Identification of Unit Costs in Rheumatoid Arthritis Research
advertisement

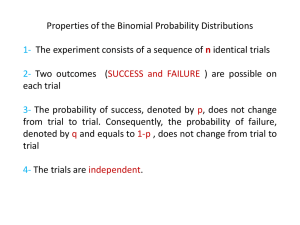
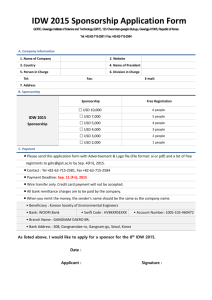
Title: (logo.eps) Creator: Adobe Illustrator(r) 6.0 Preview: Identification of Unit Costs in Rheumatoid Arthritis Research Approach and Results Rosery H., Schwander B., Bergemann R. IMOR - Institute for Medical Outcome Research GmbH Untere Herrenstrasse 25, 79539 Loerrach, Germany www.imor.com ISPOR ISPOR 6th 6thAnnual AnnualEuropean EuropeanCongress Congress PMD23 PMD23 Methods Objective In the context of a multi-center trial resource consumption of patients with rheumatoid arthritis was assessed using investigator and patient To elaborate a useful level of detail according to measurement and valuation of costs associated with rheumatoid arthritis. questionnaires. Resources were gathered as amounts and not as costs. An intensive Internet Research was performed to assess country -specific unit costs. Structure of Cost Data Cost Research Documentation TOTAL LEVEL 1 LEVEL 2 LEVEL 3 DIRECT OUTPATIENT INPATIENT LEVEL 4 LEVEL 5 LEVEL 6 INDIRECT DIRECT MEDICAL HOSP 1 DIRECT NONMEDICAL REHA Doctor Medication Specific Procedure Other Treatments Technical work and Aids Personal Help Transpor tation Unfit for work 1 3 2 11 7 16 5 7 1 We reported the type of cost item, country, total costs of one unit, name of data source, date of data, homepage address, date of review, calculation assumption and calculation method. Unit costs were assessed for ten cost domains: Doctor visit, medication, diagnostic procedures, monitoring, hospitalization, rehabilitation, personal help, stoppage, traveling and other treatments. Example of Unit Cost Values of 3 Cost Domains for 5 Countries Australia Canada France Germany Great Britain Cost item Unit costs Unit costs Unit Costs Unit costs Unit Costs Unit costs Unit costs Unit costs Unit Costs Unit costs AUD USD CAD USD FF USD DEM USD GBP USD Doctor visits Visits of general practitioner 20.33 11.82 41.96 28.28 115.00 26.81 33.58 15.86 26.75 40.54 Visits of other doctor 68.66 39.91 51.92 34.99 150.00 34.97 33.58 15.86 63.50 96.23 Outpatient department visit 44.49 25.86 46.32 31.21 132.50 30.89 33.58 15.86 45.13 68.39 Hospitalization Hospitalization per day 628.58 365.38 623.00 419.82 1732.40 403.85 568.00 268.23 258.50 391.73 Rehabilitation Rehabilitation per day 519.12 301.76 378.50 255.06 1093.00 254.80 212.95 100.56 169.00 256.10 Currency exchange rate*: 1 AUD = 0.581283 USD 1 CAD = 0.673865 USD 1 FF = 0.233117 USD 1 DEM = 0.472237 USD 1 GBP = 1.51539 USD *Reference: European Central Bank 2000, yearly average The evaluation was performed for the 5 countries: Australia, Canada, France, Germany, and Great Britain. All unit costs were given in national currency as well as US$ for comparative purposes . Results Conclusion • Unit costs – understood as multiplicative part of costs as product of • Significant differences in values of unit costs were identified with the Internet research. The country -specific values of comparative unit costs differed a lot. • England and Australia show high differences of unit costs values per type of doctor visit. All five countries have high variances within the different diagnostic procedures, the kind of personal help and the type of traveling. The most differential references for the evaluation of medication costs were found in Germany. price – have a substantial impact on health economic difference by country. amount and evaluations and the • In general the identification of unit costs has to adapt the specific payment systems of health care. It is non- permissible to transfer countryspecific results to other countries. • Because the amount of unit costs differs a lot each health economic study report has to explain and document the used calculation approach. Otherwise the user is unable to prove the robustness of data. Additionally, the performance of sensitivity analysis is aggravated.