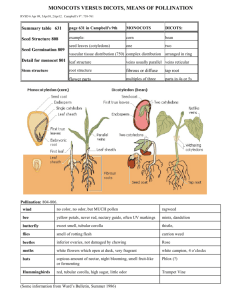
Monocots vs. Dicots
advertisement

Monocots vs. Dicots ­ There are two types of angiosperms ­ ________________ and ________________ ­ "Cot" refers to _______________________, which is the structure inside the seed which provides nutrients to the plant embryo Monocots Evolved Number of cotyledons Flower petals Leif Vein Arrangement Vascular bundles in roots Vascular bundles in stems Examples Dicots Seeds In angiosperms the seeds develop form the ______________________ of flowers after pollination and fertilization. The fruit or fleshy part of the seed is from the ovary. Seeds consist of three fundamental parts: 1. Seed coat: 2. Endosperm: 3. Embryo: a. Cotyledon (seed leaf): __________________________________ ______________. The cotyledon absorbs and stores starch from the endosperm to feed the embryo until it can feed itself through ____________________. b. Epicotyl (grows upward from the cotyledon to become the shoot). It is the first part of the plant to _____________ above the ground. c. Hypocotyl (grows downward from the cotyledon to become the roots). It is longer in dicots than monocots. ­ Monocots have a large endosperm which stores __________________ _________________ ­ Dicots digest the endosperm during seed development into the 2 cotyledons. Therefore the mature seed has large cotyledons. ­ Seed attached to pod at the hilum (the scar on a seed indicating the point of attachment) ­ Micropile ­ _____________________ at one end of hilum where the pollen tube entered the ovule of the flower, and the radicle breaks through the seed. It is the only place where water can enter the seed. Seed Dormancy: ­ Many seeds go through a dormant (______________________) period before they begin to grow or germinate ­ The dormant period varies, even within the same species. This is a survival characteristic ­ in unusually hard conditions not all seeds would be killed in a given year. Factors that Affect Dormancy: 1. Seed coat may not allow ______________________________ to reach the embryo 2. Seed coat may be so strong that the embryo can't break through 3. Time must elapse so embryo can develop further 4. Chemical inhibitors in seed prevent germination. Factors Affecting Germination: ­ ­ ­ ­ Read pages 307 ­ 309, answer #1­8