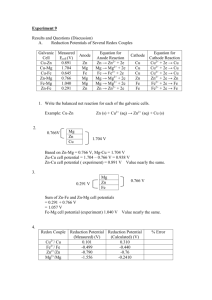
2010 Electrochemistry AP still needs 1pic
advertisement
AP Chem - Electrochemistry Princeton Review Questions 1-3 (A) MnO4(B) H+ (C) H2 (D) Na (E) Na+ 1. This is a very strong reducing agent. 2. By definition, the reduction potential for this species is equal to zero. 3. This is a very strong oxidizing agent. Questions 4-7 The choices listed below refer to n, the number of moles of electrons transferred in a reaction. (A) n = 4 (B) n = 3 (C) n = 2 (D) n = 1 (E) n = 0 4. 2 Fe3+ + Mg 2 Fe2+ + Mg2+ 5. F2 + 2 Br- 2 F- + Br2 6. NH3 + H2O NH4+ + OH7. MnO4- + Cr + 2 H2O MnO2 + Cr3+ + 4OHCr2O72- + 6 I- + 14 H+ 2 Cr3+ + 3 I2 + 7 H2O 8. Which of the following statements about the reaction given above is NOT true? a. The oxidation number of chromium changes from +6 to +3 b. The oxidation number of iodine changes from -1 to 0 c. The oxidation number of hydrogen changes from +1 to 0 d. The oxidation number of oxygen remains the same e. The reaction takes place in acidic solution 1 9. Al3+ + 3e- Al(s) Cr3+ + 3e- Cr(s) E0 = -1.66 V E0 = -0.74 V The standard reduction potentials for two half reactions are shown above. Which of the statements listed below will be true for the following reaction taking place under standard conditions? a. b. c. d. e. E0 = E0 = E0 = E0 = E0 = 2.40 V and the reaction is not spontaneous 0.92 V and the reaction is spontaneous -0.92 V and the reaction is not spontaneous -0.92 V and the reaction is spontaneous -2.40 V and the reaction is not spontaneous 10. In which of the following molecules does hydrogen have an oxidation state of -1? a. H2O b. NH3 c. CaH2 d. CH4 e. H2 11. Oxygen takes the oxidation state -1 in hydrogen peroxide, H2O2. The equation for the decomposition of H2O2 is shown below. 2 H2O2 2 H2O + O2 Which of the following statements about the reaction above is true? a. b. c. d. e. Oxygen is reduced and hydrogen is oxidized Oxygen is oxidized and hydrogen is reduced Oxygen is both oxidized and reduced Hydrogen is both oxidized and reduced Neither oxygen nor hydrogen changes oxidation state 2 12. When solid iron is brought into contact with water and oxygen, it undergoes the following half-reaction: Fe(s) Fe2+(aq) + 2eThis half reaction is instrumental in the corrosion of iron. When iron is coated with solid zinc, the half-reaction above is impeded, even if the zinc coating is incomplete. This is most likely because a. b. c. d. e. 13. Zn(s) is more easily reduced than Fe(s) Zn(s) is more easily oxidized than Fe(s) Zn2+(aq) is more easily reduced than Fe(s) Zn2+(aq) is more easily oxidized than Fe(s) Zn(s) is more easily reduced than Fe2+ 2 H2O(l) + 2e- H2(g) + 2 OH-(aq) E0 = -0.83 V Na+(aq) + e- Na(s) E0 = -2.71 V Cl2 + 2e- 2Cl- E0 = 1.36 V Talk About Based on the reduction potentials given above, which of the following would be expected to occur when electrodes connected to the terminals of a 3.0 V battery are immersed in a solution of sodium chloride in water? a. solid sodium will appear at the anode and chlorine gas will appear at the cathode b. chlorine gas will appear at the anode and solid sodium will appear at the cathode c. hydrogen gas will appear at the cathode and solid sodium will appear at the anode d. hydrogen gas will appear at the anode and chlorine gas will appear at the cathode e. chlorine gas will appear at the anode and hydrogen gas will appear at the cathode 3 14. Cu2+ + 2e- Cu E0 = +0.3 V Fe2+ + 2e- Fe E0 = -0.4 V Based on the reduction potentials given above, what is the reaction potential for the following reaction? Fe2+ + Cu Fe + Cu2+ a. b. c. d. e. 15. -0.7 V -0.1 V +0.1 V +0.7 V +1.4 V Cu2+ + 2e- Cu E0 = +0.3 V Zn2+ + 2e- Zn E0 = -0.8 V Mn2+ + 2e- Mn E0 = -1.2 V Based on the reduction potentials given above, which of the following reactions will occur spontaneously? a. b. c. d. e. Mn2+ + Cu Mn + Cu2+ Mn2+ + Zn Mn + Zn2+ Zn2+ + Cu Zn + Cu2+ Zn2+ + Mn Zn + Mn2+ Cu2+ + Zn2+ Cu + Zn 16. Which of the following is true of the oxidation-reduction reaction that takes place in a galvanic cell under standard conditions? a. b. c. d. e. G0 and E0 are positive and keq is greater than 1 G0 is negative, E0 is positive, and keq is greater than 1 G0 is positive, E0 is negative, and keq is less than 1 G0 and E0 are negative and keq is greater than 1 G0 and E0 are negative and keq is less than 1 4 17. Ni(s) + Cu2+(aq) Ni2+(aq) + Cu(s) The oxidation-reduction reaction above takes place in a galvanic cell. If the initial concentration of Ni2+ ions is increased while the initial concentration of Cu2+ ions remains constant, what will be the effect on the reaction quotient Q and the cell potential, E? a. b. c. d. e. Q and E will increase Q and E will decrease Q will increase and E will decrease Q will decrease and E will increase Q and E will not change 18. When solid copper shavings are placed in a solution of dilute HNO3, Cu2+ ions appear and NO gas bubbles from. Which of the following has occurred? a. b. c. d. e. Cu has been oxidized by H+ Cu has been oxidized by NO3Cu has been reduced by NO3NO3- has been oxidized by H+ NO3- had been reduced by H+ 19. Molten AlCl3 is electrolyzed with a constant current of 5.00 amperes over a period of 600. seconds. Which of the following expressions is equal to the maximum mass of Al(s) that plates out? (1 faraday = 96,500 coulombs) a. (600)(5.00) (96,500)(3)(27.0) b. (600)(5.00)(3)(27.0) (96,500) c. (600)(5.00)(27.0) (96,500)(3) grams d. (96,500)(3)(27.0) (600)(5.00) grams e. (96,500)(3) (600)(5.00)(27.0) grams grams grams 5 20. The half reaction at the anode of a galvanic cell is as follows: Zn(s) Zn2+ + 2eWhat is the maximum charge, in coulombs, that can be delivered by a cell with an anode composed of 6.54 grams of zinc? (1 faraday = 96,500 coulombs) a. b. c. d. e. 4820 coulombs 9,650 coulombs 19,300 coulombs 38,600 coulombs 48,200 coulombs Princeton Review Answers 1. D 2. B 3. A 4. C 5. C 6. E 7. B 8. C 9. B 10. C 11. C 12. B 13. E 14. A 15. D 16. B 17. C 18. B 19. C 20. C Barron’s 1. Balance the following half-reaction in acid solution: (remember, ½ reactions have e-) NO3- NH4+ When balanced with the smallest whole-number coefficients possible, the sum of all the coefficients is a. 13 b. 26 c. 15 d. 23 e. 21 6 2. For the reduction of MnO4- to Mn+2, the correct form of the Nernst equation is a. E = E0 + 0.0591 [ Mn 2+ ] log − + 8 3 [ MnO4 ][ H ] b. E = E0 - 0.0591 [ Mn 2+ ] log [ MnO − ][ H + ]8 5 4 c. E0 = E - 0.0591 [ Mn 2+ ] log − + 8 5 [ MnO4 ][ H ] d. E = E0 + [ MnO4 − ][ H + ]8 0.0591 log 5 [ Mn 2+ ] e. E = E0 + [ Mn 2+ ] 0.0591 log − + 8 5 [ MnO4 ][ H ] 3. The following reactions are known to occur spontaneously: Cu + 2Ag+ Cu2+ + 2Ag Zn + 2Ag+ Zn2+ + 2Ag Zn + Cu 2+ Zn2+ + Cu The activity series for the three elements as reducing agents is a. Cu > Ag > Zn b. Zn > Cu > Ag c. Ag > Cu > Zn d. Ag > Zn > Cu e. Zn > Ag > Cu 7 4. The standard reduction potential for PbO2 Pb2+ is +1.46 V, and the standard reduction potential for Fe3+ Fe2+ is +0.77 V. What is the standard cell voltage for the reaction 4 H+ + PbO2 + 2 Fe2+ 2 Fe3+ + Pb2+ + 2 H2O a. b. c. d. e. -0.08 V +0.69 V +2.33 V -0.69 V -2.33 V 5. Which of the following compounds includes an element with an oxidation number of +5 a. ClO4b. MnO4c. NO2d. SO32e. NO36. Which of the following metals does NOT react with water to produce hydrogen? a. Zn b. Li c. Ca d. Na e. Rb 7. In the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of CuNO3, which of the following is expected to occur? a. formation of O2 at the anode b. Formation of H2 at the cathode Talk c. Deposition of copper metal on the anode About d. Formation of hydroxide ions at the cathode e. Formation of H+ at the cathode 8 8. Sodium metal cannot be electrolyzed from an aqueous solution of Na2SO4 solution because a. the voltage needed is too high for any available instrument to achieve b. water is reduced to O2 before Na+ Talk c. Na+ has a high over-potential that keeps it from being About reduced d. H+ has a more favorable reduction potential than Na+ e. Na+ does electrolyze, but it immediately reacts with water again 9. Which of the following elements has the largest number of possible oxidation states? a. Fe b. Cl c. Ca d. Mn e. Na 10. For the reaction 2 I- + Cl2 2 Cl- + I2 The standard cell voltage is E0cell = 0.82 V. What is the equilibrium constant for this reaction at 45 oC? (R = 8.314 V C mol-1 K-1, and F = 96,485 C mol-1) a. b. c. d. e. 9.8 x 1025 1.0 x 10-26 1.6 x 105 6.3 x 10-6 2.27 11. Which of the following E0cell values represents a nonspontaneous reaction that produces the greatest amount of product, assuming the same number of electrons is transferred in each reaction? A. B. C. D. E. +2.31 V +0.23 V -0.12 V -1.68 V -1.14 V 9 12. A metal is electrolyzed from aqueous solution by using an electrical current of 1.23 A for 2½ h, and 3.37 g of metal is deposited. In a separate experiment the number of electrons used for the reduction of the metal is 2. What is the metal? a. b. c. d. e. Al Ni Sn Mg Au 13. A galvanic cell is set up under nonstandard state conditions, and Ecell is measured as -0.16 V. Which of the following is true about the system at standard conditions? a. The galvanic cell is set up incorrectly because of the negative value of E0cell b. If the contents of the two cells are mixed, the reaction will proceed in the forward reaction c. The reaction is definitely nonspontaneous d. If the contents of the two cells are mixed, the reaction will proceed in the reverse direction e. The reaction is definitely spontaneous 14. A galvanic cell is constructed; and when the temperature of the cell is increased from 20 oC to 30 oC, the cell voltage changes by a factor of 1.034. Which of the following conclusions may be drawn from this observation? a. ∆G0 must be positive since the reaction is not spontaneous b. The increase is due to the temperature term in ∆G0 = -RT lnK. c. The information indicates that ∆S0 for this reaction must be negative d. The reaction is spontaneous because ∆G0 is negative 15. Which of the following is NOT commonly produced by electrolysis? a. NaOCl (bleach) b. Al Talk c. Fe About d. NaOH e. H2 10 16. Which of the following compounds includes an element that has the same oxidation number as the chlorine in sodium chlorate, NaClO3? a. K3Fe(CN)6 b. KMnO4 c. Al(NO3)3 d. (NH4)2SO4 e. KClO4 17. With a current of 1.25 A, how many minutes will be required to deposit 2.00 g of copper on a platinum electrode from a copper (II) nitrate solution? (Faraday’s constant = 96,485 C mol-1) a. 4859 b. 81.0 c. 40.5 d. 1.35 e. 2430 18. What is the minimum number of electrons needed to balance the following half-reaction with whole number coefficients? IO3- I2 a. b. c. d. e. 1 2 5 10 12 19. Which of the following pairs of constants are NOT mathematically related to each other? a. equilibrium constant and Gibbs free energy b. rate constant and activation energy c. standard voltage and equilibrium constant d. standard cell voltage and rate constant e. Gibbs free energy and standard cell voltage 20. Which of the following statements is FALSE? a. Reduction involves a gain of electrons b. Batteries are galvanic cells c. A spontaneous reaction always has a positive E0cell d. Electrolysis reactions always produce a gas at at least one electrode e. Galvanic cells can be used to determine equilibrium constants 11 Barron’s Answers 1. D 2. B 3. B 4. B 5. E 6. A 7. A 8. D 9. B 10. A 11. C 12. B 13. D 14. B 15. C 16. C 17. B 18. D 19. D 20. D Kaplan 12. Consider the cell Cd(s) I Cd2+ (1.0 M) II Cu2+ (1.0 M) I Cu. In order to make this cell with a more positive voltage using the same substance, you will need to: a. increase both the [Cd2+] and [Cu2+] to 2.00 M b. increase only the [Cd2+] to 2.00 M c. decrease both the [Cd2+] and [Cu2+] to 0.100 M d. decrease only the [Cd2+] to 0.100 M e. decrease only the [Cu2+] to 0.100 M 13. The oxidation number of the nitrogen in the nitrate ion, NO3-, is: a. +1 b. +2 c. +3 d. +4 e. +5 15.The voltage of the cell Zn(s) I Zn2+ (1.0 M) Half-reaction Zn2+(aq) + 2e- Zn(s) Pb2+(aq) + 2e- Pb(s) a. b. c. d. e. II Pb2+ (1.0 M) I Pb(s) is: Reduction Potential, E0 -0.763 V -0.126 V 0.889 V 0.637 V 0.511 V -0.637 V -0.889 V 12 16.Which will reduce Ag+ to Ag but not Ni2+ to Ni? Half-reaction Mg2+(aq) Al3+(aq) Zn2+(aq) Cd2+(aq) Ni2+(aq) Pb2+(aq) Ag+(aq) a. b. c. d. e. + + + + + + + 2e- Mg(s) 3e- Al(s) 2e- Zn(s) 2e- Cd(s) 2e- Ni(s) 2e- Pb(s) e- Ag(s) Reduction Potential, E0 -2.363 V -1.662 V -0.763 V -0.410 V -0.230 V -0.126 V +0.799 V Al Cd Mg Pb Zn 17.If all species are in their standard states, which is the strongest oxidizing agent? Half-reaction Mn2+(aq) + 2e- Mn(s) Zn2+(aq) + 2e- Zn(s) Fe2+(aq) + 2e- Fe(s) Co2+(aq) + 2e- Co(s) Br2(aq) + 2e- 2 Br- (s) a. b. c. d. e. Reduction Potential, E0 -1.180 V -0.763 V -0.440 V -0.280 V +1.087 V BrCo2+ Fe2+ Mn2+ Zn2+ 18.For the net cell potential of the cell Zn(s) I Zn2+ II Cd2+ I Cd(s) is 0.360 volts. What is the standard free-energy change, ∆G0, for this reaction in kJ at 25 oC? a. b. c. d. e. -225 -34.7 -69.5 69.5 113 13 19.For the reaction between permanganate ion and oxalate ion in basic solution, the unbalanced equation is: 2 MnO4- + 3C2O42- 2 MnO2 + 6CO32Which is true regarding the number of OH- ions when the equation is balanced with smallest, whole-number coefficients? a. b. c. d. e. 0 2 on the right 2 on the left 4 on the right 4 on the left Talk About 20.The pair of vertical lines in the standard cell notation represents which connection between the anode and the cathode? a. b. c. d. e. wire voltmeter salt bridge space between the beakers separation between solution and electrodes Kaplan Answers 12. D 13. E 14. A 15. B 16. D 17. B 18. C 19. E 20. C Petersons 1. Which of the following will be the best oxidizing agent? a. b. c. d. e. Cl2 Fe Na Na+ F- 14 2. A piece of copper metal is placed into solutions containing each of the following three cations. Which ion will be reduced by the copper metal? I. Sn2+ II. Zn2+ III. Ag+ a. b. c. d. e. I only II only III only I and II only I, II and III 3. When molten CaCl2 is electrolyzed, the calcium metal collects at the __________ charged electrode, which is called the _________ and the chlorine is given off at the ________ charged electrode, which is known as the _________. a. b. c. d. e. positively, anode, negatively, cathode positively, cathode, negatively, anode negatively, anode, positively, cathode negatively, cathode, positively, anode positively, electrolyte, negatively, emf 4. If 0.500 A of current is applied for 1.50 h to an electrolytic cell containing molten lithium chloride, how many grams of lithium would be deposited on the cathode? a. 0.388 g b. 0.194 g c. 0.097 g d. 0.050 g e. 5.4 x 10-5 g 5. The reduction of 3.00 moles of Ca2+ to Ca would require how many coulombs? a. b. c. d. e. 6.22 x 10-5 C 3.22 x 104 C 1.61 x 104 C 2.90 x 105 C 5.79 x 105 C 15 6. A voltaic cell is created with one half-cell consisting of a copper electrode immersed in 1.0 M CuSO4 solution and the other half cell consisting of a lead electrode immersed in a 1.0 M Pb(NO3)2 solution. Each half-cell is maintained at 25 oC. What is the cell potential in volts? a. b. c. d. e. 0.47 V 0.21 V -0.21 V -0.47 V 2.50 V 7. For the reaction shown below, what is the equilibrium constant at 25 oC? Ag+(aq) + Fe2+(aq) Ag(s) + Fe3+(aq) a. b. c. d. e. 1.0 1.6 3.2 6.4 10.0 8. If a current of 15.0 A is applied to a solution of Cr3+ ions, how long will it take to plate out 1.86 g of chromium metal? a. b. c. d. e. 3.83 minutes 5.7 minutes 11.5 minutes 35.0 minutes 690 minutes 9. A voltaic cell is set up with two half-cells. In the first half-cell, a silver electrode is placed in an aqueous solution containing Ag+ ions. In the second half-cell, a nickel electrode is placed in an aqueous solution containing Ni2+ ions. The silver electrode is the _________ and has a ________ charge. a. b. c. d. e. cathode, positive cathode, negative anode, positive anode, negative salt bridge, positive and negative 16 10. A voltaic cell contains one half-cell with a zinc electrode in a Zn2+(aq) solution and a copper electrode in a Cu2+(aq) solution. At standard condition, E0 = 1.10 V. Which condition below would cause the cell potential to be greater than 1.10 V? a. b. c. d. e. 1.0 M Zn2+(aq), 1.0 M Cu2+(aq) 5.0 M Zn2+(aq), 5.0 M Cu2+(aq) 5.0 M Zn2+(aq), 1.0 M Cu2+(aq) 0.5 M Zn2+(aq), 0.5 M Cu2+(aq) 0.1 M Zn2+(aq), 1.0 M Cu2+(aq) 11. What is the standard free energy change (∆G0) for the reaction shown below? Fe3+(aq) + Ag(s) Fe2+(aq) + Ag+(aq) a. b. c. d. e. -2.5 kJ 2.9 kJ 8.7 kJ 10.0 kJ 29 kJ 12. An electrolytic cell contains molten CuBr2. What is the minimum voltage that must be applied to begin electrolysis? a. b. c. d. e. 0.17 V 0.34 V 0.73 V 1.07 V 1.41 V Peterson’s Answers 1. A 2. C 3. D 4. B 5. E 6. A 7. C 8. C 9. A 10. E 11. B 12. C 17 Cliff’s 1. What mass of copper would be produced by the reduction of the Cu2+ (aq) ion passing 96.487 amperes of current through a solution of copper (II) chloride for 100.0 minutes? (1 Faraday = 96,487 coulombs) a. b. c. d. e. 95.325 190.65 g 285.975 381.30 g Cannot be determined from the information provided 2. Find E0 for a cell composed of silver and gold electrodes in 1 molar solutions of their respective ions: E0red Ag = +0.80 V; E0red Au = +1.50 V a. b. c. d. e. -0.90 V 0V 0.90 V 0.70 V 2.30 V 3. .... FeCl2 + ….. KMnO4 + .... HCl .... FeCl3 + …. KCl …. MnCl2 + …. H2O When the equation for this reaction is balanced with the lowest whole number coefficients, the coefficient for H2O is a. b. c. d. e. 1 2 3 4 5 18 4. Given the following notation for an electrochemical cell: Pt(s) I H2(g) I H+(aq) II Ag+(aq) I Ag(s) Which of the following represents the overall balanced (net) cell reaction? a. b. c. d. e. H2(g) + Ag+(aq) 2 H+(aq) + Ag(s) H2(g) + 2Ag+(aq) 2 H+(aq) + 2Ag(s) H2(g) + Ag(s) H+(aq) + Ag+(aq) Ag(s) + H+(aq) Ag+(aq) + H2(g) 2 H+(aq) + Ag(s) H2(g) + Ag+(aq) 5. Given the following information, which of the statements is true? Cu2+(aq) + e- Cu+(aq) 2 H+(aq) + 2e- H2(g) Ni2+(aq) + 2e- Ni(s) Fe2+(aq) + 2e- Fe(s) a. b. c. d. e. E0red = +0.34 V E0red = +0.00 V E0red = -0.25 V E0red = -0.44 V Cu2+(aq) is the strongest oxidizing agent Cu2+(aq) is the weakest oxidizing agent Ni(s) is the strongest oxidizing agent Fe(s) would be the weakest reducing agent H+(aq) would be the strongest oxidizing agent 6. A cell has been set up as shown in the following diagram, and E0 has been measured as 1.10 V at 25 oC. Calculate ∆G0 for the reaction. Scan pg 187 a. -425 kJ b. -212 kJ c. 106 kJ d. 212 kJ e. 425 kJ 19 7. Given the following diagram, determine which of the following statements is FALSE. a. b. c. d. e. The solid zinc electrode is being reduced to Zn2+(aq) The nickel electrode is the cathode The zinc electrode is the anode The nickel(II) ions are being reduced The Zn electrode will be negative in charge 8. Given that Zn2+(aq) + 2e- Zn(s) Cr3+(aq) + 3e- Cr(s) E0red = -0.76 V E0red = -0.74 V calculate the equilibrium constant k for the following balanced reaction: 3 Zn(s) + 2 Cr3+(aq) 3 Zn2+(aq) + 2 Cr(s) a. b. c. d. k = e-0.02 k = e0.02 k = e4.7 k = e8.0 20 9. An electric current is applied to an aqueous solution of FeCl2 and ZnCl2. Which of the following reactions occurs at the cathode? a. b. c. d. e. Fe2+(aq) + 2e- Fe(s) Fe(s) Fe2+(aq) + 2eZn2+(aq) + 2e- Zn(s) Zn(s) Zn2+(aq) + 2e2 H2O2(l) O2(g) + 4H+(aq) + 4e- E0red = -0.44 V E0red = +0.44 V E0red = -0.76 V E0red = +0.76 V E0red = -1.23 V 9. For the reaction Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 4H+(aq) + 2 SO42-(aq) 2 PbSO4(s) + 2 H2O(l) which is the overall reaction in a lead storage battery, ∆H0 = -315.9 kJ/mol and ∆S0 = 263.5 J.mol. What is the proper setup to find E0 at 75 oC? a. − 315.9 − 348(0.2635) − 2(96,487 ) b. − 348 + 315.9(0.2635) 2(96,487 ) c. − 348 + 315.9(0.2635) 96,487 d. − 2(− 348) + 263.5 96,487 + 315.9 e. 2(315.9 ) − 263.5 (96,487(348)) Cliff's Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. b d d e 5. 6. 7. 8. a b a c 9. a 10. a 21