Neuroscience Test Questions: Brain & Nervous System
advertisement

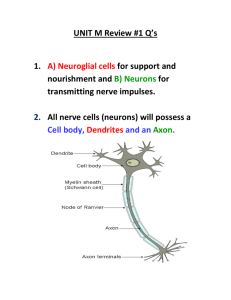
1. Which of the following is the component of the limbic system that plays an essential role in the processing of new memories? A) hypothalamus B) thalamus C) hippocampus D) medulla E) cerebellum 2. An axon is A) a cell that serves as the basic building block of the nervous system. B) a layer of fatty tissue that encases the fibers of many neurons. C) an antagonist molecule that blocks neurotransmitter receptor sites. D) the extension of a neuron that carries messages away from the cell body. E) a junction between a sending and receiving neuron. 3. Molecules that are similar enough to a neurotransmitter to bind to its receptor sites on a dendrite and block that neurotransmitter's effects are called what? A) agonists B) antagonists C) endorphins D) endocrines E) action potentials 4. Dendrites are branching extensions of A) neurotransmitters. B) endorphins. C) neurons. D) myelin. E) endocrine glands. 5. Some opiate drugs have molecular structures so similar to endorphins that they mimic endorphin's euphoric effects in the brain, making these opiate drugs which kind of molecule? A) agonists B) antagonists C) endorphins D) endocrines E) autonomics 6. Which brain area is primarily involved with controlling speech? A) sensory cortex B) angular gyrus C) association areas D) Broca's area E) hypothalamus 7. The “little brain” attached to the rear of the brainstem is called the A) limbic system. B) corpus callosum. C) cerebellum. D) reticular formation. E) thalamus. 8. As you are reading this question, the cells in your eyes are firing in response to the light coming from this paper. Which type of neuron is carrying this message to the brain? A) interneuron B) sensory C) presynaptic D) motor E) efferent 9. Neurosurgeons have severed the corpus callosum in human patients in order to reduce A) aphasia. B) epileptic seizures. C) depression. D) neural plasticity. E) reward deficiency syndrome. 10. To identify which specific brain areas are most active during a particular mental task, researchers would be most likely to make use of a(n) A) fMRI. B) hemispherectomy. C) ACh agonist. D) brain lesion. E) MRI. 11. The body's speedy, electrochemical information system is called the A) circulatory system. B) threshold. C) action potential. D) nervous system. E) endocrine system. 12. For you to experience the pain of a sprained ankle, ________ must first relay messages from your ankle to your central nervous system. A) endocrines B) interneurons C) glands D) motor neurons E) sensory neurons 13. Animal research has revealed a general reward system that triggers the release of the neurotransmitter A) ACh. B) GABA. C) dopamine. D) epinephrine. E) serotonin. 14. A football quarterback can simultaneously make calculations of receiver distances, player movements, and gravitational forces. This best illustrates the activity of multiple A) endocrine glands. B) endorphin agonists. C) neural networks. D) endorphin antagonists. E) thresholds. 15. What are the molecules that are similar enough to a neurotransmitter to bind to its receptor sites on a dendrite and mimic that neurotransmitter's effects called? A) agonists B) antagonists C) endorphins D) endocrines E) action potentials 16. A person with schizophrenia may have an overactive dopamine system. Drugs used to treat this disorder prevent the action of dopamine by keeping it from binding to its receptors. These drugs are A) agonists. B) somatic. C) sympathetic. D) antagonists. E) selectively permeable. 17. Split-brain patients have had their ________ surgically cut. A) hippocampus B) limbic system C) corpus callosum D) sensory cortex E) reticular formation 18. Psychoactive drugs interfere with normal neural transmission. Where does this interference take place? A) axon B) cell body C) myelin sheath D) synapse E) hormones 19. For you to be able to run, ________ must relay messages from your central nervous system to your leg muscles. A) interneurons B) agonists C) motor neurons D) sensory neurons E) the autonomic nervous system 20. Which brain area is primarily involved with understanding and producing meaningful speech? A) sensory cortex B) angular gyrus C) association areas D) Wernicke's area E) hypothalamus 21. Psychologist Michael Gazzaniga asked split-brain patients to stare at a dot as he flashed HE·ART on a screen. HE appeared in the left visual field, ART in the right. When asked to point to the word with their left hand, patients pointed to A) HE. B) ART. C) HEART. D) EA. E) nothing. They were unable to complete the task. 22. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate the activation of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. D) control pain through the release of opiate-like chemicals into the brain. E) transmit signals to other neurons. 23. Neural networks refer to A) the branching extensions of a neuron. B) interconnected clusters of neurons in the central nervous system. C) neural cables containing many axons. D) junctions between sending and receiving neurons. E) neurons that connect the central nervous system to the rest of the body. 24. People can simultaneously process many aspects of sensory information such as color, shape, and size. This best illustrates the functioning of multiple A) ACh agonists. B) dendrites. C) endorphins. D) neural networks. E) ACh antagonists. 25. The parietal lobes are to ________ as the occipital lobes are to ________. A) hearing; speaking B) sensing touch; seeing C) sensing pleasure; sensing pain D) tasting; smelling E) speaking; seeing 26. When the release of ACh is blocked, the result is A) depression. B) muscular paralysis. C) aggression. D) schizophrenia. E) euphoria. 27. In transmitting sensory information to the brain, an electrical signal travels from the ________ of a single neuron. A) cell body to the axon to the dendrites B) dendrites to the axon to the cell body C) axon to the cell body to the dendrites D) dendrites to the cell body to the axon E) axon to the dendrites to the cell body 28. The surgical removal of a large tumor from Dane's occipital lobe resulted in extensive loss of brain tissue. Dane is most likely to suffer some loss of A) muscular coordination. B) language comprehension. C) visual perception. D) speaking ability. E) pain sensations. 29. What is the interdisciplinary study of how brain activity is linked with our mental processes called? A) social-cultural perspective B) psychodynamic perspective C) cognitive neuroscience D) industrial-organizational psychology E) biopsychosocial approach 30. In 1861, Paul Broca studied a stroke patient he called “Tan.” He was called this because as a result of brain damage it was the only word he could pronounce. Based on Broca's early work, which of the following brain regions is involved in speech production? A) angular gyrus B) left temporal lobe C) sensory cortex D) left frontal lobe E) auditory cortex 31. A picture of a dog is briefly flashed in the left visual field of a split-brain patient. At the same time a picture of a boy is flashed in the right visual field. In identifying what she saw, the patient would be most likely to A) use her left hand to point to a picture of a dog. B) verbally report that she saw a dog. C) use her left hand to point to a picture of a boy. D) verbally report that she saw a boy. E) communicate that she saw a picture of a boy with a dog. 32. Sheelah was able to jerk her hand out of the scalding water before sensing any pain because this withdrawal reflex A) was activated by interneurons in her spinal cord. B) did not involve activity in her central nervous system. C) was activated by the rapidly responding brain. D) was activated by her self-regulating autonomic nervous system. E) was controlled by both her nervous system and impulses from her endocrine system. 33. A picture of a cat is briefly flashed in the left visual field and a picture of a mouse is briefly flashed in the right visual field of a split-brain patient. The individual will be able to use her A) right hand to indicate she saw a cat. B) left hand to indicate she saw a mouse. C) right hand to indicate she saw a mouse. D) left or right hand to indicate she saw a cat. E) left or right hand to indicate she saw a mouse. 34. Psychologist Michael Gazzaniga asked split-brain patients to stare at a dot as he flashed HE·ART on a screen. HE appeared in the left visual field, ART in the right. When asked, patients said they saw A) HE. B) ART. C) HEART. D) EA. E) nothing. They were unable to complete the task. 35. An undersupply of serotonin is most closely linked to A) Alzheimer's disease. B) schizophrenia. C) Parkinson's disease. D) depression. E) euphoria. 36. Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that travel across the A) cell body. B) synaptic gap. C) axon. D) myelin sheath. E) threshold. 37. The brains of patients with Parkinson's disease have little dopamine. Drugs used to treat such patients bind to dopamine receptors, thereby stimulating those receptors. These drugs would be considered A) antagonists. B) sympathetic. C) selectively permeable. D) endorphins. E) agonists. 38. Transferring messages from a motor neuron to a leg muscle requires the neurotransmitter known as A) dopamine. B) epinephrine. C) acetylcholine. D) insulin. E) endorphin. 39. The knee-jerk reflex is controlled by interneurons in the A) action potential. B) spinal cord. C) resting potential. D) endocrine system. E) neurotransmitters. 40. A synapse is a(n) A) chemical messenger that triggers muscle contractions. B) automatic response to sensory input. C) neural network. D) junction between a sending neuron and a receiving neuron. E) neural cable containing many axons. 41. The occipital lobes are to ________ as the temporal lobes are to ________. A) hearing; sensing movement B) seeing; sensing touch C) sensing pleasure; sensing pain D) seeing; hearing E) speaking; hearing 42. Motor neurons are to the ________ nervous system as interneurons are to the ________ nervous system. A) sympathetic; parasympathetic B) central; peripheral C) autonomic; somatic D) parasympathetic; sympathetic E) peripheral; central 43. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles located on knoblike terminals at the end of the A) dendrites. B) cell body. C) axon. D) myelin sheath. E) synapse. 44. The chemical messengers released into the spatial junctions between neurons are called A) hormones. B) neurotransmitters. C) synapses. D) sensory neurons. E) motor neurons. 45. A simple, automatic, inborn response to a sensory stimulus is called a(n) A) neural network. B) action potential. C) neurotransmitter. D) reflex. E) threshold. 46. Which neural center in the limbic system plays a central role in emotions such as aggression and fear? A) amygdala B) thalamus C) cerebellum D) medulla E) dendrite 47. Information travels from the spinal cord to the brain via A) interneurons. B) the circulatory system. C) sensory neurons. D) the sympathetic nervous system. E) the endocrine system. 48. When asked to describe a picture that showed two boys stealing cookies behind a woman's back, a patient replied, “Mother is away her working her work to get her better, but when she's looking the two boys looking the other part.” Which brain region has most likely been damaged? A) Broca's area B) angular gyrus C) corpus callosum D) Wernicke's area E) parietal lobes 49. To demonstrate that brain stimulation can make a rat violently aggressive, a neuroscientist should electrically stimulate the rat's A) reticular formation. B) cerebellum. C) medulla. D) amygdala. E) thalamus. 50. The spatial junctions where impulses are chemically transmitted from one neuron to another are called A) neurotransmitters. B) neural networks. C) synapses. D) axons. E) thresholds. You should also be able to… Describe what the Neural Chain is (list the parts) Describe what dopamine is and does in your body Describe what serotonin is and does in your body Describe what acetylcholine is and does in your body What is the difference between an agonist and antagonist? Give a description of what a drug does in your body Describe what the following areas tend to control… Frontal Lobe, Hippocampus, Cerebellum, Occipital Lobe, Parietal Lobe, Temporal Lobe, amygdala, Corpus Callosum Describe the differences between Wernicke and Broca’s area. Describe what synesthesia is Explain why Capgras Syndrom and Blindsight occur. Answer Key 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. C D B C A D C B B A D E C C A D C D C D A A B D B B D C C D D A C B D B E C B D D E C B D A A D D C