Chemistry Practice Exam #5 - Spring 2014
advertisement
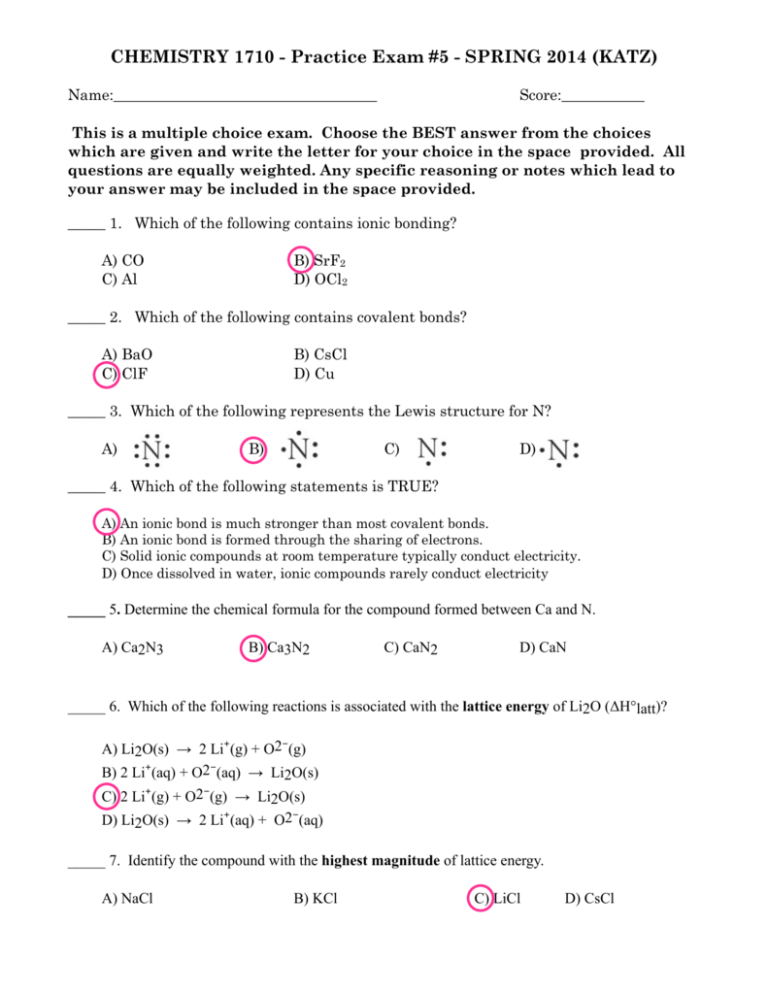
CHEMISTRY 1710 - Practice Exam #5 - SPRING 2014 (KATZ) Name:___________________________________ Score:___________ This is a multiple choice exam. Choose the BEST answer from the choices which are given and write the letter for your choice in the space provided. All questions are equally weighted. Any specific reasoning or notes which lead to your answer may be included in the space provided. _____ 1. Which of the following contains ionic bonding? A) CO C) Al B) SrF2 D) OCl2 _____ 2. Which of the following contains covalent bonds? A) BaO C) ClF B) CsCl D) Cu _____ 3. Which of the following represents the Lewis structure for N? A) B) C) D) _____ 4. Which of the following statements is TRUE? A) An ionic bond is much stronger than most covalent bonds. B) An ionic bond is formed through the sharing of electrons. C) Solid ionic compounds at room temperature typically conduct electricity. D) Once dissolved in water, ionic compounds rarely conduct electricity _____ 5. Determine the chemical formula for the compound formed between Ca and N. A) Ca2N3 B) Ca3N2 C) CaN2 D) CaN _____ 6. Which of the following reactions is associated with the lattice energy of Li2O (ΔH°latt)? A) Li2O(s) → 2 Li⁺(g) + O2⁻(g) B) 2 Li⁺(aq) + O2⁻(aq) → Li2O(s) C) 2 Li⁺(g) + O2⁻(g) → Li2O(s) D) Li2O(s) → 2 Li⁺(aq) + O2⁻(aq) _____ 7. Identify the compound with the highest magnitude of lattice energy. A) NaCl B) KCl C) LiCl D) CsCl _____ 8. Place the following in order of increasing magnitude of lattice energy. MgO LiI CaS A) CaS < MgO < LiI B) LiI < CaS < MgO C) MgO < CaS < LiI D) LiI < MgO < CaS _____ 9. A triple covalent bond contains __________ of electrons. A) 0 pairs C) 2 pairs B) 1 pair D) 3 pairs _____10. Identify the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons in water. A) 1 bonding pair and 1 lone pair C) 2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs B) 1 bonding pair and 2 lone pairs D) 2 bonding pairs and 1 lone pair _____11. Place the following elements in order of increasing electronegativity. Sr N Na A) Sr < Na < N B) Na < N < Sr C) Sr < N < Na D) N < Sr < Na _____12. Which molecule or compound below contains an ionic bond? A) CO2 B) NH4NO3 C) SiF4 D) OCl2 _____13. Arrange aluminum, nitrogen, phosphorus and indium in order of increasing electronegativity. A) Al < In < N < P C) In < Al < P < N B) Al < In < P < N D) In < P < Al < N _____14. Choose the best Lewis structure for XeI2. A) C) B) D) _____15. Choose the best Lewis structure for NO3⁻. A) B) C) D) _____16. Using Lewis structures and formal charge, which of the following ions is most stable? OCN⁻ " " ONC⁻ NOC⁻ A) OCN⁻ B) ONC⁻ C) NOC⁻ D) None of these ions are stable according to Lewis theory _____17. Use the bond energies provided to estimate ΔH°rxn for the reaction below. XeF2 + 2 F2 → XeF6 Bond Bond Energy (kJ/mol) Xe-F 147 F-F 159 A) -429 kJ B) +159 kJ C) -270 kJ D) +176 kJ ΔH°rxn = ? _____18. Which ionic compound would be expected to have the highest lattice energy? A) Rb2O B) SrO C) In2O3 D) CO2 _____19. Of the following elements, which has the highest electronegativity? A) S B) Cl C) Ti D) Se _____20. Select the Lewis structure in which formal charges are minimized for the periodate anion, IO4-. _____21. Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of CH3+1. A) eg=tetrahedral, mg=tetrahedral B) eg=tetrahedral, mg=trigonal pyramidal C) eg=trigonal planar, mg=bent D) eg=trigonal planar, mg=trigonal planar _____22. Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of NCl3. A) eg=tetrahedral, mg=tetrahedral B) eg=linear, mg=trigonal planar C) eg=trigonal planar, mg=bent D) eg=tetrahedral, mg=trigonal pyramidal _____23. Consider the molecule below. Determine the molecular geometry at each of the 2 labeled carbons. A) C1 = tetrahedral, C2 = linear B) C1 = trigonal planar, C2= bent C) C1 = bent, C2 = trigonal planar D) C1 = trigonal planar, C2 = tetrahedral _____24. What is the molecular shape of ClO3F as predicted by the VSEPR theory? (Chlorine is the central atom.) A) trigonal pyramidal B) square planar C) square pyramidal D) tetrahedral _____25. Determine the electron geometry (eg) and molecular geometry (mg) of IF2-. A) eg=tetrahedral, mg=bent C) eg=trigonal planar, mg=linear B) eg=trigonal planar, mg=bent D) eg=trigonal bipyramidal, mg=linear _____26. Place the following in order of decreasing X-A-X bond angle, where A represents the central atom and X represents the outer atoms in each molecule. N2O NCl3 NO2⁻ A) NCl3 > NO2⁻ > N2O B) NO2⁻ > N2O > NCl3 C) N2O > NO2⁻ > NCl3 D) NCl3 > N2O > NO2⁻ _____27. Which of the following molecules has a net dipole moment? A) BeCl2 C) KrF2 B) SF2 D) CO2 _____28. Describe a pi bond. A) side by side overlap of p orbitals B) end to end overlap of p orbitals C) s orbital overlapping with the end of a p orbital D) overlap of two s orbitals _____29 A molecule containing a central atom with sp hybridization has ______ geometry. A) linear B) trigonal bipyramidal C) trigonal planar D) tetrahedral _____30. List the number of sigma bonds and pi bonds in a double bond. A) 1 sigma, 1 pi B) 2 sigma, 1 pi C) 2 sigma, 2 pi D) 1 sigma, 2 pi _____31. How many of the following molecules contain at least one pi bond? C2H6 Cl2CO C2Cl4 SeS3 A) 0 B) 1 C) 3 D) 4 _____32. Which one of the following statements about orbital hybridization is incorrect ? A) The carbon atom in CH4 is sp3 hybridized B) sp hybrid orbitals lie at 180° to each other. C) The nitrogen atom in NH3 is sp2 hybridized D) sp2 hybrid orbitals are coplanar, and at 120° to each other. _____33. According to valence bond theory, the triple bond in ethyne (acetylene, C2H2) consists of A) three σ bonds and no π bonds. C) two σ bonds and one π bond. B) one σ bond and two π bonds D) no σ bonds and three π bonds. _____34. What is the O-S-O bond angle in SO32-? A) less than 109.5° C) 120° B) 109.5° D) greater than 120° _____35. Determine the shape (geometry) of PCl3 and then decide on the appropriate hybridization of phosphorus in this molecule. (Phosphorus is the central atom.) A) sp C) sp3 B) sp2 D) sp3d _____36. Give the change in conditions to go from a liquid to a gas. A) increase heat or reduce pressure C) cool or reduce pressure B) increase heat or increase pressure D) cool or increase pressure _____37. What is the strongest type of intermolecular force acting between molecules of H2? A) ion-dipole C) dispersion B) dipole-dipole D) hydrogen bonding _____38. Place the following compounds in order of increasing strength of intermolecular forces. CO2 F2 NH2CH3 A) NH2CH3 < CO2 < F2 B) F2 < NH2CH3 < CO2 C) NH2CH3 < F2 < CO2 D) F2 < CO2 < NH2CH3 _____39. Place the following substances in order of increasing boiling point. CH3CH2OH He CH3OCH3 A) He < CH3OCH3 < CH3CH2OH B) CH3CH2OH < He < CH3OCH3 C) CH3CH2OH < CH3OCH3 < He D) CH3OCH3 < He < CH3CH2OH _____40. Which is expected to have the highest magnitude of dispersion forces between molecules? A) C3H8 C) F2 B) C12H26 D) Be Cl2 _____ 41. The heat of vaporization of water at 100°C is 40.66 kJ/mol. Calculate the quantity of heat that is absorbed/released when 9.00 g of steam condenses to liquid water at 100°C. " A) 20.3 kJ of heat are absorbed. B) 20.3 kJ of heat are released. C) 81.3 kJ of heat are absorbed. D) 81.3 kJ of heat are released. _____42. Calculate the total quantity of heat required to convert 25.0 g of liquid CCl4(l) from 35.0°C to gaseous CCl4 at 76.8°C (the normal boiling point for CCl4). The specific heat of CCl4(l) is 0.857 J/(g · °C), its heat of fusion is 3.27 kJ/mol, and its heat of vaporization is 29.82 kJ/mol. A) 0.896 kJ B) 1.43 kJ C) 5.74 kJ D) 6.28 kJ

![Which is the correct Lewis structure for the nitrate ion, [NO3]– ? a) b](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008121614_1-3f41411d21eef682c95d3c7778684719-300x300.png)