Diseases - Urinary System
advertisement
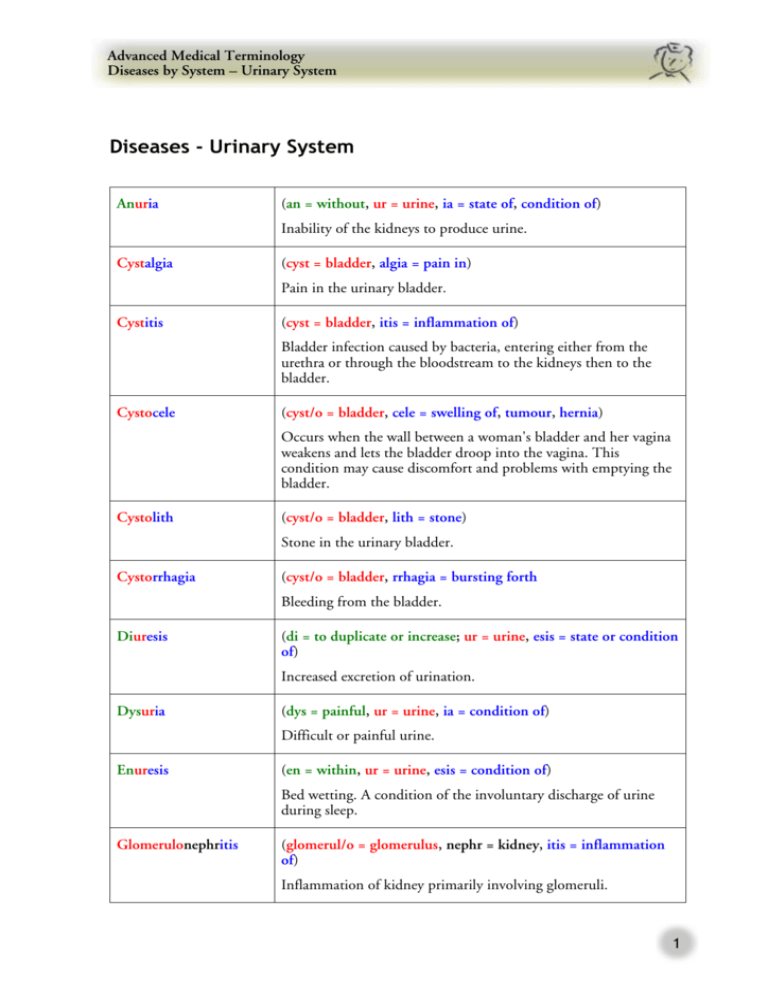
Advanced Medical Terminology Diseases by System – Urinary System Diseases - Urinary System Anuria (an = without, ur = urine, ia = state of, condition of) Inability of the kidneys to produce urine. Cystalgia (cyst = bladder, algia = pain in) Pain in the urinary bladder. Cystitis (cyst = bladder, itis = inflammation of) Bladder infection caused by bacteria, entering either from the urethra or through the bloodstream to the kidneys then to the bladder. Cystocele (cyst/o = bladder, cele = swelling of, tumour, hernia) Occurs when the wall between a woman's bladder and her vagina weakens and lets the bladder droop into the vagina. This condition may cause discomfort and problems with emptying the bladder. Cystolith (cyst/o = bladder, lith = stone) Stone in the urinary bladder. Cystorrhagia (cyst/o = bladder, rrhagia = bursting forth Bleeding from the bladder. Diuresis (di = to duplicate or increase; ur = urine, esis = state or condition of) Increased excretion of urination. Dysuria (dys = painful, ur = urine, ia = condition of) Difficult or painful urine. Enuresis (en = within, ur = urine, esis = condition of) Bed wetting. A condition of the involuntary discharge of urine during sleep. Glomerulonephritis (glomerul/o = glomerulus, nephr = kidney, itis = inflammation of) Inflammation of kidney primarily involving glomeruli. 1 Advanced Medical Terminology Diseases by System – Urinary System Haematuria (haemat = relating to blood, ur = urine, ia = state or condition of) The presence of blood in the urine either from the kidneys, one or both ureters, the bladder or urethra or as a result of injury or disease. Hypercalciuria (hyper = above, excessive; calc/i = calcium, ur = urine, ia = state or condition of) Abnormal high levels of calcium in the urine. Incontinence Inability to control excretory function. Nephritis (nephr = kidney, itis = inflammation of) Inflammation of the kidney. Nephrolith (nephr/o = kidney, lith = stone) A stone in the kidney. Nephrolithiasis (nephr/o = kidney, lithiasis = presence of stone) The presence of stones in the kidneys. Nephromalacia (nephr/o = kidney, malacia = softening of) Softening of the kidneys. Nephroptosis (nephr/o = kidney, ptosis = sagged, drooping) Prolapse of the kidney. Nephropyosis (nephr/o = kidney, py = pus, osis = condition of) Suppuration of the kidney. Nephrosclerosis (nephr/o = kidney, sclerosis = hardening) Abnormal hardening of the kidney. Nephrosis (nephr = kidney, osis = abnormal condition) Any disease condition of the kidney. Nocturia (noct = night, ur = urine, ia = condition of) Excessive urination during the night. 2 Advanced Medical Terminology Diseases by System – Urinary System Oliguria (olig = scant, few; ur = urine, ia = condition of) Scanty urination. Paraspadias (para = to bring forth or to bear; spad = to draw, to tear; ias = abnormal condition) A developmental abnormality in which the urethra opens along one side of the penis. Polyuria (poly = excessive, many; ur = urine, ia = condition of) Excessive urination. Prostatitis (prostat = prostate, itis = inflammation of) Inflammation of the prostate gland due to bacterial infection either chronic or acute. Proteinuria (protein = protein, ur = urine, ia = condition of) Presence of protein in the urine. This may indicate presence of disease or damage to kidneys. Pyelitis (pyel = renal pelvis, itis = inflammation of) An inflammation of renal pelvis. Pyelonephritis (pyel/o = renal pelvis, nephr = kidney, itis = inflammation of) Bacterial infection of the kidney substance. The kidneys become small and kidney failure begins. Renal colic Acute pain in the kidney area caused by blockage during passage of a stone. Uraemia (ur = urine, aem = blood, ia = abnormal state or condition of) Toxic condition caused by excessive waste products in the blood stream due to kidney dysfunction. Ureterolith (ureter/o = ureter, lith = stone) A stone formed in the ureter. Ureterorrhagia (ureter/o = ureter, rrhagia = bursting forth) The discharge of blood from the ureter. 3 Advanced Medical Terminology Diseases by System – Urinary System Ureterostenosis (ureter/o = ureter, stenosis = tightening or narrowing) Stricture of the ureter. Urethralgia (urethr = urethra, algia = pain in) Pain in the urethra. Urethritis (urethr = urethra, itis = inflammation of) Inflammation of the urethra. Urethrorrhagia (urethr/o = urethra, rrhagia = bursting forth) Bleeding from the urethra. Urethrorrhoea (urethr/o = urethra, rrhoea = to flow) Abnormal discharge from the urethra. Urinary incontinence Inability to control the voiding of urine. Urinary retention Inability to empty or void urine. Urolithiasis (ur/o = urine, lithiasis = presence of stones) Presence of stones in the urine. 4