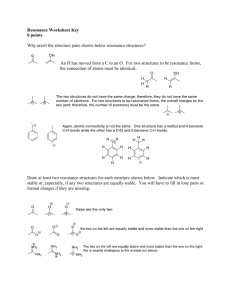
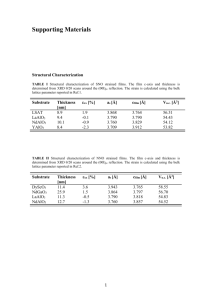
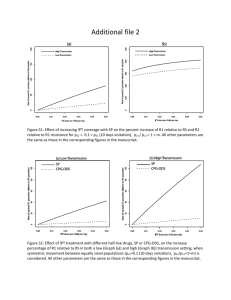
Lewis Structures and B di Bonding
advertisement

Lewis Structures and B di Bonding Chapter 3, MT 2 ... - 6 6 6UMass 6 6 Amherst Created by Karsten Theis Expanded octets; Geometries 9-Sep Ch 3 51-59 HW: Ch 3, #2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 16, 20; assign formal charges and oxidation states to Figure 3.7 Draw Lewis structures with expanded octets; predict geometries - 6 6 6 6 6 2 ... 2 Lewis Dot structures: formal charges are key! Electroneutrality: minimize formal charges (assume covalent bonds Æ shared electrons) • Expanded shells for n > 2 valence shell • Electron deficient central atoms B, Be Let oxidation states be what they may Resonance structures can be stabilizing - 6 6 6 6 6 2 ... 3 VSEPR: Electron pairs repel each other (lp > πbp > σbp); steric number (#lp + #bp) - 6 6 6 6 6 2 ... 4 Which isomer is more stable, NNO versus NON? Why? A) NNO, because it has more resonance forms B) NON, because it has more resonance forms C) NNO, because only it has an expanded octet D) NON, due to electroneutrality E) NNO, due to electroneutrality - 6 6 6 6 6 2 ... 5 Which isomer is more stable, NNO versus NON? Why? A) NNO, because it has more resonance forms B) NON, because it has more resonance forms C) NNO NNO, because only it has an expanded octet D) NON, due to electroneutrality E) NNO, due to electroneutrality - 6 6 6 6 6 2 ... 6 Lewis structures and geometries Rank in order of increasing bond angle: TeF2Br2 XeO3 ClO4CNO- BF2Cl A) CNO- < TeF2Br2 < XeO3 < ClO4- < BF2Cl B) TeF2Br2 < XeO3 < ClO4- < BF2Cl < CNOC) XeO3 < ClO4- < BF2Cl < CNO- < TeF2Br2 D) ClO4- < BF2Cl < CNO- < TeF2Br2 < XeO3 E) BF2Cl < ClO4- < TeF T F2Br B 2 < XeO X O3 < CNO- - 6 6 6 6 6 2 ... 7 Lewis structures and geometries Rank in order of increasing bond angle: TeF2Br2 XeO3 ClO4BF2Cl CNOB) TeF2Br2 < XeO3 < ClO4 < BF2Cl < CNO- - 6 6 6 6 6 2 ... 8 The Unusual [F3S≡NXeF]+ Cation with a Xe–N Bond In 2007, a paper honored Prof. Neil Bartlett (of [Xe][PtF6] fame) on the occasion of his 75th birthday. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 1369-1378. [XeF]+[AsF6]– reacted with liquid N≡SF3 to form the salt [F3S≡NXeF]+[AsF6]–. The [F3S≡NXeF]+ cation offers an unusual example of a xenon bonded to an sp-hybridized nitrogen atom. Your task is to predict (a) the structural features of the [F3S≡NXeF]+ cation; (b) the 19F NMR spectrum; and (c) the 129Xe NMR spectrum. By the way, 14N has a nuclear spin I = 1 and is 99% abundant. However, 14N can be a difficult nucleus for NMR studies due to quadrupolar line broadening. 129Xe-14N coupling was observed in the 129Xe NMR spectrum in addition to 129Xe-19F coupling (the 129Xe-19F coupling constant was significantly larger). Thanks to Margret J. Geselbracht, Reed College - 6 6 6 6 6 2 ... 9