Microscope and Cell Study Guide
advertisement

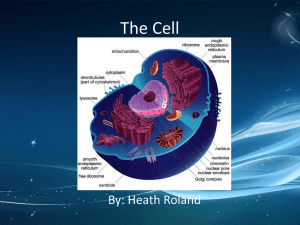
Name__________________________________ Date________________ Period____ Microscope and Cell Study Guide I. Characteristic of Living Things List the 6 characteristics of Living Things 1. Made of Cells 2. Obtain and Use Energy 3. Grow and Develop 4. Adapt 5. Respond 6. Reproduce II. Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems 1. The basic unit of life is the cells 2. Cells form tissue 3. 3 Types of Cells i. blood ii. muscle iii. bone 4. Tissues form organs 5. Skin is the fastest growing organ in your body. 6. Organs form organ systems 7. A unicellular organism is also known as a prokaryotic organism 8. A multicellular organism is also known as a eukaryotic organism 9. Give 3 examples of a prokaryotic Cell i. fungus ii. bacteria iii. archaea Name__________________________________ Date________________ Period____ Microscope and Cell Study Guide 10. Give 3 examples of an eukaryotic cell i. Humans ii. Plants iii. Animals III. Microscope Parts A. Head B. Nose piece C. High Powered Lens D. Stage E. Diaphram F. Eyepiece G. Arm H. Stage Clips J. Coarse Adjustment K. Fine Adjustmen L. Base M. Low Powered Lens N. Medium Powered Lens O. Light Source IV. Microscope Technology 1. Robert Hooke believed that only plants and fungi had cells because the cell were much easier to see in plants than animals. 2. Anton van Leeuwenhoek was the first person to see bacteria under a microscope. Name__________________________________ Date________________ Period____ Microscope and Cell Study Guide 3. In 1000AD the first vision aid was invented called a reading stone 4. In 1590AD the Janssen’s put many Lenses in a tube to enlarge objects V. Animal and Plant Cells Starting on the left going down and then to the right going down LEFT 1. Cell Wall 2. Cell Membrane 3. Vacuole 4. Nucleus 5. Nucleolus 6. SKIP 7. Chloroplast 8. Mitochondria RIGHT 9. Cytoplasm 10. Lysosomes 11. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) 12. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) 13. Ribosomes 14. Golgi Body Name__________________________________ Date________________ Period____ Microscope and Cell Study Guide Starting on the left going down and then to the right going down LEFT 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Cell Membrane Lysosomes Nucleus Nucleolus SKIP Vacuole Mitochondria RIGHT 8. SKIP 9. Cytoplasm 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) 11. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) 12. Ribosomes 13. Golgi Body VI. Cell Functions Directions: Decide if the statement is true or false and correct the false statements. 1. true | false The vacuole produces enzymes. The Vacuole stores raw materials (water, waste and food) Name__________________________________ Date________________ Period____ Microscope and Cell Study Guide 2. true | false The Golgi body processes, sorts, and packages proteins. 3. true | false Ribosomes produce proteins. 4. true | false The rough endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for calcium storage and release. The rough endoplasmic reticulum delivers and transports proteins and other materials 5. true | false The nucleus is commonly called the control center of the cell. 6. true | false The cell wall can be found in animal cells. The cell wall can only be found in plant cells. 7. true | false The nucleus is usually spherical and is the largest structure in the cell. 8. true | false The cell membrane controls what moves into and out of the cell. 9. true | false The chloroplast is where photosynthesis occurs. Name__________________________________ Date________________ Period____ Microscope and Cell Study Guide 10. true | false The mitochondria does not produce ATP The mitochondria does produce ATP. VII. Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis 1. What is the equation for photosynthesis? 2. What is the equation for cellular respiration? 3. What is photosynthesis? The process of making food in a plant cell 4. What is cellular respiration? The process of digesting food in a plant cell and animal cell 5. Where does photosynthesis take place? plant cell 6. Where does cellular respiration take place? plant cell and animal cell Name__________________________________ Date________________ Period____ Microscope and Cell Study Guide VII. Osmosis and Diffusion 1. What is osmosis? Is a special type of diffusion. It describes the movement of water molecules in and out of the cell membrane. 2. What is Diffusion? Is the movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration 3. Which direction does the water move? LEFT TO RIGHT Æ 4. Which way does the nutrients move? It doesn’t move 5. Draw what the beaker will look like after osmosis and diffusion happen.