Study Guide for the LS
advertisement

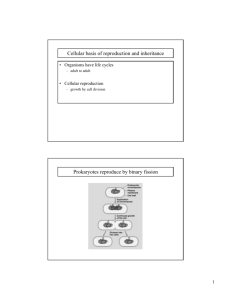
Name:__________________________________________________Test Date: Wed., 12/3 or Thurs., 12/4 Cell Division Assessment Study Guide Chromosomes are organized structures of DNA. Three Types of Cell Division: Binary fission , Mitosis, Meiosis Prokaryotic Cells (Bacterial Cells) Binary fission a simple cell division in which one cell splits into two identical cells Prokaryotic cells and single-celled organisms reproduce by binary fission Mitosis-occurs in body cells like nerve cells and blood cells Mitosis is a type of cell division in which one parent cell goes through simple cell division to split and produces two identical “daughter cells”. Each of the new cells is identical to the parent cells and contains 46 chromosomes in humans. Meiosis: is the process in which one cell goes through two divisions to become four separate sex cells Sperm and egg cells have half the amount of chromosomes Know the difference between mitosis and meiosis: Kind of cell made Number of cells made Mitosis body cell 2 Meiosis sex cell (egg or sperm) 4 Number of chromosomes made same as original (parent) cell Half as many as the original cell Purpose of cell Growth and Repair Reproduction Eukaryotic Cells (Plant and Animal Cells) Most eukaryotic cells go through a cell cycle. The life cycle of a cell has three main stages, IMC: interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. Interphase (Stage 1) In Interphase the chromosomes and other cell materials (organelles) are copied. The nucleus is visible. Mitosis (Stage 2) The starting cell is called the parent cell which divides to make two identical daughter cells that have identical chromosomes. PMAT-Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase chromosomes Phase 1: Prophase Cell is PREPARING for division, chromosomes fully visible. Phase 2: Metaphase Chromosomes line up at the center MEET in the middle Phase 3: Anaphase Chromatids move APART Phase 4: Telophase Cell TEARS into two cells connected by cytoplasm Cytokinesis (Stage 3) Once mitosis is completed Cytokinesis occurs. Cytokinesis is the process of splitting the cytoplasm forming two new daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. A plant cell forms a cell plate in cytokinesis.