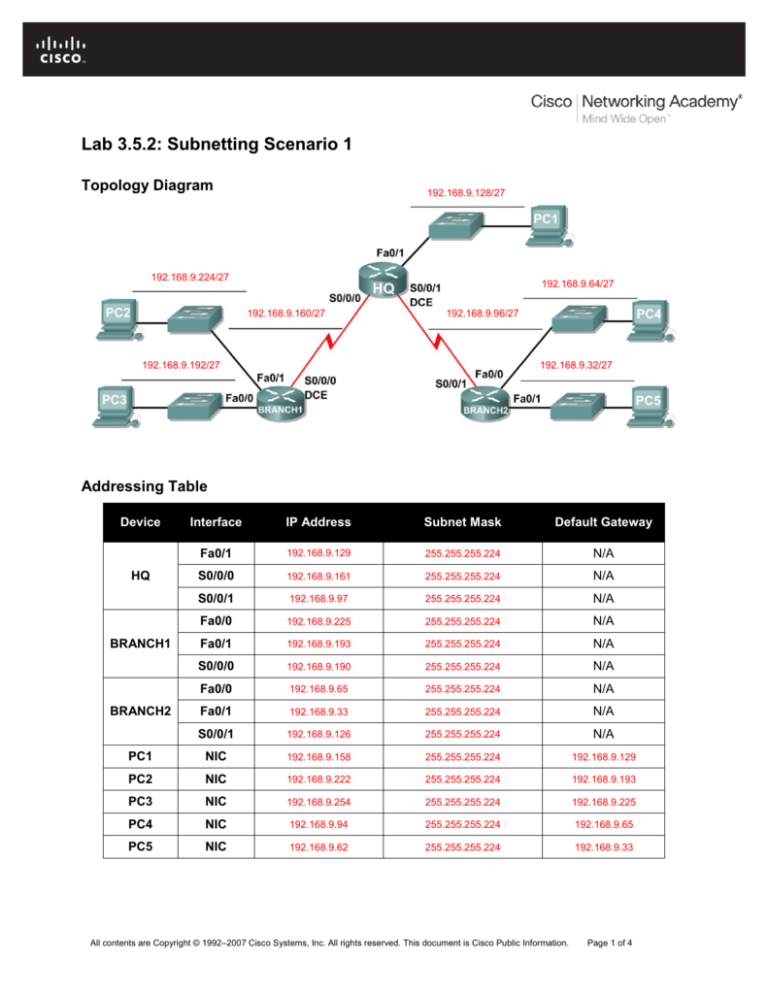
Lab 3.5.2: Subnetting Scenario 1
Topology Diagram
192.168.9.128/27
192.168.9.224/27
192.168.9.64/27
192.168.9.160/27
192.168.9.96/27
192.168.9.192/27
192.168.9.32/27
Addressing Table
Device
Interface
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
Fa0/1
192.168.9.129
255.255.255.224
N/A
S0/0/0
192.168.9.161
255.255.255.224
N/A
S0/0/1
192.168.9.97
255.255.255.224
N/A
Fa0/0
192.168.9.225
255.255.255.224
N/A
Fa0/1
192.168.9.193
255.255.255.224
N/A
S0/0/0
192.168.9.190
255.255.255.224
N/A
Fa0/0
192.168.9.65
255.255.255.224
N/A
Fa0/1
192.168.9.33
255.255.255.224
N/A
S0/0/1
192.168.9.126
255.255.255.224
N/A
PC1
NIC
192.168.9.158
255.255.255.224
192.168.9.129
PC2
NIC
192.168.9.222
255.255.255.224
192.168.9.193
PC3
NIC
192.168.9.254
255.255.255.224
192.168.9.225
PC4
NIC
192.168.9.94
255.255.255.224
192.168.9.65
PC5
NIC
192.168.9.62
255.255.255.224
192.168.9.33
HQ
BRANCH1
BRANCH2
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 1 of 4
CCNA Exploration
Routing Protocols and Concepts:
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
Activity 3.5.2: Subnetting Scenario 1
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to:
Determine the number of subnets needed.
Determine the number of hosts needed.
Design an appropriate addressing scheme.
Assign addresses and subnet mask pairs to device interfaces and hosts.
Examine the use of the available network address space.
Determine how static routing could be applied to the network.
Scenario
In this lab, you have been given the network address 192.168.9.0/24 to subnet and provide the IP
addressing for the network shown in the Topology Diagram. The network has the following addressing
requirements:
The BRANCH1 LAN 1 will require 10 host IP addresses.
The BRANCH1 LAN 2 will require 10 host IP addresses.
The BRANCH2 LAN 1 will require 10 host IP addresses.
The BRANCH2 LAN 2 will require 10 host IP addresses.
The HQ LAN will require 20 host IP addresses.
The link from HQ to BRANCH1 will require an IP address for each end of the link.
The link from HQ to BRANCH2 will require an IP address for each end of the link.
(Note: Remember that the interfaces of network devices are also host IP addresses and are included
in the above addressing requirements.)
Task 1: Examine the Network Requirements.
Examine the network requirements and answer the questions below. Keep in mind that IP addresses will
be needed for each of the LAN interfaces.
7
How many subnets are needed? __________
21
What is the maximum number of IP addresses that are needed for a single subnet? __________
11
How many IP addresses are needed for each of the branch LANs? __________
69
What is the total number of IP addresses that are needed? __________
Task 2: Design an IP Addressing Scheme.
Step 1: Subnet the 192.168.9.0 network into the appropriate number of subnets.
255.255.255.224
What will the subnet mask be for the subnetworks? __________________________
30
How many usable host IP addresses are there per subnet? __________
Fill in the following chart with the subnet information.
Subnet
Number
0
1
2
Subnet Address
First Usable
Host Address
Last Usable
Host Address
Broadcast
Address
192.168.9.0
192.168.9.32
192.168.9.64
192.168.9.1
192.168.9.30
192.168.9.31
192.168.9.33
192.168.9.62
192.168.9.63
192.168.9.65
192.168.9.94
192.168.9.95
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 2 of 4
CCNA Exploration
Routing Protocols and Concepts:
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
Subnet
Number
3
4
5
6
7
Subnet Address
192.168.9.96
192.168.9.128
Activity 3.5.2: Subnetting Scenario 1
First Usable
Host Address
Last Usable
Host Address
Broadcast
Address
192.168.9.97
192.168.9.126
192.168.9.95
192.168.9.129
192.168.9.158
192.168.9.159
192.168.9.160
192.168.9.161
192.168.9.190
192.168.9.191
192.168.9.192
192.168.9.193
192.168.9.222
192.168.9.223
192.168.9.224
192.168.9.225
192.168.9.254
192.168.9.255
Step 2: Assign the subnets to the network shown in the Topology Diagram.
When assigning the subnets, keep in mind that routing will need to occur to allow information to be sent
throughout the network. The subnets will be assigned to the networks to allow for route summarization on
each of the routers.
1. Assign first subnet (lowest subnet) to the LAN connected to the Fa0/1 interface of BRANCH2.
192.168.9.32/27
What is the subnet address? ____________________
2. Assign second subnet to LAN connected to the Fa0/0 interface of BRANCH2. What is the subnet
192.168.9.64/27
address? ____________________
3. Assign third subnet to LAN connected to the Fa0/0 interface of BRANCH1. What is the subnet
192.168.9.96/27
address? ____________________
4. Assign fourth subnet to LAN connected to the Fa0/1 interface of BRANCH1. What is the subnet
192.168.9.128/27
address? ____________________
5. Assign fifth subnet to the WAN link from HQ to BRANCH1. What is the subnet address?
192.168.9.160/27
____________________
192.168.9.192/27
6. Assign sixth subnet to the WAN link from HQ to BRANCH2. ____________________
7. Assign seventh subnet to LAN connected to the Fa0/1 interface of HQ. What is the subnet
192.168.9.224/27
address? ____________________
Note: The highest subnet will not be required in this topology.
Task 3: Assign IP Addresses to the Network Devices
Assign the appropriate addresses to the device interfaces. Document the addresses to be used in the
Addressing Table provided under the Topology Diagram.
Step 1: Assign addresses to the HQ router.
1. Assign the first valid host address in the HQ LAN subnet to the LAN interface.
2. Assign the first valid host address in link from HQ to BRANCH1 subnet to the S0/0/0 interface.
3. Assign the first valid host address in link from HQ to BRANCH2 subnet to the S0/0/1 interface.
Step 2: Assign addresses to the BRANCH1 router.
1. Assign the first valid host address in the BRANCH1 LAN 1 subnet to the Fa0/0 LAN interface.
2. Assign the first valid host address in the BRANCH1 LAN 2 subnet to the Fa0/1 LAN interface.
3. Assign the last valid host address in link from HQ to BRANCH1 subnet to the WAN interface.
Step 3: Assign addresses to the BRANCH2 router.
1. Assign the first valid host address in the BRANCH2 LAN 1 subnet to the Fa0/0 LAN interface.
2. Assign the first valid host address in the BRANCH2 LAN 2 subnet to the Fa0/1 LAN interface.
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 3 of 4
CCNA Exploration
Routing Protocols and Concepts:
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
Activity 3.5.2: Subnetting Scenario 1
3. Assign the last valid host address in link from HQ to BRANCH2 subnet to the WAN interface.
Step 4: Assign addresses to the host PCs.
1. Assign the last valid host address in the HQ LAN subnet to PC1.
2. Assign the last valid host address in the BRANCH1 LAN 1 subnet to PC2.
3. Assign the last valid host address in the BRANCH1 LAN 2 subnet to PC3.
4. Assign the last valid host address in the BRANCH2 LAN 1 subnet to PC4.
5. Assign the last valid host address in the BRANCH2 LAN 2 subnet to PC5.
Task 4: Test the Network Design.
Apply your addressing scheme. Check to see that all devices on directly connected networks can ping
each other.
Task 5: Reflection
185
How many IP address in the 192.168.9.0 network are unused or unusable in this design? __________
What would the command be to add a default static route on the WAN interface of the BRANCH1 router?
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0
___________________________________________________________________________________
yes
Can both of the BRANCH1 LANs be summarized into one route on the HQ router? _________
What would be the command used to add this summary route to the routing table?
ip route 192.168.9.192 255.255.255.192 s0
___________________________________________________________________________________
yes
Can both of the BRANCH2 LANs be summarized into one route on the HQ router? __________
What would be the command used to add this summary route to the routing table?
ip route 192.168.9.0 255.255.255.128 s0
___________________________________________________________________________________
Can the HQ LAN and both of the BRANCH1 LANs be summarized into one route on the BRANCH2
router? This summarized route should also include the link between the HQ and BRANCH1 routers.
yes
__________
What would be the command used to add this summary route to the routing table?
ip route 192.168.9.128 255.255.255.128 s1
___________________________________________________________________________________
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 4 of 4
Lab 3.5.3: Subnetting Scenario 2
Topology Diagram
172.16.16.0/23
172.16.18.0/23
172.16.14.0/23
172.16.12.0/23
172.16.20.0/23
172.16.10.0/23
172.16.24.0/23
172.16.8.0/23
172.16.22.0/23
172.16.6.0/23
172.16.2.0/23
172.16.4.0/23
172.16.26.0/23
172.16.28.0/23
172.16.30.0/23
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 1 of 7
CCNA Exploration
Routing Protocols and Concepts:
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
Activity 3.5.3: Subnetting Scenario 2
Addressing Table
Device
Interface
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
ISP
S0/0/0
209.165.200.227
255.255.255.224
N/A
Fa0/0
172.16.16.1
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/0/0
172.16.14.1
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/0/1
172.16.18.1
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/1/0
209.165.200.226
255.255.255.224
N/A
Fa0/0
172.16.12.1
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/0/0
172.16.15.254
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/0/1
172.16.8.1
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/1/0
172.16.10.0
255.255.254.0
N/A
Fa0/0
172.16.20.1
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/0/0
172.16.19.254
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/0/1
172.16.22.1
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/1/0
172.16.24.1
255.255.254.0
N/A
Fa0/0
172.16.2.1
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/0/0
172.16.9.254
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/0/1
172.16.6.1
255.255.254.0
N/A
Fa0/0
172.16.4.1
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/0/0
172.16.11.254
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/0/1
172.16.7.254
255.255.254.0
N/A
Fa0/0
172.16.28.1
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/0/0
172.16.23.254
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/0/1
172.16.26.1
255.255.254.0
N/A
Fa0/0
172.16.30.1
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/0/0
172.16.25.254
255.255.254.0
N/A
S0/0/1
172.16.27.254
255.255.254.0
N/A
PC1
NIC
172.16.17.254
255.255.254.0
172.16.16.1
PC2
NIC
172.16.13.254
255.255.254.0
172.16.12.1
PC3
NIC
172.16.21.254
255.255.254.0
172.16.20.1
PC4
NIC
172.16.3.254
255.255.254.0
172.16.2.1
PC5
NIC
172.16.5.254
255.255.254.0
172.16.4.1
PC6
NIC
172.16.29.254
255.255.254.0
172.16.28.1
PC7
NIC
172.16.31.254
255.255.254.0
172.16.30.1
HQ
West
East
Branch 1
Branch 2
Branch 3
Branch 4
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 2 of 7
CCNA Exploration
Routing Protocols and Concepts:
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
Activity 3.5.3: Subnetting Scenario 2
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to:
Determine the number of subnets needed.
Determine the number of hosts needed.
Design an appropriate addressing scheme.
Assign addresses and subnet mask pairs to device interfaces and hosts.
Examine the use of the available network address space.
Determine how static routing could be applied to the network.
Scenario
In this lab, you have been given the network address 172.16.0.0/16 to subnet and provide the IP
addressing for the network shown in the Topology Diagram. The network has the following addressing
requirements:
The Branch 1 LAN will require 100 host IP addresses.
The Branch 2 LAN will require 100 host IP addresses.
The Branch 3 LAN will require 100 host IP addresses.
The Branch 4 LAN will require 100 host IP addresses.
The West LAN will require 400 hosts.
The East LAN will require 400 hosts.
The HQ LAN will require 500 host IP addresses.
The links between each of the routers will require an IP address for each end of the link.
(Note: Remember that the interfaces of network devices are also host IP addresses and are included
in the above addressing requirements.)
The IP addresses for the link from the HQ router to the ISP have already been assigned. The Serial 0/1/0
address of the HQ router is 209.165.200.226/27. The IP address of the Serial 0/0/0 of the ISP router is
209.165.200.227/27.
Task 1: Examine the Network Requirements.
Examine the network requirements and answer the questions below. Keep in mind that IP addresses will
be needed for each of the LAN interfaces.
15
How many subnets are needed? __________
501
What is the maximum number of IP addresses that are needed for a single subnet? __________
101
How many IP addresses are needed for each of the branch LANs? __________
16
How many IP addresses are needed for all of the connections between routers? __________
1723
What is the total number of IP addresses that are needed? __________
Task 2: Design an IP Addressing Scheme.
Step 1: Subnet the 172.16.0.0 network based on the maximum number of hosts required by the
largest subnet.
255.255.254.0
What will the subnet mask be for the subnetworks? _________________________
510
How many usable host IP addresses are there per subnet? __________
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 3 of 7
CCNA Exploration
Routing Protocols and Concepts:
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
Activity 3.5.3: Subnetting Scenario 2
Fill in the following chart with the subnet information.
Subnet
Number
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Subnet IP
172.16.0.0
172.16.2.0
172.16.4.0
172.16.6.0
172.16.8.0
172.16.10.0
172.16.12.0
172.16.14.0
172.16.16.0
172.16.18.0
172.16.20.0
172.16.22.0
172.16.24.0
172.16.26.0
172.16.28.0
172.16.30.0
First Usable Host IP
172.16.0.1
172.16.2.1
172.16.4.1
172.16.6.1
172.16.8.1
172.16.10.1
172.16.12.1
172.16.14.1
172.16.16.1
172.16.18.1
172.16.20.1
172.16.22.1
172.16.24.1
172.16.26.1
172.16.28.1
172.16.30.1
Last Usable Host IP
172.16.1.254
172.16.3.254
172.16.5.254
172.16.7.254
172.16.9.254
172.16.11.254
172.16.13.254
172.16.15.254
172.16.17.254
172.16.19.254
172.16.21.254
172.16.23.254
172.16.25.254
172.16.27.254
172.16.29.254
172.16.31.254
Broadcast
Address
172.16.1.255
172.16.3.255
172.16.5.255
172.16.7.255
172.16.9.255
172.16.11.255
172.16.13.255
172.16.15.255
172.16.17.255
172.16.19.255
172.16.21.255
172.16.23.255
172.16.25.255
172.16.27.255
172.16.29.255
172.16.31.255
Step 2: Assign the subnets to the network shown in the Topology Diagram.
When assigning the subnets, keep in mind that routing will need to occur to allow information to be sent
throughout the network. The subnets will be assigned to the networks to allow for route summarization on
each of the routers.
Note: The lowest subnet (subnet 0) will not be assigned in this lab. You should start assigning with the
second lowest subnet (subnet 1).
172.16.2.0/23
1. Assign subnet 1 to the Branch 1 LAN subnet: ____________________
172.16.4.0/23
2. Assign subnet 2 to the Branch 2 LAN subnet: ____________________
172.16.6.0/23
3. Assign subnet 3 to the link between the Branch 1 and Branch 2 routers: ____________________
172.16.8.0/23
4. Assign subnet 4 to the link between the Branch 1 and West routers: ____________________
172.16.10.0/23
5. Assign subnet 5 to the link between the Branch 2 and West routers: ____________________
172.16.12.0/23
6. Assign subnet 6 to the West LAN subnet: ____________________
172.16.14.0/23
7. Assign subnet 7 to the link between the West and HQ routers: ____________________
172.16.16.0/23
8. Assign subnet 8 to the HQ LAN subnet: ____________________
172.16.18.0/23
9. Assign subnet 9 to the link between the HQ and East routers: ____________________
172.16.20.0/23
10. Assign subnet 10 to the East LAN subnet: ____________________
172.16.22.0/23
11. Assign subnet 11 to the link between the Branch 3 and East routers: ____________________
172.16.24.0/23
12. Assign subnet 12 to the link between the Branch 4 and East routers: ____________________
172.16.26.0/23
13. Assign subnet 13 to the link between the Branch 3 and Branch 4 routers: ___________________
172.16.28.0/23
14. Assign subnet 14 to the Branch 3 subnet: ____________________
172.16.30.0/23
15. Assign subnet 15 to the Branch 4 subnet: ____________________
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 4 of 7
CCNA Exploration
Routing Protocols and Concepts:
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
Activity 3.5.3: Subnetting Scenario 2
Task 3: Assign IP Addresses to the Network Devices.
Assign the appropriate addresses to the device interfaces. Document the addresses to be used in the
Addressing Table provided under the Topology Diagram.
Step 1: Assign addresses to the HQ router.
1. Assign the first valid host address in the HQ LAN subnet to the LAN interface.
2. Assign the first valid host address in the link from HQ to West subnet to the S0/0/0 interface.
3. Assign the first valid host address in the link from HQ to East subnet to the S0/0/1 interface.
Step 2: Assign addresses to the West router.
1. Assign the first valid host address in the West LAN subnet to the LAN interface.
2. Assign the last valid host address in the link from HQ to West subnet to the S0/0/0 interface.
3. Assign the first valid host address in the link from West to Branch 1 subnet to the S0/0/1
interface.
4. Assign the first valid host address in the link from West to Branch 2 subnet to the S0/1/0
interface.
Step 3 Assign addresses to the East router.
1. Assign the first valid host address in the East LAN subnet to the LAN interface.
2. Assign the last valid host address in the link from HQ to East subnet to the S0/0/0 interface.
3. Assign the first valid host address in the link from East to Branch 3 subnet to the S0/0/1 interface.
4. Assign the first valid host address in the link from East to Branch 4 subnet to the S0/1/0 interface.
Step 4 Assign addresses to the Branch 1 router.
1. Assign the first valid host address in the Branch 1 LAN subnet to the LAN interface.
2. Assign the last valid host address in the link from West to Branch 1 subnet to the S0/0/0 interface.
3. Assign the first valid host address in the link from Branch 1 to Branch 2 subnet to the S0/0/1
interface.
Step 5 Assign addresses to the Branch 2 router.
1. Assign the first valid host address in the Branch 2 LAN subnet to the LAN interface.
2. Assign the last valid host address in the link from West to Branch 2 subnet to the S0/0/0 interface.
3. Assign the last valid host address in the link from Branch 1 to Branch 2 subnet to the S0/0/1
interface.
Step 6 Assign addresses to the Branch 3 router.
1. Assign the first valid host address in the Branch 3 LAN subnet to the LAN interface.
2. Assign the last valid host address in the link from East to Branch 3 subnet to the S0/0/0 interface.
3. Assign the first valid host address in the link from Branch 3 to Branch 4 subnet to the S0/0/1
interface.
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 5 of 7
CCNA Exploration
Routing Protocols and Concepts:
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
Activity 3.5.3: Subnetting Scenario 2
Step 7 Assign addresses to the Branch 4 router.
1. Assign the first valid host address in the Branch 4 LAN subnet to the LAN interface.
2. Assign the last valid host address in the link from East to Branch 4 subnet to the S0/0/0 interface.
3. Assign the last valid host address in the link from Branch 3 to Branch 4 subnet to the S0/0/1
interface.
Step 8 Assign addresses to the host PCs
1. Assign the last valid host address in the HQ LAN subnet to PC1.
2. Assign the last valid host address in the West LAN subnet to PC2.
3. Assign the last valid host address in the East 1 LAN subnet to PC3.
4. Assign the last valid host address in the Branch 1 LAN subnet to PC4.
5. Assign the last valid host address in the Branch 2 LAN subnet to PC5.
6. Assign the last valid host address in the Branch 3 LAN subnet to PC6.
7. Assign the last valid host address in the Branch 4 LAN subnet to PC7.
Task 4: Test the Network Design.
Apply your addressing scheme. Check to see that all devices on directly connected networks can ping
each other.
Task 5: Reflection
63811
How many IP address in the 172.16.0.0 network are wasted in this design? __________
What would the command be to add a default static route for your entire network design from the HQ
router to the ISP router?
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 209.165.200.2274
___________________________________________________________________________________
Can the West, Branch 1, and Branch 2 networks be summarized into one route on the HQ router? This
summarized route should also include the serial links that connect the West, Branch 1, and Branch 2
yes
routers. __________
What would be the command used to add this summary route to the routing table?
ip route 172.16.0.0 255.255.240.0 s0/0
___________________________________________________________________________________
Can the East, Branch 3, and Branch 4 networks be summarized into one route on the HQ router? This
summarized route should also include the serial links that connect the East, Branch 3, and Branch 4
yes
routers. __________
What would be the command used to add this summary route to the routing table?
ip route 172.16.16.0 255.255.240.0 s0/1
___________________________________________________________________________________
What would the command be to add a default static route on the West router to send traffic for all
unknown destinations to the HQ router?
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0
___________________________________________________________________________________
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 6 of 7
CCNA Exploration
Routing Protocols and Concepts:
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
Activity 3.5.3: Subnetting Scenario 2
What would the command be to add a default static route on the East router to send traffic for all
unknown destinations to the HQ router?
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0
___________________________________________________________________________________
Can the Branch 1 and Branch 2 networks be summarized into one route on the West router? This
summarized route should also include the serial link that connects the Branch 1 and Branch 2 routers.
yes
__________
What would be the command used to add this summary route to the routing table? Use the S0/0/1
interface of the West router as the exit interface.
ip route 172.06.0.0 255.255.248.0 s0/1
___________________________________________________________________________________
Can the Branch 3 and Branch 4 networks be summarized into one route on the East router? This
summarized route should also include the serial link that connects the Branch 3 and Branch 4 routers.
yes
__________
What would be the command used to add this summary route to the routing table? Use the S0/0/1
interface of the East router as the exit interface.
ip route 172.16.24.0 255.255.248 s0/1
___________________________________________________________________________________
The Branch 1 router requires a static route for traffic destined for Branch 2. All other traffic should be sent
to the West router using a default static route. What commands would be used to accomplish this?
ip route 172.16.4.0 255.255.254.0 s0/1
___________________________________________________________________________________
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0
___________________________________________________________________________________
The Branch 2 router requires a static route for traffic destined for Branch 1. All other traffic should be sent
to the West router using a default static route. What commands would be used to accomplish this?
ip route 172.16.2.0 255.255.254.0 s0/1
___________________________________________________________________________________
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0
___________________________________________________________________________________
The Branch 3 router requires a static route for traffic destined for Branch 4. All other traffic should be sent
to the East router using a default static route. What commands would be used to accomplish this?
ip route 172.16.30.0 255.255.254.0 s0/1
___________________________________________________________________________________
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0
___________________________________________________________________________________
The Branch 4 router requires a static route for traffic destined for Branch 3. All other traffic should be sent
to the East router using a default static route. What commands would be used to accomplish this?
ip route 172.16.28.0 255.255.254.0 s0/1
___________________________________________________________________________________
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 s0/0
___________________________________________________________________________________
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 7 of 7
Lab 3.5.4: Subnetting Scenario 3
Topology Diagram
Addressing Table
Device
HQ
BRANCH1
BRANCH2
Interface
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
Fa0/0
N/A
S0/0/0
N/A
S0/0/1
N/A
Fa0/0
N/A
Fa0/1
N/A
S0/0/0
N/A
S0/0/1
N/A
Fa0/0
N/A
Fa0/1
N/A
S0/0/0
N/A
S0/0/1
N/A
PC1
NIC
PC2
NIC
PC3
NIC
PC4
NIC
PC5
NIC
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 1 of 3
CCNA Exploration
Routing Protocols and Concepts:
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
Activity 3.5.4: Subnetting Scenario 3
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this lab, you will be able to:
Determine the number of subnets needed.
Determine the number of hosts needed.
Design an appropriate addressing scheme.
Conduct research to find a possible solution.
Scenario
In this lab, you have been given the network address 192.168.1.0/24 to subnet and provide the IP
addressing for the network shown in the Topology Diagram. The network has the following addressing
requirements:
The BRANCH1 LAN 1 will require 15 host IP addresses.
The BRANCH1 LAN 2 will require 15 host IP addresses.
The BRANCH2 LAN 1 will require 15 host IP addresses.
The BRANCH2 LAN 2 will require 15 host IP addresses.
The HQ LAN will require 70 host IP addresses.
The link from HQ to BRANCH1 will require an IP address for each end of the link.
The link from HQ to BRANCH2 will require an IP address for each end of the link.
The link from HQ to BRANCH1 to BRANCH2 will require an IP address for each end of the link.
(Note: Remember that the interfaces of network devices are also host IP addresses and are included
in the above addressing requirements.)
Task 1: Examine the Network Requirements.
Examine the network requirements and answer the questions below. Keep in mind that IP addresses will
be needed for each of the LAN interfaces.
How many subnets are needed? __________
What is the maximum number of IP addresses that are needed for a single subnet? __________
How many IP addresses are needed for each of the branch LANs? __________
What is the total number of IP addresses that are needed? __________
Task 2: Design an IP Addressing Scheme
Subnet the 192.168.1.0/24 network into the appropriate number of subnets.
Can the 192.168.1.0/24 network be subnetted to fit the network requirements? __________
If the “number of subnets” requirement is met, what is the maximum number of hosts per subnet?
__________
If the “maximum number of hosts” requirement is met, what is the number of subnets that will be available
to use? __________
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 2 of 3
CCNA Exploration
Routing Protocols and Concepts:
Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
Activity 3.5.4: Subnetting Scenario 3
Task 3: Reflection
You do not have enough address space to implement an addressing scheme. Research this problem and
propose a possible solution. Increasing the size of your original address space is not an acceptable
solution. (Hint: We will discuss solutions to this problem in Chapter 6.)
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
Attempt to implement your solution. Successful implementation of a solution requires that:
Only the 192.168.1.0/24 address space is used.
PCs and routers can ping all IP addresses.
All contents are Copyright © 1992–2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 3 of 3