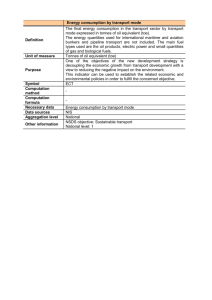
What are sesamoids? - Consulting Foot Pain

Factsheet 3. Sesamoids usefully improve great toe function
(Standard - moderately technical)
The anatomy of the sesamoid, and the local bones, provide you with some idea why podiatrists believe that the sesamoid is critical for normal function. We can summarise this as:
• Stabilising the great toe
• Making toe propulsion more effective
• Converting tendon pull into an efficient level using sesamoids as a pulley
Sole%of%the%foot% sesamoids%
Skin%peeled%% back%to%reveal% sesamoids%si5ng% under%the% metatarsal% metatarsal%
The$foot$seen$from$ the$toes$and$sole$(A).$
Cross$sec5on$to$show$ metatarsals$and$sesamoid$
$ bones.$$
$
Side$(lateral$view)$ view$showing$length$of$ metatarsal$and$sesamoids$(B)$$
A
B car5lage$
The big toe relies on two small bones called sesamoids. These are often known as seed-like bones and may at first appear to have little responsibility in foot function.
Many patients look at x-rays that I show them and ask what are those bones? They are sesamoids and they are important. Before 10 years of age they are cartilage and do not show up on x-ray. If you liken them to the knee cap (patella) this is the largest and best known sesamoid in the body.
So what do they do? We have to discuss the technical aspect and use ‘basic physical mechanics’. If we want to move a heavy object we can do so using a pulley. This converts the pull into an effective advantage, which takes less effort because of the design. The basic pulley effect can be applied by using an object between the rope and the object. To avoid friction a small wheel works better.
Pulley#/fulcrum#
Effort#from# pulling#
10#Kg#
Load#to#be#pulled#
Basic#physics#–#simple#pulley#effect#allows#high#load#to#be#pulled#
With#lower#effort.#This#is#related#to#improved#mechanical#efficiency##
2
Heel)end)
If we want to improve of the toe
Front)of) foot) downwards a pulley effect works for us at the point where the sesamoid bone lies. The bones, lined with
Triangle)works)like)a)fulcrum.)This)is)
Where)the)sesamoid)sits.)The)bar)is)the) metatarsal) cartilage and the tendons lined with a lubricating fluid replace the small wheel. The big toe uses the sesamoids to angle the tendon creating more mechanical advantage. The diagram above pulls a load. In the foot that load is the great toe. The pulley is the sesamoid, which also acts as a fulcrum. This is the point where leverage works best. Think of a wheelbarrow moving a load levering around its wheels.
The big toe must stay on the ground during walking. To be more precise it must stay flat against the ground when the heel lifts. Failure to achieve contact at a time we call propulsion, affects the foot function at a critical point in walking. This is known as the toe off phase. metatar sal(
A" d(
B" p(
A" s"
B"
B(–(the(long(flexor(exerts(a(pull(on(the(4p(of(the(great(toe((d)(keeping(it(on(the(ground.(
A(–(the(short(flexor(uses(the(sesamoid((S)more(to(hold(the(nearer(bone((P)(on(the(ground.(
(
The(sesamoids(therefore(act(to(stabilise(the(great(toe(when(we(walk.(Flexor(muscle(tendons( are(important(for(their(downward(thrust.(Without(sesamoids(we(would(have(weaker( stability.((
Failure to work is identified as a tell tale sign because the toe does not sit correctly, or that the skin print is smooth due to loss of use. Skin that is overused thickens. The clinician will check for the presence of a skin print, as it is not an ideal situation to have soft toe skin. The function of the print prevents slippage and shows that the toe works normally. Absence of skin print implies poor toe function, OR in the case of after surgery, the toe may be raised. This is not always a bad thing as the surgery probably is helping sort out joint pain, which is more important.
The'problem'with'hallux'valgus'(bunion)'
Sesamoids' moved'out' of'posi5on.'
Inside'sesamoid' rubs'over'crista'
Crista'is'central'part' that'helps'keep'the'' sesamoids'in'place'
Correct'aligment'
Factsheet. The function of the sesamoids affecting the great toe www.Consultingfootpain.co.uk
© Busypencil Case Communications Ltd. June 2015
3
Usually there are only 2 sesamoids; A medial and a lateral sesamoid. The sesamoids are held track bound by ligaments and a central ridge called the Crista. Again we can liken this to the knee patella which can become track bound causing knee pain. The position of the sesamoids is important. Too much displacement affects toe function as in Hallux Valgus, better know as a bunion.
The bones may divide into two or more. A two-part sesamoid is known as a bipartite.
Each division is given another name. Three – tripartite and so on. I have seen up to five on one side (quinti-partite). In reality if the bone splits up the mechanical efficiency changes little.
There are other small bones in the foot but the big toe sesamoids are the most important. Other seed like bones are often known as ossicles and take the prefix ‘os’ as in Latin, still used by us to describe bones. The most important others include Os
Trigonum and Os Tibiale Externum. In both cases these are not always present. USA sources suggest 7-8% of the population have these. There are many more but we do not need to worry about these here.
Problems can arise with sesamoid bones. The condition form a lose expression
‘sesamoiditis’ .
Further references are available on my website www.consultingfootpain.co.uk
Factsheet. The function of the sesamoids affecting the great toe www.Consultingfootpain.co.uk
© Busypencil Case Communications Ltd. June 2015