Data Flow Diagram - E-Learning | STMIK AMIKOM Yogyakarta
advertisement

Mata kuliah Analisis dan Desain Sistem Informasi
Data Flow Diagram
{Diagram Arus Data}
Arif Akbarul Huda, S.Si, M.Eng
Data Flow Diagrams (DFD)
●
DFDs describe the flow of data or
information into and out of a system
–
●
what does the system do to the data?
A DFD is a graphic representation of the
flow of data or information through a
system
3
DFD is not a “flow chart”
Flow chart shows “ flow of Control “ .
DFD shows “ flow of Data
The flowchart describes boxes that
describe
computations,
decisions,
interactions & loops.
It is important to keep in mind that
data flow diagrams are not flowcharts
and should not include control elements
.
TYPES OF DFD
Data flow diagrams (DFDs) are categorized as
either logical or physical.
1) LOGICAL DFD:- A logical DFD focuses on the
business and how the business operates. It
describes the business events that take place
and the data required and produced by each
event.
2) PHYSICAL DFD:- A physical DFD shows how
the system will be implemented.
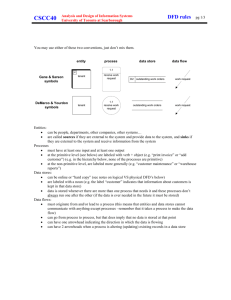
DFD COMPONENTS
Data Flow Diagrams are composed of the four
basic symbols shown below:Data Flow
Process box
External
Entity
D
Data Store
4 Main Elements
external entity - people or organisations
that send data into the system or receive
data from the system
process - models what happens to the data
i.e. transforms incoming data into outgoing
data
data store - represents permanent data
that is used by the system
data flow - models the actual flow of the
data between the other elements
1)External Entity: The sharp cornered rectangles(or simply
boxes) in a DFD indicates entities.
The External Entity symbol represents sources
of data to the system or destinations of data
from the system.
Entities are people things, organizations etc
Entity
ENTITIES
Doctor
Student
Cashier
Teacher
Manager
Customer
User
2) Process: The rounded cornered rectangles in a DFD
indicate processes
The Process symbol represents an activity
that transforms or manipulates the data
(combines, reorders, converts, etc.).
Process
Processes
Accounting
System
Grading System
Reservation
System
Marketing
System
Patient
Administration
System
3) Data Store: Opened sided rectangles in DFD indicates
data store.
The Data Store symbol represents data
that is not moving (delayed data at rest).
A Data Store is a repository of data.
Data can be written into the data store.
This is depicted by an incoming arrow.
Two data stores cannot be connected by a
data flow.
Data can be read from a data store. This is
depicted by an outgoing arrow.
External entity cannot read or write to the data
store.
Data Store
4) Data Flow:
Arrow symbol in DFD indicate data flow
The Data Flow symbol represents
movement of data
Data
RULES OF DATA
FLOW
• Data can flow from
-external entity to process
-process to external entity
-process to store and back
-process to process
• Data cannot flow from
-external entity to external entity
-external entity to store
-store to external entity
-store to store
EXAMPLE 1
This
diagram represents
a
banking process, which maintains
customer accounts.
In this example, customers can withdraw or
deposit cash, request information about
their account or update their account details.
The five different symbols used in this example
represent the full set of symbols required
to draw any business process diagram.
LEVELS OF DFD
Level 0 DFD
• The level 0 DFD (also known as the
context level DFD ) is the simplest DFD.
• The outermost level (Level 0) is
concerned with how the system
interacts with the outside world.
• This level basically represents the input
and output of the entire system.
How to create Level
0 DFD
1. Identify your main system
2. Identify the external people who interact with
the system
3. Decide what data these entities will enter into
the system
4. Determine what these entities expect as
output from the system
Context Level DFD for a Mail
Order Business
CUSTOMER
ORDER
ORDER PROCESSING
DELIVERY
Level 1 DFD
The
basic
module
of
the
system
are
represented in this phase and how data
moves through different module is shown.
The level 1 DFD provides a high –level view
of the system that identifies the major
processes and data stores.
How to create Level
1 DFD
1. Focus on your process and break it into 2
or more sub-processes
2. Identify what data flows between these
processes and between the entities
3. Identify
What permanent data files are
used in this system
4. Note
that
introduced
no
new
entities
can
be
Level 1 DFD for a Mail
Order Business
Order
CUSTOMER
SALES
PROCESSING
Delivery
Credit
Order
Status
Order
CUSTOMER
DATABASE
Credit
Status
Customer
no.
ORDERS
ACCOUNTING
SYSTEM
2-Level DFD and other
level of DFD
Each process from level 1 is exploded even
more into sub processes. This decomposition
continues for each level.
The number of levels possible depends on the
complexity of the system
LEVELLING DFD
A context diagram is expanded into a
number of inter-related processes. Each
process may be further expanded into a set of
inter-connected sub processes. This
procedure of expanding a DFD is known as
leveling.
The value of a
DFD
With a dataflow diagram, users are able to
visualize how the system will operate, what
the system will accomplish, and how the
system will be implemented
2. Data flow diagrams can be used to provide
the end user with physical idea of how the
data they input ultimately has an effect
upon the structure of the whole system.
3. The old system’s dataflow diagrams can also
be drawn up and compared with the new
system’s
dataflow
diagrams
to
draw
comparisons in order to help implement a
1.
Order
OrderSystem
System
New customer
Order
Customer
Invoice
Ship
Statement
Order
System
Picking Slip
Order
Warehouse
Order
OrderSystem
System
New
info
New customer
1
D Customer
1 Master
Add
Customer
2
Customer
Order
Cust Info
Process
Customer
Order
Pending
Order
Backorder
D Back
3 Order
Proc
Info
D Inventory
2 Master
3
Warehouse
Picking
Slip
Produced
Packing
slip
Warehouse
Order
Picked
4
Ship N/A
D Customer
1 Master
Bill N/A
Bill Info
Shipping
Prepare
Ship statement
Customer
Shipping B/O info
5
Customer
Bill
Produce
Cust Bill
Order
OrderSystem
System
2.1
Customer
Order
Need to
establish
D Customer
1 Master
Verify
Customer
Valid
2.2
Customer
Order
Notify
D Inventory
2 Master
Verify
Item
Update
2.4
Valid
Item
Avail
2.3
Check
Available
Back
Order
D Back
3 Order
Update
Commit
D Shipping
4 Taxes
Tax
2.5
Create
Order
Ord D Inventory
2 Master
Pending Order
Questions ?
Your Assignment
References
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Physical_Data_Flow
http://www.visual-paradigm.com/product/bpva/tutorials/dfd.
jsp
http://www.civil.utm.my/staff /file/141/file/CIMLectureNotes2
011.pdf
http://spot.colorado.edu/~kozar/DFDtechnique.html
http://www.fbk.eur.nl/PRJ/MEETEYEES/dfd.htm
Http://ratandon.mysite.syr.edu/cis453/notes/DFD_over_Flow
charts.pdf
http://www.slideshare.net/mohit4192/dfd-examples
http://ecourses.vtu.ac.in/nptel/courses/Webcourseconten
ts/IIScBANG/System%20Analysis%20and%20Design/pdf/module
5.pdf