Urinary System Notes
advertisement

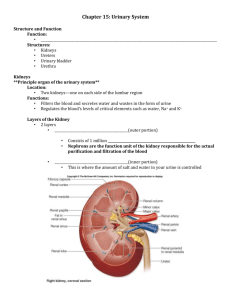
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY & CONTRAST STUDIES URINARY SYSTEM TERMINOLOGY Ectopic - Congenital disorder in which kidneys fail to assume their proper position in abdomen Frequency - Having to urinate often Hematuria - Blood in urine Horseshoe Kidney - Congenital condition in which the lower poles of the kidneys are fused together Hydronephrosis - Dilation of renal pelvis & calyces with urine due to ureteral obstruction URINARY SYSTEM TERMINOLOGY Hypertension - High blood pressure, may be caused by narrowing of the renal arteries, the large amount of blood which is delivered to the kidneys (25% of stroke volume) can cause increased pressure if the flow is restricted by a narrowed renal artery Incontinence - Inability to control micturation, involuntary urination Micturation - The act of urination URINARY SYSTEM TERMINOLOGY Nephrolithotripsy - Procedure in which renal calculi are broken up, or fragmented, into smaller pieces to facilitate removal, may be done percutaneously as a surgical-type procedure or with sound waves in a water bath Polycystic Kidney - Congenital condition in which fluid-filled sacs are present in renal parenchyma, often fatal in newborns, also seen in older adults Ptosis - Condition in which kidney drops from its normal position in abdomen, usually from weakness of the abdominal muscles URINARY SYSTEM TERMINOLOGY Pyelocystitis - Inflammation of bladder & renal pelvis Pyelolithotomy - Surgical removal of kidney stones through an incision into renal pelvis Pyelonephritis - Inflammatory disorder of renal parenchyma & pelvis Reflux - Abnormal backflow of urine from bladder into ureters Retention - Inability to void URINARY SYSTEM TERMINOLOGY Retrograde - Against flow, type of urographic exam done in surgery where contrast is injected by catheter placed from the urethra into renal pelvis Suppression - When kidneys are not producing urine Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (T.U.R.P.) Surgical procedure in which prostate is removed by placing a cutting device into prostate via urethra Urinary Stone (kidney stone or renal calculi) - Calculi formed in collecting tubules & migrate to renal pelvis, attributed to abnormal metabolism Uremia - Excessive amounts of urea in blood URINARY SYSTEM Anatomy Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Bladder (1) Urethra (1) Adrenals (2) Kidneys Ureters not strictly part of urinary system Bladder URINARY SYSTEM Kidney Anatomy Location Lie on either side of spine at the level of T-11 to L-3 Right kidney is lower than left Retroperitoneal Physical Characteristics Bean-shaped Size: » 11 cm long » 6 cm wide » 3 cm thick » Weighs 150 g. URINARY SYSTEM Kidney Anatomy Physical Characteristics Functional part of system Blood supply » Renal Artery » Renal vein Movement: » Respiratory • Normal - 3 cm • Deep - 5 cm » Prone to erect - 5 cm URINARY SYSTEM Kidney Physiology Functions: Remove nitrogenous wastes Regulate fluid balance Regulate Acid-Base balance Removes 180 L. of filtrate/day, but 99% is reabsorbed. Produces 1.5 L. of urine/day - requires 2.5 L. fluid intake/day URINARY SYSTEM Kidney - Macroscopic Anatomy Adipose Capsule Perirenal fat Fibrous Capsule Cortex Highly vascular Functional area Contains nephron units Medulla - Collecting area Collecting tubules Renal pyramids - 8-18 funnelshaped Minor calyces - 4-13 cup-shaped Major calyces - 2-3 Renal Pelvis Hilum - Entry/Exit for: Renal artery Renal vein Ureter URINARY SYSTEM - Kidney Microscopic Anatomy - Nephron Units Glomeruli (capillary tuft) - filtration area Afferent Arteriole - provides blood supply to glomeruli Efferent Arteriole - returns blood from glomeruli Bowman’s Capsule - surrounds glomeruli Convoluted tubule - readsorption area Proximal Loop of Henle Distal Collecting Tubules URINARY SYSTEM Ureter Anatomy Function - Transport urine to bladder by peristalsis & gravity Physical Characteristics 28-34 cm long 1 mm diameter S-shaped, following curvature of spine Three points of narrowing: » Ureteropelvic junction » pelvic brim » Ureterovesical junction URINARY SYSTEM Bladder Anatomy Musculomembranous sac Elastic - balloon-like as it fills, normally flat Holds 500+ cc’s, urge to urinate at 250 cc’s Trigone Defined by the entry of the 2 ureters & exit of urethra Contains “bladder flaps” to prevent reflux Apex is marked by the internal urethral orifice URINARY SYSTEM Urethra Anatomy Function - Transport urine to exterior of body Physical Characteristics Female - 4 cm long URINARY SYSTEM Urethra Anatomy Physical Characteristics Male - 20 cm long » Proximal (prostatic portion) - 3 cm » Middle (membranous portion) - 2 cm » Distal (cavernous portion) - 15 cm URINARY SYSTEM Contrast Studies Urography - General term denoting study of the urinary system. Purpose - Conventional radiography does not adequately differentiate soft tissue. The introduction of contrast media into the structure facilitates differentiation. URINARY SYSTEM Contrast Studies Contrast Media Types - Water-soluble Iodine » Injectible - Renografin, Hypaque, Isovue, etc.. » Non-injectible - Cystografin, Cysto-Conray, Retrografin, etc.. Concentration - varies with study & routing » Drip infusion - low concentration » IV bolus - medium concentration » Retrograde - high concentration Routing » Indirect - IVP » Direct - all others URINARY SYSTEM Contrast Studies Injection Procedure Prepare patient psychologically & physically Obtain patient history Select & prepare contrast media Check availability of crash cart or emergency tray BE PREPARED FOR A REACTION! URINARY SYSTEM Intravenous Pyelogram Most common urographic study More correctly it is Excretory Urography (XU), however, it is more commonly referred to as an Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP) This is a functional exam, assessing the filtration system and visualizing the minor calyces, major calyces, renal pelvis, ureters, & bladder URINARY SYSTEM IVP Indications Renal failure Abdominal/pelvic mass Renal/ureteral calculi Kidney trauma Flank pain Hematuria Preop pelvic surgery Hypertension Urinary tract infection (UTI) Contraindications Anuria Hypersensitivity to contrast Increased risk » Multiple myeloma » Diabetes » Severe hepatic or renal disease » Congestive anemia » Dehydration URINARY SYSTEM IVP Patient Preparation Light dinner the night before. Laxative &/or enema No food for 8-12 hours, liquids permitted. Have patient empty bladder just before exam. Have patient remove all clothing except shoes & socks & put on gown. URINARY SYSTEM IVP Room Preparation Draw up contrast Gather venipuncture supplies Check Crash cart/drug box Cassettes & markers available Doctor available Scout film - KUB Used by Radiologist to check prep & abnormalities. Used by Tech. to check positioning & technique. Used by both to check position of various structures. URINARY SYSTEM IVP Stasis - Stagnation of normal fluid flow Trendelenburg Compression - do not use if: » Stones » Mass » Aortic aneurysm » Recent surgery » Severe pain » Acute Trauma URINARY SYSTEM IVP Routine Procedure - overhead films, conventional tomography optional Films are taken at specific time intervals to provide best visualization of various parts. Timing begins with start of injection/infusion. Routines vary, see local protocol First film is a nephrogram because opacification of the nephron units permit visualization of the cortex (30 sec. to 1 min.) URINARY SYSTEM IVP Routine Procedure - example 1 min. - AP supine centered at kidneys (11 x 14 cw) 5 min. - AP supine centered at kidneys (11 x 14 cw) 10 min. - AP supine, RAO, LAO centered at kidneys (11 x 14 cw) OPTIONAL - Tomos instead of obliques 15 min. - KUB (14 x 17 lw) Erect or prone post-void centered at bladder (10 x 12 cw) URINARY SYSTEM IVP Variation - Hypertensive IVP - same are regular IVP except filming is accelerated: AP supine centered at kidneys (11 x 14 cw) at 30 sec., 1, 2, 3, 4, & 5 min. Continue as for Routine IVP URINARY SYSTEM IVP AP supine centered at kidneys (11 x 14 cw) Place bottom of cassette at level of ASIS & center to film URINARY SYSTEM IVP AP Oblique Projections - 30° Oblique CR – Level of Crest, 2” lat. to midline on elevated side URINARY SYSTEM IVP OPTIONAL - Tomos instead of obliques URINARY SYSTEM IVP KUB CR – MSP & Iliac crest URINARY SYSTEM IVP Erect or prone postvoid centered at bladder 10 x 12 cw CR – 10 ° -15° caudal CR 2” above pubic symphysis & center cassette to CR URINARY SYSTEM Retrograde Pyelogram Non-functional exam Generally surgical w/ sedation or under general Contrast injected directly into collecting system through a catheter 3-5 cc’s of iodinated contrast Filming routine AP scout AP Pyelogram AP Ureterogram URINARY SYSTEM Cystogram Non-functional exam Visualizes urinary bladder only 150-500 cc’s of contrast introduced by gravity via a catheter Filming routine o AP - 15 caudad o Both obliques - 60 Optional - Lateral URINARY SYSTEM Cystogram o AP - 15 caudad URINARY SYSTEM Cystogram Both obliques – 40°-60° CR – perpendicular, 2” above Pubic Symphysis & 2” medial to ASIS URINARY SYSTEM Voiding Cystourethrogram Same as cystogram except that after bladder is filled, catheter is remove & radiographs are taken as patient voids Filming - as previously stated plus o Male - 30 RPO Female - AP URINARY SYSTEM Miscellaneous Bead-Chain Cystogram Performed only on females with stress-incontinence Chain used to determine anatomical relationship between bladder & urethra Requires about 60 cc’s contrast - only voiding films are needed Filming - AP & Lat... relaxed & straining (4 films) URINARY SYSTEM Miscellaneous Retrograde Urethrogram Performed to visualize full length of the male urethra Utilizes a Brodney Clap attached to glans of penis 50 cc’s Iodinated contrast media mixed with KY jelly o Filming - 30 RPO URINARY SYSTEM Miscellaneous Renal Arteriogram – demonstrating pronounced nephrogram phase in upper pole of the left kidney.