Time Range Strategic Capacity Planning
advertisement

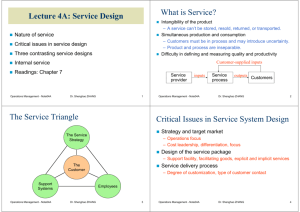
Lecture 6: Strategic Capacity Management Time range of capacity planning Strategic capacity planning Capacity utilization & service quality R di Readings: Ch Chapter t 4 Why do We Need to Plan for Capacity? If you plan to open a restaurant on campus campus, you must decide how many customers it should be able to serve. • • • • Kitchen Tables Employees … Capacity is the amount of output that a system is capable of achieving over a specific period of time. Operations Management - Note06 Dr. Shenghao ZHANG 1 Long term range Capacity can be more generally defined as the ability to hold, receive, store, or accommodate. Strategic capacity planning is to determine the overall capacity level of capital intensive resources, including facilities facilities, equipment equipment, and overall labor force size, in a long term range. – Greater than one year. Productive resources such as buildings, equipment, or facilities. Involves top management. 2 Intermediate term range – Monthly or quarterly plans plans. Hiring Hiring, layoffs layoffs, new tools tools, minor equipment purchases and subcontracting. Involves middle g management. Dr. Shenghao ZHANG Strategic Capacity Planning Time Range Operations Management - Note06 Short term range – Less than on month. month Over time time, personnel transfers and alternative production routings. Involves lower level g management. Operations Management - Note06 Dr. Shenghao ZHANG 3 Operations Management - Note06 Dr. Shenghao ZHANG 4 Economies & Diseconomies of Scale The Experience Curve Economies of Scale and the Experience p Curve working g As plants produce more products, they gain experience in the best production methods and reduce their costs per unit. Average unitit costt of output Cost or price per unit 100-unit plant p 200-unit plant 300-unit plant l t 400-unit plant Diseconomies of Scale start working Total accumulated production of units Operations Management - Note06 Dr. Shenghao ZHANG 5 Best Operating Level Volume Dr. Shenghao ZHANG 6 Capacity Planning Factors/Considerations Average unit cost of output Over-utilization Under-utilization Operations Management - Note06 Best Operating Level Experience curve and economies of scale System balance Frequency of capacity additions External sources of capacity: subcontracting and capacity sharing Volume Operations Management - Note06 Dr. Shenghao ZHANG 7 Operations Management - Note06 Dr. Shenghao ZHANG 8 M ki Capacity Making C it Decision D ii D t Determining i i Capacity C it Requirements R i t Please read Note07 – Decision Analysis Operations Management - Note06 Dr. Shenghao ZHANG 9 Forecast sales within each individual product line. Calculate C l l t equipment i t and d llabor b requirements i t tto meet the forecasts. Operations Management - Note06 Dr. Shenghao ZHANG Capacity Flexibility C Capacity i Cushion C hi Fl ibl plants Flexible l t A capacity cushion is the difference between the capacity and the expected demand. Flexible processes Can the capacity cushion be negative? Flexible workers Operations Management - Note06 Dr. Shenghao ZHANG 10 11 Operations Management - Note06 Dr. Shenghao ZHANG 12 C Capacity it Utilization Utili ti & Service S i Quality Q lit Pl i Service Planning S i Capacity C i Time dependent Location dependent M More volatile l til d demand d Utili ti iimpacts Utilization t service i quality lit di directly tl Operations Management - Note06 Dr. Shenghao ZHANG 13 Rule of thumb: best operating point is near 70% of capacity. capacity From 70% to 100% of service capacity, p y, what do you think happens to service quality? Operations Management - Note06 Dr. Shenghao ZHANG 14