IR Exercise
advertisement

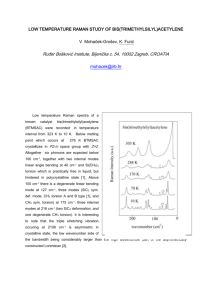
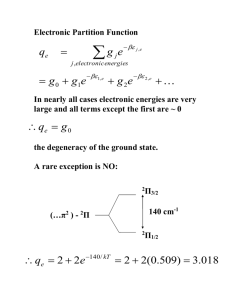
IR Exercise Match the following 10 compounds with the 10 spectra on the following pages. Label the major diagnostic peaks on each spectrum to receive full credit. 1-butanol HOCH2CH2CH2CH3 CH2OH benzyl alcohol N-methylcyclohexylamine aniline NHCH3 NH2 O 2-pentanone H3C C CH2CH2CH3 O C acetophenone ethyl acetate 1-hexene pentane H 3C O C O CH3 CH2CH3 CH2=CHCH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 butyraldehyde H3CH2CH2C O C H Reference Some IR Stretching Frequencies 3400-3250 cm-1 N–H (1˚, 2˚ amines) 1680-1640 cm-1 C=C (alkenes) 3500-3200 cm-1 O–H (alcohols) 1600-1585 cm-1 C–C (aromatics) 3100-3000 cm-1 C–H (alkenes, aromatics) 1500-1400 cm-1 C–C (aromatics) 3000-2850 cm-1 C–H (alkanes) 1335-1250 cm-1 C–N ( aromatic amines) 2830-2695 cm-1 C–H (aldehydes) 1250-1020 cm-1 C–N (aliphatic amines) 1750-1665 cm-1 C=O (see discussion on back) 1300-1050 cm-1 C–O (alcohols, esters) Carbonyl Stretching Frequencies The exact position of the carbonyl band in the 1760-1665 cm-1 range is determined by the constituents neighboring the carbonyl group. Some examples are: range 1750-1735 cm-1 type of carbonyl examples saturated aliphatic esters O C R 1740-1720 cm-1 1730-1715 cm-1 saturated aliphatic aldehydes R O C O H !,"-unsaturated esters R' "R saturated aliphatic ketones 1715 cm-1 1710-1665 cm-1 R' R O C O C O C OR OR R' !,"-unsaturated alde- hydes and ketones R' "R O C R' H "R O C O C H O C R R Another way of looking at the correlation between wavenumber and functional group stretch: C H O 4400 C C H H C C O H H C H (or R) H (or R) O C C C O N } increasing band intensity N } H (or R) 4000 3750 3500 3250 3000 2750 2500 2250 2000 1750 1500 1250 1000 750 450 cm 1 2 3 4 5 6 A 7 8 9 A 10