Unit 16/Chapter 11 Study Guide 1.
advertisement

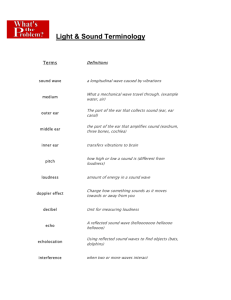
Name: _____________________________________________ Date: _________________ Period: _________ Unit 16/Chapter 11 Study Guide 1. What is the frequency range of human hearing? ______ Hz to ________________ Hz 2. The function of the cochlea is to convert sound waves into _______________________________________. 3. The unit used to measure loudness is ______________________. 4. The unit used to measure frequency is _______________________. 5. The speed of sound depends on the _____________________________. 6. Sound travels in a __________________________ wave. 7. Many reflections of sound (like in concert halls) causes _____________________________________. 8. As the intensity of sound increases, the _____________________________ increases. 9. As amplitude increases, ___________________________ increases. 10. What is the function of the outer ear? ________________________________________________________ 11. The length of a vibrating tube determines the ________________ produced. 12. Most musical instruments have a __________________________________ to amplify sound. 13. ________________________________ is the study of sound. 14. The way your brain interprets intensity of sound is ________________________________. 15. As frequency increases, __________________ increases. 16. A system that uses reflection of sound waves underwater is ____________________________. 17. Frequencies below 20 Hz are called _____________________________ or ___________________; frequencies above 20,000 Hz are called ______________________________. 18. Sound intensity above _____________ dB can cause permanent hearing damage. 19. Bats use _____________________________ to navigate and find prey. 20. The three bones in the middle ear are the ____________________________________________________. 21. The quality of sound is ___________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________________ 22. List the medical uses of sound waves: _______________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 23. Beats are caused by _____________________________________________________________________. 24. ________________________ instruments are played by being hit in some way; ______________________ instruments are played by plucking, striking, or drawing a bow across strings; __________________ and ______________________________ instruments are played by blowing air into a tube. 25. How would you reduce reverberation? ______________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________________________ 26. A combination of sound with a distinct pitch and specific pattern is ________________________. 27. Sound travels faster in a medium with a _____________________ temperature. 28. Sound travels fastest in ____________________________. 29. For the ___________________________________________________ to occur, either the source or the listener must be moving. 30. Label the parts: anvil outer ear cochlea stirrup ear canal eardrum hammer visible ear **higher energy = higher amplitude = higher intensity = louder sound **high pitch = sound waves compressed = decreased wavelength low pitch = sound waves stretch = increased wavelength inner ear middle ear Answers 1. 20 to 20,000 2. Nerve impulses 3. decibel (dB) 4. hertz (Hz) 5. medium 6. compressional 7. reverberation 8. loudness 9. energy 10. funnel or gather sound waves 11. pitch 12. resonator 13. acoustics 14. loudness 15. pitch 16. sonar 17. infrasonic, subsonic, ultrasonic 18. 120 19. echolocation 20. hammer, anvil, stirrup 21. the difference between sounds of the same pitch and loudness 22. pregnancy, certain types of heart disease, cancer, and kidney stones 23. different frequencies interfering 24. percussion; strings; brass and woodwinds 25. use absorbent materials such as carpets and tapestries 26. music 27. higher 28. solids 29. Doppler effect 30. Top: outer ear, middle ear, inner ear middle: hammer, anvil bottom: visible ear, ear canal, ear drum, stirrup, cochlea