Chapter 9
advertisement

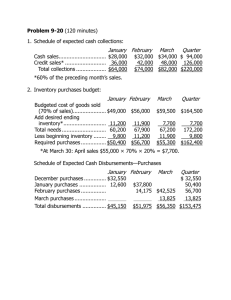
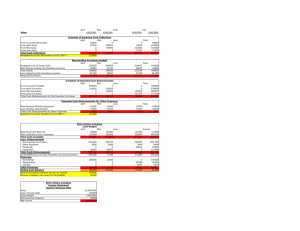
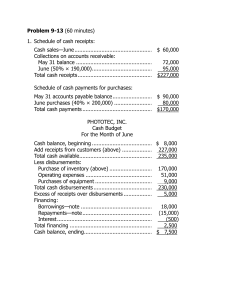
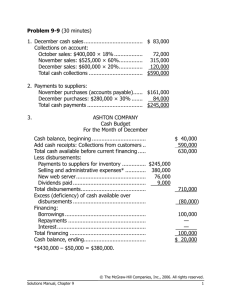
Problem 9-14 (45 minutes) 1. Schedule of expected cash collections: Month May April June From accounts receivable ..................... $141,000 $ 7,200 From April sales: 20% _ 200,000.............. 40,000 75% _ 200,000.............. 150,000 4% _ 200,000 ............... $ 8,000 From May sales: 20% _ 300,000.............. 60,000 75% _ 300,000.............. 225,000 From June sales: 20% _ 250,000.............. 50,000 Total cash collections ........ $181,000 $217,200 $283,000 Quarter $148,200 40,000 150,000 8,000 60,000 225,000 50,000 $681,200 Problem 9-14 (continued) 2. Cash budget: Cash balance, beginning.................... Add receipts: Collections from customers ................ Total available ................ Less disbursements: Merchandise purchases................. Payroll ........................ Lease payments........... Advertising.................. Equipment purchases ... Total disbursements........ Excess (deficiency) of receipts over disbursements ............. Financing: Borrowings.................. Repayments ................ Interest ...................... Total financing ............... Cash balance, ending April Month May June Quarter $ 26,000 $ 27,000 $ 20,200 $ 26,000 181,000 207,000 217,200 244,200 283,000 303,200 681,200 707,200 108,000 9,000 15,000 70,000 8,000 210,000 120,000 9,000 15,000 80,000 — 224,000 180,000 8,000 15,000 60,000 — 263,000 408,000 26,000 45,000 210,000 8,000 697,000 20,200 40,200 10,200 (3,000) 30,000 — — 30,000 $ 27,000 — — — (30,000) — (1,200) — (31,200) $ 20,200 $ 9,000 30,000 (30,000) (1,200) (1,200) $ 9,000 3. If the company needs a minimum cash balance of $20,000 to start each month, the loan cannot be repaid in full by June 30. If the loan is repaid in full, the cash balance will drop to only $9,000 on June 30, as shown above. Some portion of the loan balance will have to be carried over to July, at which time the cash inflow should be sufficient to complete repayment. Problem 9-16 (60 minutes) 1. The sales budget for the third quarter: July Aug. Sept. Quarter Budgeted sales (pairs) ...... 6,000 7,000 5,000 18,000 Selling price per pair ......... _ $50 _ $50 _ $50 _ $50 Total budgeted sales......... $300,000 $350,000 $250,000 $900,000 The schedule of expected cash collections from sales: July Aug. Sept. Quarter Accounts receivable, beginning balance.......... $130,000 $130,000 July sales: $300,000 _ 40%, 50% ... 120,000 $150,000 270,000 August sales: $350,000 _ 40%, 50% ... 140,000 $175,000 315,000 September sales: $250,000 _ 40%............ 100,000 100,000 Total cash collections ........ $250,000 $290,000 $275,000 $815,000 2. The production budget for July through October: Budgeted sales (pairs) ....................... Add desired ending inventory ............. Total needs....................................... Less beginning inventory.................... Required production (pairs) ................ July Aug. Sept. Oct. 6,000 7,000 5,000 4,000 700 500 400 300 6,700 7,500 5,400 4,300 600 700 500 400 6,100 6,800 4,900 3,900 Problem 9-16 (continued) 3. The materials purchases budget for the third quarter: Required production—pairs (above)............................. Raw materials needs per pair .................................. Production needs (kgs.) ........ Add desired ending inventory .......................... Total needs.......................... Less beginning inventory....... Raw materials to be purchased ......................... Cost of raw materials to be purchased at $2.50 per kg. ................................... July Aug. Sept. Quarter 6,100 6,800 4,900 17,800 _ 2kgs. 12,200 _ 2kgs. 13,600 _ 2kgs. 9,800 _ 2kgs. 35,600 2,720 14,920 2,440 1,960 15,560 2,720 1,560 * 11,360 1,960 1,560 37,160 2,440 12,480 12,840 9,400 34,720 $31,200 $32,100 $23,500 $86,800 *3,900 pairs (October) _ 2 kgs. per pair= 7,800 kgs.; 7,800 kgs. _ 20% = 1,560 kgs. The schedule of expected cash disbursements: July Aug. Sept. Quarter Accounts payable, beginning balance................................... $11,400 $11,400 July purchases: $31,200 _ 60%, 40% ............... 18,720 $12,480 31,200 August purchases: $32,100 _ 60%, 40% ............... 19,260 $12,840 32,100 September purchases: $23,500 _ 60%........................ 14,100 14,100 Total cash disbursements ............ $30,120 $31,740 $26,940 $88,800 Problem 9-19 (120 minutes) 1. Schedule of expected cash collections: April May June Total Cash sales ............................... $14,000 $17,000 $18,000 $ 49,000 Credit sales.............................. 48,000 56,000 68,000 172,000 Total collections........................ $62,000 $73,000 $86,000 $221,000 2. a. Inventory purchases budget: Budgeted cost of goods sold...... Add desired ending inventory* .. Total needs.............................. Less beginning inventory........... Required purchases .................. April May June Total $42,000 $51,000 $54,000 $147,000 15,300 16,200 9,000 9,000 57,300 67,200 63,000 156,000 12,600 15,300 16,200 12,600 $44,700 $51,900 $46,800 $143,400 * At April 30: $51,000 _ 30% = $15,300. At June 30: $50,000 July sales _ 60% _ 30% = $9,000. b. Schedule of cash disbursements for purchases: April May June Total For March purchases ................ $18,300 $18,300 For April purchases................... 22,350 $22,350 44,700 For May purchases ................... 25,950 $25,950 51,900 For June purchases .................. 23,400 23,400 Total cash disbursements .......... $40,650 $48,300 $49,350 $138,300 Problem 9-19 (continued) 3. Schedule of cash disbursements for operating expenses: April May June Total $ 7,500 $ 7,500 $ 7,500 $22,500 4,200 5,100 5,400 14,700 6,000 6,000 6,000 18,000 2,800 3,400 3,600 9,800 Salaries and wages....................... Shipping...................................... Advertising .................................. Other expenses............................ Total cash disbursements for operating expenses.................... $20,500 $22,000 $22,500 $65,000 4. Cash budget: April May Cash balance, beginning ............... $ 9,000 $ 8,350 Add cash collections ..................... 62,000 73,000 Total cash available.................... 71,000 81,350 Less disbursements: For inventory purchases ............. 40,650 48,300 For operating expenses .............. 20,500 22,000 For equipment purchases ........... 11,500 3,000 For dividends ............................ 0 0 Total disbursements...................... 72,650 73,300 Excess (deficiency) of cash............ (1,650) 8,050 Financing: Borrowings ............................... 10,000 0 Repayments .............................. 0 0 Interest* .................................. 0 0 Total financing ............................. 10,000 0 Cash balance, ending.................... $ 8,350 $ 8,050 * $10,000 _ 12% _ 3/12 = $300. June Total $ 8,050 $ 9,000 86,000 221,000 94,050 230,000 49,350 138,300 22,500 65,000 0 14,500 3,500 3,500 75,350 221,300 18,700 8,700 0 10,000 (10,000) (10,000) (300) (300) (10,300) (300) $ 8,400 $ 8,400 Problem 9-19 (continued) 5. Income Statement: NORDIC COMPANY Income Statement For the Quarter Ended June 30 Sales........................................................ Less cost of goods sold: Beginning inventory (given) ..................... $ 12,600 Add purchases (Part 2) ............................ 143,400 Goods available for sale ........................... 156,000 Ending inventory (Part 2)......................... 9,000 Gross margin ............................................ Less operating expenses: Salaries and wages (Part 3) ..................... 22,500 Shipping (Part 3) .................................... 14,700 Advertising (Part 3) ................................. 18,000 Depreciation........................................... 6,000 Other expenses (Part 3) .......................... 9,800 Net operating income ................................ Less interest expense (Part 4)..................... Net income ............................................... $245,000 147,000 98,000 71,000 27,000 300 $ 26,700 Problem 9-19 (continued) 6. Balance sheet: NORDIC COMPANY Balance Sheet June 30 Assets Current assets: Cash (Part 4)................................................................. $ 8,400 Accounts receivable (80% _ $90,000) .............................. 72,000 Inventory (Part 2) .......................................................... 9,000 Total current assets .......................................................... 89,400 Buildings and equipment, net ($214,100 + $14,500 – $6,000) ...................................... 222,600 Total assets ..................................................................... $312,000 Liabilities and Equity Current liabilities: Accounts payable (Part 2: 50% _ $46,800)...... Shareholders’ equity: Capital stock................................................. $190,000 Retained earnings* ....................................... 98,600 Total liabilities and equity ................................. * Retained earnings, beginning..................... Add net income........................................ Total ....................................................... Less dividends ......................................... Retained earnings, ending ......................... $ 75,400 26,700 102,100 3,500 $ 98,600 $ 23,400 288,600 $312,000