the plan complete? © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-44 Business Unit Strategic Planning - Contents of a Marketing Plan Executive summary & table of contents Situation analysis Marketing strategy Financial projections Implementation controls © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-45 Final discussion Marketing Debate — What Good is a Mission Statement? Virtually all firms have mission statements to help guide and inspire employees as well as signal what is important to the firm to those outside the firm. Mission statements are often the product of much deliberation and discussion. At the same time, some critics claim that mission statements Sometimes lack “teeth” and specificity. Moreover, critics also maintain that in many cases, mission statements do not vary much from firm to firm and make the same empty promises. Take a position: Mission statements are critical to a successful marketing organization, or Mission statements rarely provide useful marketing value. Marketing Discussion Consider Porter’s value chain and the holistic marketing orientation model. What implications do they have for marketing planning? How would you structure a marketing plan to incorporate some of their concepts? © Kotler, Keller, Ang, Leong & Tan Marketing Management An Asian Perspective 2-46