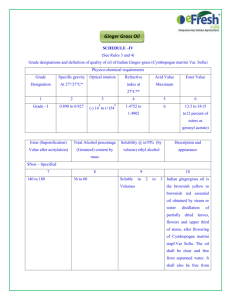
Section 7 ppapers
advertisement

Taylor High School Higher Chemistry 1. Which of the following is an ester? Unit 2 Section 7 4. The structural formula for glycerol is 2. Fats and oils can be classified as 5. Which consumer product is least likely to contain esters? A B C D A B C D soaps fatty acids esters polyesters 6. Fats have a higher melting points than oils because comparing fats to oils 3. The conversion of linoleic acid, C18H32O2, into stearic, C18H36O2, is likely to be achieved by A B C D Flavourings Perfumes Solvents Toothpaste A fats have more hydrogen bonds B fats have more cross-links between molecules C fat molecules are more loosely packed D fat molecules are more saturated hydrogenation hydrolysis hydration dehydration 1 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry 7. An ester has the structural formula: Unit 2 Section 7 9. In the formation of “hardened” fats from vegetable oils, the hydrogen On hydrolysis, the ester would produce A causes cross-linking between chains B causes hydrolysis to occur C increases the carbon chain length D reduces the number of carbon to carbon double bonds A B C D 10. Olestra is a calorie free fat made by reacting fatty acids with sucrose. The structure of a sucrose molecule can be represented as shown. ethanoic acid and propan-1-ol ethanoic acid and propan-2-ol propanoic acid and propan-1-ol propanoic acid and propan-2-ol 8. An ester is prepared from methanoic acid and ethanol. Which of the following is the full structural formula for the ester produced. How many fatty acid molecules can react with one molecule of sucrose? A B C D 3 5 8 11 11. The compound CH3CH2COO-Na+ is formed by reaction between sodium hydroxide and A B C D 2 propanoic acid propan-1-ol propene propanal Taylor High School Higher Chemistry 12. Aspirin is one of the most widely used pain relievers in the world. It has the structure: 15. Fats are formed by the condensation reaction between glycerol molecules and fatty acid molecules. In this reaction the mole ratio of glycerol molecules to fatty acid molecules is: A B C D Which two functional groups are present in an aspirin molecule? A B C D Aldehyde and ketone Carboxyl and ester Ester and aldehyde Hydroxyl and carboxyl CH3CH2CH2COOCH2CH3 The name of the ester is: propyl propanoate ethyl butanoate butyl ethanoate ethyl propanoate 14. Which of the following compound would react with sodium hydroxide solution to form a salt? A B C D 1:1 1:2 1:3 3:1 16. Which of the following reactions takes place during the “hardening” of vegetable oil? A B C 13. An ester has the following structural D formula: A B C D Unit 2 Section 7 CH3CHO CH3COOH CH3COCH3 CH3CH2OH 3 Addition Hydrolysis Dehydration Oxidation Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 17. The following triglyceride is found in some fats and oils. (a) The hydrolysis of the triglyceride produces an alcohol and long chain fatty acids. Name the alcohol produced by the hydrolysis of the triglyceride> 1 (b) What happens to triglyceride molecules in the conversion of oils to hardened fats? 1 18. Esters are important compounds which have many applications. (a) Some of the instructions outlining the laboratory preparation of an ester are shown below. 1. Mix 1 cm3 of the alkanol with 1 cm3 of the alkanoic acid in a test tube. 2. 3. 4. After 20 mins, pour the contents of the test tube into a beaker containing sodium hydrogen carbonate solution. 4 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 Add appropriate instructions for steps 2 and 3. 2 (b) The full structural formula for an ester is shown below. Give the systematic name of the alkanol used in making this ester. 1 (c) State a use of esters. 1 5 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 19. Two reaction of propanoic acid are shown. (a) Draw the full structural formula for ester X. 1 (b) Give a name for compound Y, which reacts with propanoic acid to form sodium propanoate. 1 20. Perfumes normally contain three groups of components called top note, the middle note and the end note. (a) The top note components of a perfume form vapours easily. Two compounds found in top note components are: (i) With reference to the structure of these compounds, why are they likely to have pleasant smells? 1 6 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 (ii) Describe a chemical test which would distinguish between these two compounds and give the result of the test. 1 (b) The middle note compounds form vapours less readily than the top note compounds. A typical compound of the middle note is: Due to the hydrogen bonding 2-phenylethanol forms a vapour less readily than p -cresyl acetate. In the box above, draw another molecule of 2-phenylethanol and use a dotted line to show where a hydrogen bond exists between the two molecules. 1 (c) The end note of a perfume has a long lasting odour which stays with the user. An example of an end note compound is: Draw the structure of the alcohol which would be formed by the reduction of civetone. 1 7 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 21. Biodiesel is a mixture of esters which can be made by heating rapeseed oil with methanol in the presence of a catalyst. (a) Name compound X. 1 (b) A typical diesel molecule obtained from crude oil has the molecular formula C16H34 (hexadecane). Other than the ester group, name a functional group present in biodiesel molecules which is not present in hexadecane. 1 (c) Vegetable oils like rapeseed oil are converted into fats for use in the food industry. What name is given to this process? 1 22. The structure of a molecule found in olive oil can be represented as shown. 8 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry 22. continued (a) Olive oil can be hardened using a nickel catalyst to produce a fat. (i) What type of catalyst is nickel in this reaction? Unit 2 Section 7 1 (ii) In what way does the structure of a fat molecule differ from that of an oil molecule? 1 (b) Olive oil can be hydrolysed using sodium hydroxide solution to produce sodium salts of fatty acids. (i) Name the other product of this reaction. 1 (ii) Give a commercial use for the sodium salts of fatty acids. 1 23. The structure of a fat molecule is shown below. (a) When the fat is hydrolysed, a fatty acid is obtained. Name the other product in this reaction. 1 (b) Oils are liquid at room temperature; fats are solid. Why do oils have lower melting points than fats? 1 9 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 24. An ester can be prepared by the following sequence of reactions. (a) (i) Draw a structural formula for compound A. 1 (ii) But-2-ene and compound A undergo the same type of reaction in step 2. Name this type of reaction. 1 10 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 (iii)Acidified potassium dichromate solution can be used to carry out Step 3. What colour change would be observed? (iv) Name compound B. 1 1 (b) (i) What evidence would show that an ester had been formed in Step 4? 1 (ii) Give one use for esters. 1 25. Ethyl pentanoate is an ester. It can be prepared in the lab as shown below. (a) (i) Why is a water bath used for heating? 1 (ii) What is the purpose of the wet paper towel? 1 (b) Draw a structural formula for ethyl pentanoate. 1 (c) on next page. 11 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 (c) Starting with a mass of 3.6 g of ethanol, and a slight excess of pentanoic acid, a student achieved a 70% yield of ethyl pentanoate (mass of 1 mole = 130g). Calculate the mass of ester obtained. Show your working clearly. 2 26. (a) Ethanol and propanoic acid can react to form an ester. (i) Draw the structural formula for this ester. 1 (ii) Draw a labelled diagram of the assembled apparatus that could be used to prepare this ester in the lab. 1 12 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 26. continued (iii) Due to hydrogen bonding, ethanol and propanoic acid are soluble in water whereas the ester produced is insoluble. In each of the boxes below, draw a molecule of water and use a dotted line to show where a hydrogen bond could exist between the organic molecule and the water molecule. 1 (b) Pyrolysis (thermal decomposition) of esters can produce two compounds, an alkene and an alkanoic acid, according to the following equation. (R and R’ represent alkyl groups) Draw a structural formula for the ester that would produce 2-methylbut-1-ene and methanoic acid on pyrolysis. 1 13 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 27. (a) Acidified potassium dichromate solution can be used to oxidise some alcohols to aldehydes and then to carboxylic acids, eg ethanol ethanal ethanoic acid (i) Name the type of alcohol that can be oxidised to an aldehyde. (ii) What colour change would be observed when acidified potassium dichromate solution is used to produce ethanoic acid from ethanal? 1 1 (b) Ethanol (GFM = 46 g) and ethanoic acid (GFM = 60 g) react to form the ester ethyl ethanoate (GFM = 88 g). ethanol + ethanoic acid ethyl ethanoate + water (i) Describe how the reaction mixture would be heated in the lab formation of the ester. 1 (ii) Use the above information to calculate the percentage yield of ethyl ethanoate if 5.0 g of ethanol produced 5.8 g of ethyl ethanoate on reaction with excess ethanoic acid. Show your working clearly. 2 14 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 28. Glycerol trinitrate is an explosive with the structure shown. (a) Glycerol trinitrate is produced from glycerol. (i) Draw the structural formula for glycerol. 1 (ii) Name the group of naturally occurring esters that can be hydrolysed to obtain glycerol. 1 (b) When exploded, glycerol trinitrate decomposes to give nitrogen, water, carbon dioxide and oxygen. Balance the equation for this reaction. C3H5N3O9(l) N2(g) + H2O(g) + CO2(g) 15 + O2(g) 1 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 29. When a mixture of solid sodium hydroxide and solid sodium ethanoate is heated, methane gas and solid sodium carbonate are produced. NaOH (s) + CH3COONa (s) CH4 (g) + Na2CO3 (s) (a) Draw a diagram of an apparatus which could be used for this reaction showing how the methane gas can be collected and its volume measured. 2 (b) Name the gas produced when sodium propanoate is heated with solid sodium hydroxide. 1 30. One of the chemicals released in a bee sting is an ester that has the structure shown. This ester can be produced by the reaction of an alcohol with an alkanoic acid. (a) Name this acid. 1 16 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 30. continued (b) The ester can be prepared in the lab by heating a mixture of the reactants with a catalyst. (i) Name the catalyst used in the reaction. 1 (ii) What improvement could be made to the experiment set-up shown in the diagram? 1 (c) If there is a yield of 65%, calculate the mass of ester produced, in grams, when 4.0 g of the alcohol reacts with a slight excess of the acid. GFM of alcohol = 88g GFM of ester = 130g. Show your working clearly. 2 17 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 31. A typical triglyceride found in olive oil is shown below. (a) To which family of organic compounds do triglycerides belong? 1 (b) Olive oil can be hardened for use in margarines. What happens to the triglyceride molecules during the hardening of olive oil? (c) Give one reason why oils can be a useful part of a balanced diet. 1 32. Alkanols can be oxidised to alkanoic acids (a) (i) Why can step 1 be described as an oxidation reaction? 1 (ii) Acidified potassium dichromate solution can be used to oxidise propanal in step 2. What colour change would be observed? 1 18 Taylor High School Higher Chemistry Unit 2 Section 7 32. continued (b) Propan-1-ol and propanoic acid react to form an ester. The mixture of excess reactants and product is poured onto sodium hydrogencarbonate solution. (i) What evidence would show that an ester is formed? 1 (ii) Draw the structure of this ester. 1 19