Microscope - Exercise 1
advertisement

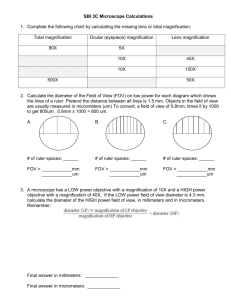
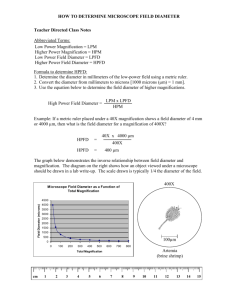
Microscope - Exercise 1 Objectives -Familiarize parts and functions of the microscope. -Calculate total magnifications. -Determining the Diameter of the field of view for different magnifications. -Estimate size of an object under the microscope. -Identify parts (organelles) in animal and plant cells. Condenser: It will gather the light from the illuminator and focus it on the specimen lying on the stage. The function of the condenser is to focus the light rays from the light source onto the specimen. Iris diaphragm lever: This allows the amount of light passing through the condenser to be regulated to see the object. Microscope You have to learn how to use the microscope if your going to take Anatomy & Physiology, BI203, or any other science related courses, so get a good hang out of it now. Also, learn the parts and functions of the microscope. Measuring Objects with the Microscope -To focus on an object, you must first center the object to the center of the field of view, and remember to do this every time you switch to a higher magnification. -The field of view refers to the total area that is visible through the microscope. The field of view is circular. The field gets smaller as the magnification increases. It is possible to measure the diameter of the field of view, and that measurement can then be used to construct reasonable estimates of the size of any specimen contained within the field of view. Page 11 – Lab Book Known magnification ----------------------------X original um = Diameter of Unknown magnification Field of View Measuring Objects with the Microscope With the 4x objective lens in place, look through the microscope and adjust the ruler so that it lies on a diameter of the field of view. Calculating the Diameter of the Field of View at other Magnifications There is an inverse relationship between the total magnification and the diameter of the field of view – i.e., as magnifications increases the diameter of the field decreases in proportion, so the diameter of field of view at different magnification can be calculated mathematically, using the formula. Dimensional Analysis • You are converting um (10-6 m) mm (10-3 m) • 1um 10-6 m • 1 mm 10-3 m 10-6 - 10-3 = 10-3 1um x 10-6 m x 1 mm = 10-3 aka 1,000 um/mm 1 um 10-3m • Determining the Diameter of the field of view at 40x (low power) (Ruler) • With the 4x objective lens (40 magnification) in place, look through the microscope and adjust the ruler so that it lies on a diameter of the field of view. • Diameter of the field of view at 40x (low power) which is objective lens 4. To convert the diameter of field to micrometer you just multiply it by 1,000, and you could get whatever you measured your ruler. So lets say we measured our ruler to be 4mm, so we multiply it by 1,000, and we get 4,000 um. Now, we could get other diameter of fields with different magnifications using a formula. • For example, say we have to find the diameter of field of 100x? • The first thing you do is put 40, which is your total magnification that you started with, over your unknown magnification, then you multiply that by your total micrometers, so for this case its 4,000, and you get a diameter of field of 1600 um. • Now, say their asking us for 430x magnification, so what we do is put 40 over 430, and you multiply that by 4,000 which you would get 372 um. Estimate size of an object under the microscope The approach you would take to estimate the size of a microscopic object, if you are given the diameter of field of views at different magnifications. • Step 1: Focus on the object at certain magnification and note the diameter of the field of view at that magnification. • Step 2: Determine (guesstimate) the percent of the diameter of the field of view is occupied by the object (image). • Step 3: Use the following formula….. Percent Object Size = ------------------ X diameter of field of view = 100 Estimate size of an object under the microscope The size of a specimen can be estimated by comparing it to the known diameter of the field of view at any magnification. First, you have to estimate how much of an object is occupying the field of view of the microscope, so your not going to get an accurate answer, but your answer should get an answer that’s going to be within a range. Ok, your still using the 4,000 um that you get previously and say you have a flea, and that flea takes up about 40% of your microscope, so what you do is covert the 40% into a decimal by dividing it by 100, and you get .40 then you multiply that by 4,000 um and you should get an answer, which is 1600 um. Now, they can ask you to estimate another size of an object. For example, say the Flea’s eye covers about 5%. So you divide that 100, you should get .05 and multiply that by 4,000 um, and you should get 200 um. Note: You could be asked this at different magnifications. Your going to be ask to identify parts of both animal and plant cells, such as chloroplast, nucleus of a cell, and those sorts of things, so review them on your own. Human epithelial cell – From Rust – 1a & 1b • You will need to identify the nucleus, cytoplasm, and the cell membrane under a microscope. Elodea Leaf cell – From Rust – 1c & 1d • You will need to identify the cytoplasm, cell wall, and chloroplast under a microscope. What is the function of the chloroplasts? What is the function of the chloroplasts? Photosynthesis to make food for the plant. Calculate the diameter of the field of view occupied by the flea. The diameter field of view is 100x magnification of the microscope is 380 micrometer. You have to estimate the percentage of the flea that occupies the microscope. This is subjective. Questions 1. In the diameter of field of view of a light microscope at 40X magnification is 6,000 micrometer (um), what would be the field of view at 400X magnification? 2. An elodea cell was found occupying 40% of field of view’s diameter at 400X magnification. At this magnification the field of view of the microscope is 200 micrometer. What is the size of the elodea cell? Remember this is a gesstimate percent of the diameter of the field of view is occupied by the object (image). Questions 1. In the diameter of field of view of a light microscope at 40X magnification is 6,000 micrometer (um), what would be the field of view at 400X magnification? 40 x 6000 = 600 um 400 2. An elodea cell was found occupying 40% of field of view’s diameter at 400X magnification. At this magnification the field of view of the microscope is 200 micrometer. What is the size of the elodea cell? Remember this is a gesstimate percent of the diameter of the field of view is occupied by the object (image). 40 = .4 100 .4 x 200 = 80 um