REGIONS FORMAL REGION FUNCTIONAL REGION
advertisement

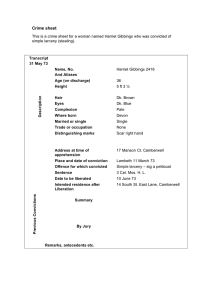
Unit 1 (Geography Basics) Region Types AP Human Geography Mr. Montgomery REGIONS A region is an area of the Earth defined my one or more characteristics: CULTURAL (language, religion, etc.) ECONOMIC (agriculture, industry, etc.) PHYSICAL (climate, vegetation, etc.) Regions gain uniqueness from a combination of human and environmental characteristics. As they interact with their environment, human’s activities produce distinctive landscapes that do not derive primarily from physical features. The Term REGION applies to any area larger than a point and smaller than the planet. FORMAL REGION ALIASES Uniform Region Homogenous Region DEFINITION 1. Areas of essential uniformity in one or a limited combination of physical or cultural features 2. Whatever the basis of its definition, the formal region is the largest area over which a valid generalization of attribute uniformity can be made--- Whatever is stated about one part holds true for its remainder 3. When regions display a measurable and often visible internal homogeneity they are formal or uniform regions **Formal regions are marked by uniform sameness. EXAMPLES Siberia (a republic within Russia) India (a state ruled by a national government) Latin America (a macrocultural region) FUNCTIONAL REGION ALIASES Nodal Region DEFINITION 1. A region that is NOT marked by its internal sameness, but by its functional integrationthe way it works. 2. A functional region’s parts are interdependent, and throughout its extent the functional region operates as a dynamic, organizational unit. 3. A functional region is forged by a structured, urban-centered system of interaction. 4. A functional region has a core where its characterizing features are most clearly defined; they lessen in prominence toward the region’s margins or periphery. EXAMPLES regional city hubs of Atlanta for the south, Chicago for the Midwest, etc. the entire urban area and surrounding area of a central city the area of a newspaper’s circulation the area of local TV station broadcasting VERNACULAR REGION ALIASES Perceptual Region DEFINITION 1. Less rigorlessly structured than formal and functional regions. 2. Perceptual regions reflect feelings and images rather than objective data 3. These regions may be primarily in the minds of the people who live there and are therefore very different EXAMPLES What people think of as “Dixie” or the south What some people consider as “Little Italy” in Boston Tennessee Vols territory