CRUCIBLE FURNACE
advertisement
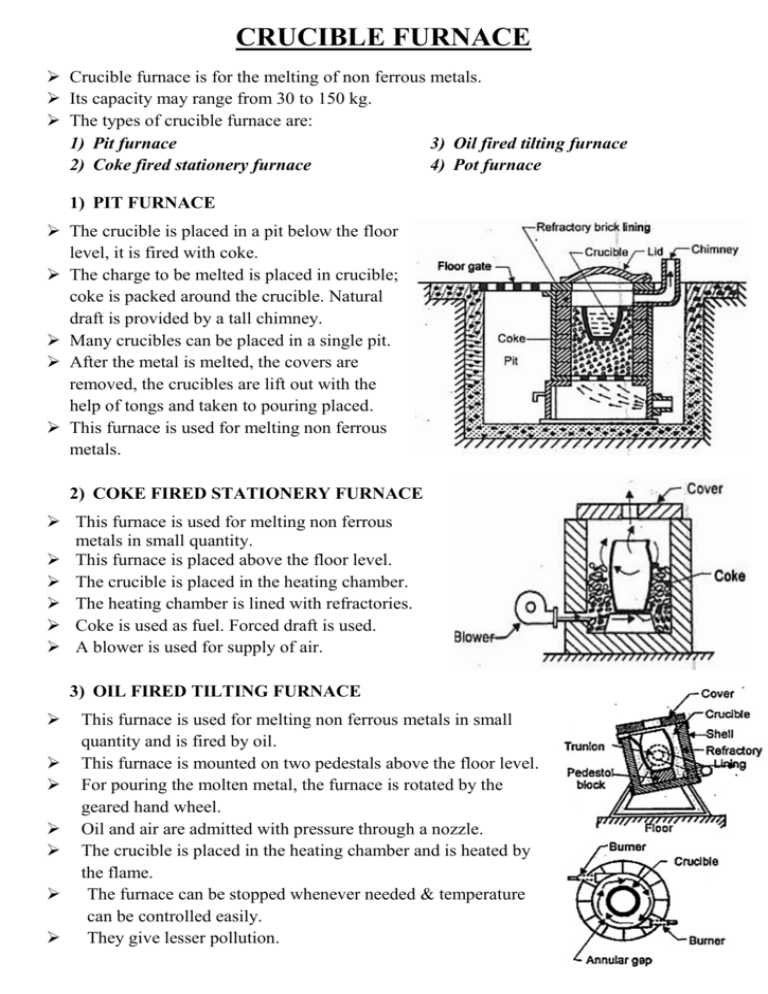
CRUCIBLE FURNACE Crucible furnace is for the melting of non ferrous metals. Its capacity may range from 30 to 150 kg. The types of crucible furnace are: 1) Pit furnace 3) Oil fired tilting furnace 2) Coke fired stationery furnace 4) Pot furnace 1) PIT FURNACE The crucible is placed in a pit below the floor level, it is fired with coke. The charge to be melted is placed in crucible; coke is packed around the crucible. Natural draft is provided by a tall chimney. Many crucibles can be placed in a single pit. After the metal is melted, the covers are removed, the crucibles are lift out with the help of tongs and taken to pouring placed. This furnace is used for melting non ferrous metals. 2) COKE FIRED STATIONERY FURNACE This furnace is used for melting non ferrous metals in small quantity. This furnace is placed above the floor level. The crucible is placed in the heating chamber. The heating chamber is lined with refractories. Coke is used as fuel. Forced draft is used. A blower is used for supply of air. 3) OIL FIRED TILTING FURNACE This furnace is used for melting non ferrous metals in small quantity and is fired by oil. This furnace is mounted on two pedestals above the floor level. For pouring the molten metal, the furnace is rotated by the geared hand wheel. Oil and air are admitted with pressure through a nozzle. The crucible is placed in the heating chamber and is heated by the flame. The furnace can be stopped whenever needed & temperature can be controlled easily. They give lesser pollution. 4) POT FURNACE Pot furnace is used for melting non ferrous metals like aluminum, magnesium, tin, lead etc. The pot is made up of cast iron or steel. The furnace may be fired by gasoline oil or coke. The molten metal is taken out of the pot furnace by using ladles. Normally the capacity of pot furnace is around 500 kg. ELECTRICAL RESISTANT HEATING FURNACE In resistance heating furnaces, the resistance heating elements are used to generate the heat in a heating chamber. The electrical resistance of an electrical element measures its opposition to the passage of an electric current. A heating element converts electricity into heat through the process of Joule heating. Electric current through the element encounters resistance, resulting in heating of the element. The heating elements used are Nichrome wire (80% nickel, 20% chromium), Kanthal wire (Kanthal is the trademark for a family of iron-chromium-aluminium (FeCrAl) alloys) or Graphite rods depending upon the temperature requirements. Metal charge is placed in a crucible or pot which is indirectly heated by heating elements. The temperature is controlled using thermostats and the temperature is monitored by thermocouples. The heating chamber is constructed by M.S. Sheets and channels and for thermal Insulation, fire clay bricks and refractory bricks are used.