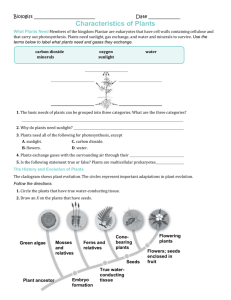
Fungi and plants practice

Name: ___________________________________ Period: ________ Date: ________________ ID: A
Fungi and plants practice
Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Indicate your answer choice with an UPPER CASE letter in the space provided.
____ 1. Fungi exhibit certain characteristics. One of these characteristics is that they
A.
reproduce using seeds and pollen. B.
are prokaryotes. C.
lack cell nuclei. D.
are capable of carrying on photosynthesis. E.
reproduce using spores.
____ 2. An example of a single-celled fungus would be
A.
yeast. B.
hypha. C.
mycelia. D.
eukaryote. E.
chitin.
____ 3. The cell walls of fungi are composed mainly of
A.
hyphae. B.
cellulose. C.
chitin. D.
phospholipids. E.
mycelia.
____ 4. This characteristic allows fungi to withstand heat and drought conditions.
A.
hyphae B.
cell walls C.
mycelia D.
specialized organelles E.
spores
____ 5. In fungi, a fruiting body is involved in
A.
protection from drought and heat. B.
protection from cold. C.
reproduction. D.
digestion.
E.
interactions with plants.
____ 6. Although there are similarities between animal and fungal digestion, there is a major difference.
Identify this difference.
A.
Animal digestion uses enzymes; fungal digestion does not. B.
Only animals begin the digestive process outside the body. C.
Larger nutrient molecules are absorbed through the animal cell membrane than through fungal cell membranes. D.
A fungus will digest nutrient matter outside of its body. E.
Under certain conditions, fungi can produce their own nutrients.
____ 7. The major causes of plant diseases are
A.
protozoa. B.
viruses. C.
bacteria. D.
worms. E.
fungi.
____ 8. When a haploid "plus" mating type fungal cell fuses with a haploid "minus" mating type cell, this can lead to a single cell containing two haploid nuclei called a
A.
spore. B.
dikaryon. C.
fruiting body. D.
haploid-diploid. E.
fusion product.
____ 9. In fungal reproduction, sexual fusion refers to
A.
the combining of cells of opposite mating types. B.
fusion between spores of different mating types. C.
fusion between hyphae from fungi of different mating types. D.
fusion between haploid nuclei in a dikaryon. E.
the dominance of the haploid phase in the fungal life cycle.
____ 10. The fungal-plant root combination is referred to as
A.
mycorrhizae. B.
symbiosis. C.
hyphae. D.
mycelia. E.
lichen.
____ 11. Lichens are
A.
parasitic interactions between a fungus and an alga. B.
only found growing on living matter.
C.
symbiotic associations between a fungus and an alga. D.
capable of causing some obscure diseases.
E.
insensitive to changes in the environment.
1
Name: ______________________ ID: A
____ 12. Lichens are used by scientists as an indicator of pollution because they
A.
require nonpolluted water to grow. B.
are extremely sensitive to sulfur dioxide. C.
react to small amounts of carbon monoxide. D.
are very sensitive to ultraviolet radiation. E.
respond to increased levels of chlorofluorocarbons.
____ 13. Green algae such as Ulva demonstrate an alteration of generations. The diploid phase is called the
A.
gametophyte generation. B.
embryo. C.
sporophyte generation. D.
diploid generation.
E.
zygote.
____ 14. In plants, the secondary metabolites are primarily responsible for
A.
nutrition. B.
food gathering. C.
overcoming air pollutants. D.
defense. E.
protection against ultraviolet radiation.
____ 15. In bryophytes, the rhizoids
A.
serve as attachment structures. B.
obtain nutrients. C.
obtain water. D.
lure possible prey.
E.
are involved in reproduction.
____ 16. The vascular transport tubes of plants are reinforced with
A.
cellulose. B.
chitin. C.
rhizoids. D.
mycorrhizae. E.
lignin.
____ 17. Some plants require water for reproduction. This is because
A.
it is needed for germination of the spores. B.
the eggs would dry out otherwise. C.
the sperm are motile and need to swim to the egg to accomplish fertilization. growing in order to reproduce.
D.
the plants must be actively
E.
the seeds will be carried on the water to new sites.
____ 18. In gymnosperms, the formation of the female gametophyte takes place in the
A.
microspores. B.
megaspores. C.
macrospores. D.
ovule. E.
rhizomes.
____ 19. All of the following are parts of a flower except the
A.
carpel. B.
stamen. C.
ovary. D.
fruit. E.
cuticle.
____ 20. In general, mammals are not good at dispersing chili plant seeds because
A.
the seeds die as they pass through the digestive tract. B.
the mammals do not travel very far before they release the chili seeds. C.
the chili seeds do not stick to the mammals' fur. D.
chili seeds are dispersed mainly by the wind. E.
the mammals are the main pollinators for the chili plant.
____ 21. Arrange the following characteristics in order from the earliest to the most recent to evolve.
1. fruits
2. ovules
3. multicellular embryos
4. vascular system
5. alternation of generations
A.
1, 2, 3, 4, 5 B.
3, 2, 4, 5, 1 C.
5, 2, 4, 3, 1 D.
5, 3, 4, 2, 1 E.
3, 5, 4, 2, 1
____ 22. Which of the following is an adaptation to land characteristic of gymnosperms but not ferns?
A.
seeds B.
spores C.
vascular system D.
alternation of generations E.
flowers
____ 23. Which of the following are adaptations to land of both gymnosperms and angiosperms but are lacking in ferns and mosses?
A.
pollen and seeds B.
fruits and flowers C.
vascular system D.
true roots, stems, and leaves
E.
spores
2
Name: ______________________ ID: A
____ 24. Which of the following plant groups specifically need water for sperm transport?
A.
mosses, ferns, conifers, flowering plants B.
mosses, ferns, conifers C.
mosses, ferns
D.
mosses only E.
flowering plants only
____ 25. Which plant group has a dominant gametophyte generation when compared to the sporophyte generation?
A.
flowering plants B.
gymnosperms C.
ferns D.
horsetails E.
bryophytes
____ 26. Which of the following is an adaptation to land seen in ferns but not in mosses?
A.
vascular system
B.
alternation of generations
C.
ovules
D.
seeds
E.
spores
Text Section:12.3 - plant evolution, adaptation to land
____ 27. A dikaryotic cell will originate from
A.
a sperm that fertilizes an egg. B.
a spore that germinates into a hypha. C.
alternation of generations. D.
pollination. E.
fusion of haploid cells from plus and minus mating types.
____ 28. Which of the following is not a type of true fungus?
A.
puff balls B.
mushrooms C.
slime molds D.
morels E.
yeasts
____ 29. The principal polysaccharide found in fungal cell walls is also found in
A.
archaebacterial cell walls. B.
eubacterial cell walls. C.
cell walls of land plants. D.
cell walls of red algae. E.
insect exoskeletons.
____ 30. Fungi digest organic matter
A.
by using bacterial endosymbionts. B.
with extracellular enzymes. C.
in their fruiting bodies.
D.
inside the hyphal cells, after phagocytosis. E.
by using hydrolytic enzymes of their host cells.
____ 31. Fungi and plants resemble each other because they both
A.
have cells surrounded by cell walls. B.
are typically heterotrophic. C.
often cause disease.
D.
are composed of cells with two different nuclei. E.
have flagellated cells.
____ 32. Asexually produced fungal spores are ______, whereas fungal cells produced sexually, by the fusion of two mating strains, are _______.
A.
haploid; dikaryons B.
haploid; diploid C.
diploid; dikaryons D.
diploid; haploid
E.
dikaryons; diploid
____ 33. The mycorrhizae found interacting with the roots of land plants are
A.
pathogens, feeding on plant tissue they have damaged with toxins. B.
parasites, draining sugar from the plant's vascular system. C.
saprophytes, stripping dead tissue from the root.
D.
symbionts, facilitating the plant's uptake of minerals. E.
commensals, exploiting a benign environment, but neither helping nor harming the plant.
____ 34. What do fungi contribute to the survival of lichens?
A.
trap solar energy B.
protect the partnership from air pollution C.
provide the motility needed to relocate when conditions become unfavorable D.
promote rapid growth of the overall structure
E.
absorb and retain water
3
Name: ______________________ ID: A
____ 35. The principal criterion used to classify fungi into divisions (the equivalent of phyla) is
A.
the pigments found in the hyphal cells. B.
the components of their cell walls. C.
the biochemistry of their plasma membranes. D.
the morphology of the sexual spore-bearing structures.
E.
the pattern of cilia on their external surfaces.
____ 36. Unlike land plants, green algae do not have
A.
chlorophyll b. B.
carotenoids. C.
embryos. D.
diploid generations. E.
flagellated cells.
____ 37. In algae and plants with a life cycle characterized by alternation of generations, the _____ produces spores by ______.
A.
zygote; meiosis B.
gametophyte; mitosis C.
gametophyte; meiosis D.
sporophyte: mitosis
E.
sporophyte; meiosis
____ 38. Which of the following characteristics does the life cycle of the alga Ulva share with the life cycle of seed plants?
A.
male and female gametes that look the same B.
male and female gametes produced by mitosis
C.
sporophytes and gametophytes that look the same D.
diploid spores E.
fertilization in the open water
____ 39. Plants have adapted to dry land by evolving all of the following except
A.
association with mycorrhizae to improve mineral uptake. B.
secreting a waxy coating to prevent water loss. C.
forms of chlorophyll more efficient at capturing light. D.
tissues to conduct water through the plant. E.
structures to protect reproductive cells and embryos.
____ 40. Bryophytes differ from other land plants in that they do not have
A.
lignified water transport tissue. B.
protected sporophyte embryos. C.
spores. D.
a gametophyte generation. E.
a diploid generation.
____ 41. Gymnosperms (such as conifers) and angiosperms (such as lilies) differ in that only the angiosperms have
A.
lignified transport tissues. B.
leaves. C.
seeds. D.
fruits. E.
swimming sperm.
____ 42. The chile plant produces a fruit that promotes a symbiotic relationship with
A.
bees. B.
birds. C.
bats. D.
rodents. E.
beetles.
Matching
Match the following trait with the correct adaptive advantage.
A.
increases the chances of pollination
B.
protection from desiccation
C.
decreases predation
D.
increases gas exchange
E.
allows movement of nutrients and water throughout plant
F.
increases chance of wide dispersal of offspring
____ 43. Vascular systems
____ 44. Flowers
____ 45. Seeds and fruits
____ 46. Cuticles
4
Name: ______________________ ID: A
____ 47. Stomata
Match the following characteristics with the correct group of plants.
A.
flowering plants
B.
ferns
C.
mosses
D.
algae
E.
pine trees
____ 48. These land plants have a more conspicuous gametophyte than sporophyte generation.
____ 49. These are the first land plants that produced ovules.
____ 50. This group does not generally produce multicellular embryos.
____ 51. The ovules of these plants are encased in a "vessel."
____ 52. This group of land plants was the first to evolve xylem and phloem.
Match the following characteristics with the correct group of organisms.
A.
bacteria
B.
green algae
C.
fungi
D.
bryophytes
E.
ferns
F.
gymnosperms
G.
angiosperms
____ 53. Members of this group are heterotrophic or autotrophic and contain prokaryotic cells
____ 54. All members of this group are heterotrophic and contain eukaryotic cells
____ 55. Members of this group are autotrophic, eukaryotic, produce ovules, but lack flowers.
____ 56. These organisms are autotrophic and eukaryotic but lack multicellular embryos.
____ 57. These autotrophic, eukaryotic organisms contain a vascular system but lack seeds.
Match each property to the appropriate group or groups of land plants.
A.
mosses only
B.
ferns only
C.
angiosperms only
D.
mosses and ferns only
E.
ferns and angiosperms only
F.
mosses, ferns, and angiosperms
____ 58. This group has two free-living independent generations.
____ 59. This group produces seeds.
____ 60. Most of the organism's photosynthesis is carried out by the gametophyte generation in this group.
____ 61. Fertilization of egg by sperm produces the beginning of the sporophyte generation for this group.
____ 62. This group has support and water conduction tissues with lignin in the cell wall.
____ 63. Sperm must swim to fertilize the egg in this group.
5
Fungi and plants practice
Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE
25. E
26. A
27. E
28. C
29. E
30. B
31. A
32. A
17. C
18. B
19. E
20. A
21. D
22. A
23. A
24. C
9. D
10. A
11. C
12. B
13. C
14. D
15. A
16. E
1. E
2. A
3. C
4. B
5. C
6. D
7. E
8. B
33. D
34. E
35. D
36. C
37. E
38. B
1
ID: A
39. C
40. A
41. D
42. B
MATCHING
43. E
44. A
45. F
46. B
47. D
48. C
49. E
50. D
51. A
52. B
53. A
54. C
55. F
56. B
57. E
58. B
59. C
60. A
61. F
62. E
63. D
2
ID: A