Cell Structure Flashcards
advertisement

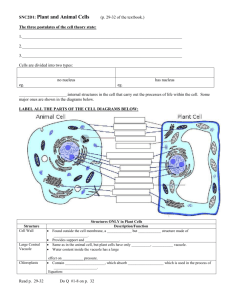
CELL STRUCTURE FLASHCARDS Directions: 1. Obtain two Bacterial Cell flashcard sheets. Each sheet has six flashcards illustrating a bacterium. 2. Neatly cut out the six flashcards on each Bacterial Cell sheet for a total of 12 flashcards. 3. Choose one flashcard and write the word “nucleoid” in the space titled ‘Structure.’ 4. In the space titled ‘Function,’ describe the function of the nucleoid. 5. Identify the nucleoid in the flashcard illustration and use a color pencil or marker to color it in. You may instead choose to draw a colored line or arrow pointing at the structure. 6. In column 1 of the table below, you will find the flashcard number for ‘Nucleoid’ is the number “1”. In the small box located in the corner of the illustration side of the flashcard, write the number “1.” 7. Fold the flashcard along the dashed line. When placed on the table, the flashcard should resemble a little tent. Other flashcards can then be stacked on top of each other. 8. Repeat steps 3-7 for the other bacterial structures listed in column 2 of the table below. 9. Make an envelope to store your 12 bacterial cell flashcards in. Title the envelope ‘BACTERIAL CELL’ and write your name and period number on it. 10. Repeat steps 1-9 to complete a set of Animal cell and Plant cell flashcards too. Flashcard Number 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Prokaryote Bacterial cell Nucleoid Plasmid Plasma membrane Cell wall Capsule Ribosome Cytoplasm Flagellum (flagella) Pilus (pili) or fimbriae Mesosome Inclusion or granule Conjugation “F” pilus Eukaryote Animal cell Nucleus Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) Mitochondrion Food vacuole Contractile vacuole Golgi apparatus Cytoplasm Centrioles Lysosome Cilium (cilia) Microvillus (microvilli) Cytoskeleton (microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments) Plant cell Nucleolus Plasma membrane Cell wall Chromosome Chloroplast Central vacuole Ribosome Nuclear pore Vesicle Peroxisome Plasmodesmata Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) Fold Fold Fold Structure Structure Structure Function Function Function Fold Fold Fold Structure Structure Structure Function Function Function Fold Fold Fold Structure Structure Structure Function Function Function Fold Fold Fold Structure Structure Structure Function Function Function Fold Fold Fold Structure Structure Structure Function Function Function Fold Fold Fold Structure Structure Structure Function Function Function PROKARYOTE: BACTERIAL CELL 12 5 1 10 2 4 3 6 9 11 7 8 EUKARYOTE: ANIMAL CELL 5 12 11 6 10 Vesicles SER 9 Ribosome 7 Chromosome 4 12 Peroxisome Nucleolus 3 1 Nuclear pore 2 8 12 Plasma membrane EUKARYOTE: PLANT CELL 3 Mitochondrion 9 10 Golgi Apparatus Cytoplasm 11 7 6 4 2 Nucleus 1 Tonoplast 5 RER 8 12 PROKARYOTE: BACTERIAL CELL Mesosome — An extension of the cell membrane that folds into the cytoplasm and increases surface area. Nucleoid — An area of the cytoplasm where a bacterium’s single circular chromosome is located. Capsule — A protective covering made up of polysaccharides that helps keep the bacterium from drying out. Plasmid — A small circular DNA molecule which may be transferred to other bacteria through F-pili. Cell wall — A semirigid casing made of peptidoglycan that provides structural support and shape for the cell. Plasma membrane — A thin sheet of lipid and protein that surrounds the cytoplasm and controls the flow of materials into and out of the cell. Ribosome — Tiny particles composed of protein and RNA that synthesize polypeptides. Cytoplasm — The gel-like substance residing within the cell membrane that acts as a medium of suspension for a cell’s ribosomes and inclusions. F pilus — An elongated, hollow appendage used in transfers of plasmids (DNA) to other cells. Inclusion / Granule —Stored nutrients such as fat, phosphate, or glycogen deposited in dense crystals or particles that can be tapped into when needed. Flagellum — A long whip-like appendage serving as an organ of locomotion. Pilus — A short hairlike appendage that is used to attach the bacterium to a surface. EUKARYOTE: ANIMAL CELL Cytoskeleton – A network of protein filaments in a eukaryotic cell that gives the cell its shape and internal organization and is involved in movement. Contractile vacuole — A vacuole involved in osmoregulation by moving excess water out of the cell. Microvillus — Short, membrane protrusion that increases the surface area of cells allowing for faster absorption of nutrients. Cilium — A short, hair-like appendage serving as an organ of locomotion. Golgi Apparatus — Modifies, sorts, and ships substances such as proteins and lipids to destinations in and out of the cell. Vesicle — A membrane sac that transports substances in and out of the cell. SER – A membrane system where drugs and toxins are broken down, and steroids and lipids are made. Lysosome — A membrane sac that contains digestive enzymes that break down large molecules and damaged organelles. Ribosome – Comprised of two subunits made up of RNA and protein, it is where polypeptides are made. Cytoplasm — The gel-like substance residing within the cell membrane and outside the nucleus. It acts as a medium of suspension for a cell’s organelles. Chromosome – A compact structure visible under a light microscope that is made up of DNA and associated proteins. Food vacuole— A membrane sac that stores substances that can be used as a source of energy. Peroxisome— A membrane sac that contains enzymes that break down hydrogen peroxide and long fatty acid chains. Nucleolus – A region of the nucleus where ribosomal subunits are made. Nuclear pore – A hole in the nuclear membrane that allows substances to move in and out of the nucleus. Mitochondrion— Transfers chemical energy from sugars, lipids, and amino acids into ATP. Nucleus – The control center of the cell that regulates all cell activity. RER – Ribosomestudded membranes that synthesize lipids and proteins. Plasma membrane—A thin sheet of lipid and protein that surrounds the cytoplasm and controls the flow of materials into and out of the cell. Centrioles – Structures made of tubulin and associated with microtubule production. Cytoskeleton Filaments Intermediate filaments – A thread-like structure made of keratin protein that helps support cell organelles and maintain cell shape. (8 – 12 nm) Microtubule – Thin, tube-like structure made of tubulin proteins that helps support the cell and transport materials. (25 nm) Microfilament – A thread-like structure made of actin protein that helps the cell move. It also acts as scaffolding for cell support. (7 nm) EUKARYOTE: PLANT CELL Peroxisome— A membrane sac that contains enzymes that break down hydrogen peroxide and long fatty acid chains. Cell wall – Made primarily of cellulose, it protects the cell from pathogens and prevents the cell from bursting under osmotic pressure. Mitochondrion— Transfers chemical energy from sugars, lipids, and amino acids into ATP. Vesicle — A membrane sac that transports substances in and out of the cell. Golgi Apparatus — Modifies, sorts, and ships substances such as proteins and lipids to destinations in and out of the cell. Cytoplasm — The gel-like substance residing within the cell membrane and outside the nucleus. It acts as a medium of suspension for a cell’s organelles. Plasmodesmata — small openings in the cell wall that allow cytosol to flow out and into adjacent cells. Ribosome – Comprised of two subunits made up of RNA and protein, it is where polypeptides are made. Central vacuole —A large vacuole that stores sap. It also provides turgor to the cells and tissues of plants to help keep plants firm and upright. Chromosome – A compact structure visible under a light microscope that is made up of DNA and associated proteins. Plasma membrane—A thin sheet of lipid and protein that surrounds the cytoplasm and controls the flow of materials into and out of the cell. Nucleus – The control center of the cell that regulates all cell activity. Tonoplast—The membrane of the central vacuole. Nucleolus – A region of the nucleus where ribosomal subunits are made. RER – Ribosome-studded membranes that synthesize lipids and proteins. Nuclear pore – A hole in the nuclear membrane that allows substances to move in and out of the nucleus. Chloroplast—An organelle that contains the pigment chlorophyll. It converts solar energy into chemical energy. SER – A membrane system where drugs and toxins are broken down, and steroids and lipids are made.