Sound
advertisement

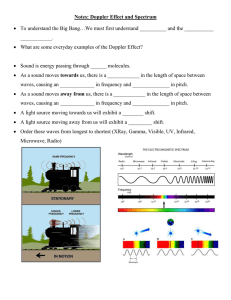
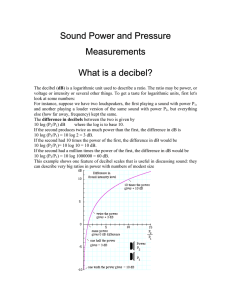
Sound Properties of Sound Sound waves are longitudinal! Sound can be explained by understanding: ◦ Speed ◦ Intensity and loudness ◦ Frequency and pitch Most people hear sound between the frequency of 20Hz and 20,000Hz. Anatomy of Sound External Ear: ◦ Focus the sound into the ear canal. Middle Ear: ◦ Amplifies the vibrations. Inner Ear: ◦ Senses the vibrations and signals the brain. Anatomy of Sound The Middle Ear is made up of 3 tiny bones known as the hammer (malleus), anvil (incus) and stirrup (stapes). A. Speed The speed of sound (in dry air at 20°C) is 342m/s. The speed of sound varies with the temperature and phase of matter it is traveling through. ◦ Most fast is solids ◦ slowest in gases B. Intensity and Loudness Intensity refers to the rate at which sound waves travel in a given area. ◦ Depends upon the amplitude of the sound waves and the distance from the source. Loudness is a subjective term. It is the physical response to sound intensity. Depends upon a person’s health, age, etc. B. Intensity and Loudness Intensity is measured in Bels (decibels, dB). The scale is more logarithmic ◦ 0dB can barely be heard. ◦ 20dB is 100 times more power than 0dB. C. Frequency and Pitch Sound frequency depends upon how fast the source of the sound is vibrating. ◦ Longer waves produce lower sounds frequency ◦ Shorter waves produce high frequency Pitch is a person’s perception of sounds frequency. (Subjective) ◦ High pitch = high frequency ◦ Low pitch = low frequency Ultrasound Ultrasound waves are used in medicine and sonar techniques. Ultrasound can be used to construct images of internal structures. D. The Doppler Effect The Doppler Effect explains how the pitch of a sound can change as it passes a person or point. It is the change in sounds frequency caused by motion of the sounds source, motion of the listener, or both. As a sound source approaches the frequency increases. As the source moves away the frequency drops.